Chatanga (river)
|
Chatanga Russian Хатанга |
||
|
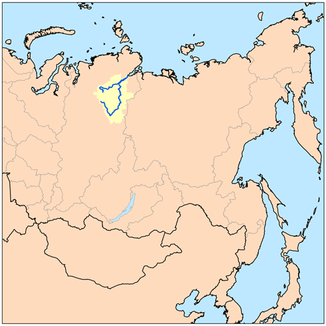
Northern and eastern Russia with Chatanga, source rivers Cheta (left) and Kotui (right) and the Chatangagolf estuary , which leads to the Laptev Sea ( Arctic Ocean ) (top center) |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 17040400112117600006917 | |
| location | Taimyr Depression , North Siberian Lowland , Krasnoyarsk Region , Siberia , Russia ( Asia ) | |
| River system | Chatanga | |
| origin | Confluence of the Cheta and Kotui at Kresty 71 ° 54 ′ 56 ″ N , 102 ° 6 ′ 10 ″ E |
|
| Source height | approx. 1 m | |
| muzzle | in the Chatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea ( Arctic Ocean ) Coordinates: 73 ° 11 ′ 14 " N , 106 ° 12 ′ 25" E 73 ° 11 ′ 14 " N , 106 ° 12 ′ 25" E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | approx. 1 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 0 ‰ | |
| length | approx. 227 km (from the union of Cheta and Kotui ) approx. 1,636 km (from the source of Kotui ) |
|
| Catchment area | approx. 364,000 km² | |
| Discharge at the Chatanga gauge |
NNQ (1966-04) MQ HHQ (1990-06) |
241 m³ / s 2517 m³ / s 17,553 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Selebir , Ulachan-Jurjach , Novaya , Little Balachnja , Mardy-Rassocha | |
| Right tributaries | Shdanicha , Nizhnyaya , Lukunskaya , Bludnaja , Popigai | |
| Communities | Chatanga | |
| Ports | Chatanga | |
| Navigable | in summer over the entire length | |
The Chatanga ( Russian Хатанга ) is about 227 km and together with its source river Kotui approximately 1,636 km long stream in the northeast of the Krasnoyarsk region and the north of Siberia and Russia ( Asia ), and also the main tributary of the Chatangagolfs and tributary of the Laptev Sea , a part of the Arctic Ocean .
course
The Chatanga arises around 600 km north of the Arctic Circle in the Taimyr Depression , the central part of the North Siberian Lowland , through the confluence of its source rivers Cheta , which is around 604 km long and flows from the southwest, and Kotui , which is located directly at the settlement of Kresty Is 1,409 km long and comes from the south-southeast.
From then on, the Chatanga - south of the Taimyr Peninsula and north of the Central Siberian Mountains - runs in a wide valley northeast through the Taimyr Depression. It forms several arms of the river that unite several times, and there are also many river islands. In a sparsely populated area, about 15 km below Kresty, it passes the larger town of Chatanga with its port and airfield, and a little further downriver it begins its second longest tributary, the Novaya . Later it passes the further northeastern settlements of Schdanicha , at the mouth of the Schdanicha, and Novorybnaja , near the mouth of the Bludnaja . Shortly afterwards, the Popigai flows in as the longest tributary.
About 28 km to the north joins the Chatanga between Cape Turupkin the west and Big Kap Korga the east in the 220 km long estuary khatanga gulf which is part of the Arctic Ocean belonging Laptev Sea is.
Catchment area, lakes and tributaries
The catchment area of the Chatanga is around 364,000 km². In this area there are over 112,000 lakes with a total area of 11,600 km².
The source rivers of the Khatanga are Cheta and Kotui and their tributaries include (viewed downstream): Selebir, Shdanicha, Ulachan-Jurjach, Novaya, Nizhnyaya, Lukunskaya, Little Balachnja, Bludnaja, Popigai and Mardy-Rassocha.
Climate, hydrology and hydrography
The winters on the Chatanga are long and extremely cold, the summers short and cold. As a rule, the river is covered by ice from late September or early October to early June , so that it is only navigable in summer - with a port at Chatanga . When the permafrost thaws in summer and ice and snow melt, strong floods often occur . Especially then, the Chatanga Gulf has a strong north-east flowing current, driven by the water masses of the Chatanga, which drives them through the Gulf into the Laptev Sea. At the Chatanga gauge , the mean discharge (MQ) is 308 m³ / s in April and 12,889 m³ / s in June, the annual mean is 3,320 m³ / s and the maximum is 18,300 m³ / s. The Chatanga is included in the hydrological zone of the Lena .
Flora and fauna
The Chatanga flows through landscapes of frost rubble deserts and tundra with mosses and lichens as well as numerous lakes and swamps . In the fish-rich river live among other vendace , Muksune , Omule , char and White Salmon . There is commercial fishing.
See also
|
Average discharge ( m³ / s ) at the Chatanga station (1961 to 1994) 
|
Individual evidence
- ↑ Topographic map (1: 200.000, p. R-48-I, II, ed. 1986), Chatanga origin (top left) through the confluence of the Cheta (from left) and Kotui (from right and below) near Kresty u. a. with the village of Chatanga (top center left) on mapr48.narod.ru (with heights above sea level )
- ↑ Topographic map (1: 200.000, p. S-48-XXIX, XXX, edition 1986), Chatanga estuary (top left) - at the transition from river to gulf between Cape Turupkin and Great Cape Korga - in the southwest part of Chatanga gulf (above) u. a. with Popigai estuary (river coming from the right) into Chatanga, on maps48.narod.ru (with heights above sea level)
- ↑ a b c d Хатанга (Chatanga with Kotui ) in the State Water Register of Russia (Russian)
- ↑ a b c d e f g Article Хатанга in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ a b c d Chatanga at the Chatanga gauge - hydrographic data at R-ArcticNET