British Antarctic Territory
| British Antarctic Territory | |||||
| British Antarctic Territory | |||||
|
|||||
| Capital | Rothera station | ||||
| surface | 1,709,400 km² | ||||
| population | approx. 200 | ||||
| currency | Pound Sterling | ||||
The British Antarctic Territory (English British Antarctic Territory , shortly BAT ) is a claimed by the United Kingdom overseas territory in the Antarctic . It is not recognized internationally.
history
The area has been expressly claimed by Great Britain since July 21, 1908 and was considered a dependency of the Falkland Islands until 1962 . After the conclusion of the Antarctic Treaty , the new administrative division of British Antarctic Territory was formed on March 3, 1962 from the former Falkland Island Dependencies Grahamland , South Orkney Islands and South Shetland Islands .
geography
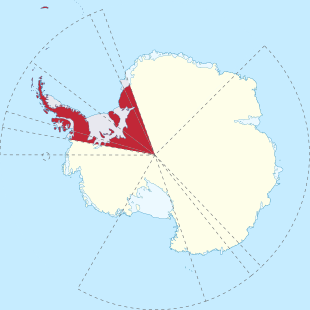
The territory comprises the area of Antarctica south of the 60th parallel south and between 20 ° and 80 ° west longitude .
In addition to a sector of the Antarctic mainland up to the South Pole , which includes the entire Antarctic Peninsula , the island groups of the Southern Orkney Islands and the Southern Shetland Islands are also part of the BAT.
politics
UK claims to the territory are not recognized internationally. Currently the political status of the continent is regulated by the Antarctic Treaty, which came into force in 1961, which grants citizens of all nations free access for peaceful purposes. Every visitor or resident is still subject to the legal status of their country of origin.
British territory is administered directly by the Foreign and Commonwealth Office as far as British activities in the area are concerned. With the exception of the sector between 20 ° W and 25 ° W, which is claimed by Great Britain alone, the greater part of the area is also claimed by Chile and Argentina . The claims of all three countries overlap on the Antarctic Peninsula. The UK has two research stations ( Rothera and Halley ) which are manned year-round and which also have post offices selling stamps issued specifically for the BAT. Another post office is operated in Port Lockroy in the former British research station (Station A), which is now operated as a museum by the United Kingdom Antarctic Heritage Trust. Numerous other nations also have research stations in the area. Except for two small civilian settlements in the vicinity of the Chilean and Argentine main bases on King George Island and in Hope Bay , it is uninhabited.
Web links
- Britain in Antarctica. British Antarctic Survey (BAS)website.
Individual evidence
- ^ British Antarctic Territory. In: World Statesmen.org. Retrieved January 21, 2017 .
- ^ Foreign & Commonwealth Office: South America and South Atlantic Islands - Antarctica: Geography. (No longer available online.) In: UK Government Web Archive. The National Archives (TNA), archived from the original on June 11, 2008 ; accessed on January 21, 2017 (English). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.