Brimonidine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
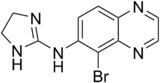
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Brimonidine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 10 BrN 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 292.1 g · mol | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
207.5 ° C (tartrate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Brimonidine is a drug from the group of sympathomimetics . It is used in the form of eye drops to reduce increased intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma and in the form of a gel for use on the skin for the symptomatic treatment of facial erythema in rosacea . Brimonidine was developed and patented by the pharmaceutical company Pfizer in the 1970s .
chemistry
Chemically, brimonidine is an imidazoline with a structural relationship to other therapeutically used representatives of this class of substances, such as clonidine , moxonidine and xylometazoline . The tartaric acid salt ( tartrate ) of brimonidine is used pharmaceutically.
The synthesis takes place by reacting 6-amino-5-bromoquinoxaline with ammonium thiocyanate to give the corresponding thioureid . After the addition of ethylenediamine , the imidazoline ring closes to form brimonidine.
pharmacology
Mode of action
Brimonidine is a selective agonist at α 2 -adrenoceptors with a selectivity of over 1000 times that of α 1 -adrenoceptors . Brimonidine shows comparable pharmacological potency on the three subtypes of the receptor , with subtype 2A acting as a full agonist and on subtypes 2B and 2C as a partial agonist . Based on the activation of α 2 -adrenoceptors in the eye, brimonidine leads to a reduced formation of aqueous humor and also increases uveoscleral outflow. Because of its high selectivity for α 2 -adrenoceptors, fewer α 1 -adrenoceptor-mediated side effects, including mydriasis , are to be expected with brimonidine than with clonidine or apraclonidine . In the face area, brimonidine leads to a constriction of small blood vessels via α 2 -adrenoceptor activation and thus reduces the erythema .
Pharmacokinetics
After ingestion, brimonidine is absorbed quickly and almost completely. The active ingredient can also be detected in the plasma after administration to the eye. The mean plasma half-life with topical therapy is around 3 hours. Excretion takes place mainly after biotransformation in the liver via the kidneys (75%) in the form of its metabolites .
Medical use
application areas
Brimonidine is approved in the form of eye drops for lowering increased pressure in the eye in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension . It is a reserve resource. Its use as a monotherapeutic agent is restricted to patients for whom locally applied beta blockers may not be used. It is available in combination with other drugs that lower intraocular pressure if the target value cannot be achieved with these alone.
In addition, brimonidine in the form of a gel is approved for the symptomatic treatment of facial erythema in rosacea.
Contraindications
Local use of brimonidine is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the active substance . There is also a contraindication in children under 2 years of age, as symptoms of overdose such as unconsciousness , lethargy , somnolence , hypotension , bradycardia , hypothermia , cyanosis , paleness, respiratory depression and apnea were particularly common in this age group when taking brimonidine . Brimonidine also leads to an increased risk of somnolence in children from 2 to 7 years of age or a body weight of up to 20 kg and should therefore only be used under close observation. Due to an increased effect there is also a restriction on use in patients concurrently with MAO inhibitors , such as moclobemide and selegiline , or to an increase in the activity of norepinephrine leading tri- and tetracyclic antidepressants are treated.
Interactions
To interactions of locally-applied brimonidine with other drugs are hardly any data. Due to its mechanism of action and the observed side effects , concomitant use of antihypertensive drugs , digitalis glycosides , α-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists, and drugs that affect the uptake and metabolism of circulating biogenic amines should be carried out with caution.
unwanted effects
In the local application of brimonidine, the side effects at the administration site are in the foreground. When applied to the eye, local irritation, including hyperemia , stinging and stinging of the eyes, can be observed with a frequency of 22 to 25% . Symptoms of allergic reactions to the eye and blurred vision are also very common (> 10%). Local irritation of the eyelid and conjunctiva, photophobia, corneal erosion or discoloration, dry eye, conjunctival pallor, visual disturbances and conjunctivitis occur frequently (1 to 10%) . Iritis and miosis are very rare side effects (<0.01%) of brimonidine use in the eye.
Furthermore, dry mouth , headache , fatigue and - especially in children - somnolence as well as frequently dizziness, changes in taste, gastrointestinal symptoms, asthenia were observed after application to the eye . Occasionally (0.1 to 1%), dry nose, palpitations, cardiac arrhythmias, depression and systemic allergic reactions occur. Other systemic side effects such as hypotension, syncope , insomnia, and dyspnea are rare (0.01 to 1%) or very rare (<0.01%).
When applied to the skin, the main local side effects are erythema, burning and itching (1 to 10%) as well as rosacea, dermatitis , skin irritations, overheated or dry skin, pain, rash and acne (0.1 to 1%).
Trade names
Alphagan (D), Mirvaso (D), Generics (D)
- In combination with timolol : Combigan (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on brimonidine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 27, 2019.
- ↑ a b data sheet UK 14,304 from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 7, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b Jürgen Engel, Axel Kleemann, Bernhard Kutscher, Dietmar Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances. Syntheses, Patents and Applications of the most relevant APIs , 5th edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-179275-2 , pp. 169-170.
- ↑ TM Barrie & WM Trevely (1976). DE2538620: Process for the production of quinoxaline and quinazoline derivatives.
- ↑ D. Cambridge: UK-14,304, a potent and selective alpha2-agonist for the characterization of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes . In: Eur J Pharmacol . 72, No. 4, 1981, pp. 413-415. PMID 6115759 .
- ^ J. Burke, M. Schwartz: Preclinical evaluation of brimonidine . In: Surv Ophthalmol . 41, No. Suppl 1, November 1996, pp. S9-18. PMID 8970245 .
- ↑ JM Peltonen, M. Pihlavisto, M. Scheinin: Subtype-specific stimulation of [35S] GTPgammaS binding by recombinant alpha2-adrenoceptors . In: Eur. J. Pharmacol . 355, No. 2-3, 1998, pp. 275-279. PMID 9760042 .
- ↑ JR Jasper, JD Lesnick, LK Chang, SS Yamanishi, TK Chang, SA Hsu, DA Daunt, DW Bonhaus, RM Eglen: Ligand efficacy and potency at recombinant alpha2 adrenergic receptors: agonist-mediated [35S] GTPgammaS binding . In: Biochem Pharmacol . 55, No. 7, 1998, pp. 1035-1043. PMID 9605427 .
- ^ DS Greenfield, JM Liebmann, R. Ritch: Brimonidine: a new alpha2-adrenoreceptor agonist for glaucoma treatment . In: J. Glaucoma . 6, No. 4, August 1997, pp. 250-258. PMID 9264305 .
- ^ LB Cantor: The evolving pharmacotherapeutic profile of brimonidine, an alpha 2-adrenergic agonist, after four years of continuous use . In: Expert Opin Pharmacother . 1, No. 4, May 2000, pp. 815-834. doi : 10.1517 / 14656566.1.4.815 . PMID 11249518 .
- ↑ a b c d e f Technical information Alphagan 0.2% m / v (2 mg / ml) as of June 2014.
- ↑ a b Technical information Mirvaso 3 mg / g as of February 2014.