Cefotiam
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
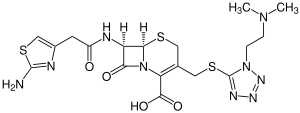
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Cefotiam | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 23 N 9 O 4 S 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Disturbance of cell wall synthesis |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 525.62 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Cefotiam is an antibiotic that is used to treat severe infections caused by sensitive bacteria. It is produced semisynthetically and comes from the class of the cephalosporins of the 3rd generation.
Cefotiam was patented by Takeda in 1976 . In 1981 it came onto the market in Germany as Spizef . In 2010 Grünenthal waived its approval and since 2013 Spizef has no longer been available in Germany.
indication
Cefotiam is a broad spectrum antibiotic , so it has a broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms . Cefotiam is indicated for the treatment of severe acute and chronic bacterial infections of the kidneys and lower urinary tract, the genital organs, the respiratory tract, the ear, nose and throat area, the abdominal and pelvic organs, the skin and soft tissue, the bones and joints as well as the eyes. Even with sepsis cefotiam may be indicated.
In France, an orally effective formulation (Cefotiamhexetil, trade name Texodil ) is approved for the treatment of infections of the sinuses , throat and middle ear .
Working principle
The cefotiam molecules bind - like all cephalosporins - to specific penicillin-binding proteins , which are required to rebuild the bacterial cell wall. This prevents further synthesis of the bacterial cell wall.
synthesis
First, 7-Acetoacetamidocephalosporansäure is (1) with 1- (2-dimethyl-aminoethyl) -1 H -tetrazol-5-thiol (2) reacted. 7-Acetoacetamidocephalosporanic acid is a derivative of 7-ACA, which is produced by a chemical reaction from penicillin G with the help of N , N ′ -bis (trimethylsilyl) urea . After the two starting materials have first been heated at neutral pH with the addition of sodium hydrogen carbonate , they are acidified with the aid of hydroxylamine hydrochloride . The intermediate product (3) is formed . This then reacts with 2-amino-4-thiazolacetic acid hydrochloride (4) with the addition of N -hydroxysuccinimide , dicyclohexylcarbodiimide , triethylamine and dichloromethane to give the desired product cefotiam (5) . The synthesis of cefotiam takes place via a semisynthesis , which in this case means the acylation of an amino group .
Application
Cefotiam is infused intravenously or given by intramuscular injection . The bioavailability after intramuscular injection is 60%. Esterification of the carboxyl group gives cefotiamhexetil. Due to its higher lipophilicity , this active ingredient can also be administered orally; it acts as a prodrug .
Side effects
An overdose of the antibiotic may cause the following side effects: nausea, vomiting, stomach upset, diarrhea and cramps.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet Cefotiam dihydrochloride hydrate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 22, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on Cefotiam. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 22, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Cefotiam in the DrugBank of the University of Alberta , accessed May 22, 2019.
- ↑ a b F. Kees: Oral Cephalosporins. Medical monthly journal for pharmacists, 15th year, 1992, issue 1, p. 2 ff.
- ↑ Drug Update: Fluoroquinolones. German STI Society - Society for the Promotion of Sexual Health, accessed on May 17, 2019 .
- ↑ Instructions for use Spizef 2.0 g powder for solution for infusion , status July 2008. Retrieved from www.medikamio.com on May 23, 2019.
- ↑ Texodil in the ANSM drug database , accessed on May 23, 2019.
- ^ Kleemann, Axel: Pharmaceutical substances: syntheses, patents, and applications of the most relevant AIPs. 5th ed., Completely rev. Thieme, Stuttgart 2009, ISBN 978-1-62198-377-4 , p. 245 + 246 .
- ↑ Alle Bruggink (Ed.): Synthesis of β-Lactam Antibiotics: Chemistry, Biocatalysis & Process Integration. Springer Science + Business Media, ISBN 978-0-7923-7060-4 , p. 15 .
