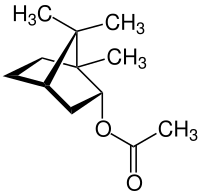
Bornyl acetate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Structure of (-) - bornyl acetate | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Bornyl acetate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 20 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
|
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 196.29 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.981-0.99 g cm -3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
25-29 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
224-226 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4635 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Bornyl acetate is the acetic acid ester of the terpene borneol .
Isomers
Bornyl acetate is always endo -configured, the exo -configuration is called isobornyl acetate . There are two isomeric forms, (-) - and (+) - bornyl acetate [synonyms: (1 S , 2 R , 4 S ) -boronyl acetate and (1 R , 2 S , 4 R ) -boronyl acetate], which are often used as 1: 1 mixture ( racemate ) occur.
| Isomers of Bornyl Acetate | ||
| Surname | (-) - Bornyl acetate | (+) - Bornyl acetate |
| other names | (1 S , 2 R , 4 S ) -1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo [2.2.1] hept-2-yl acetate | (1 R , 2 S , 4 R ) -1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo [2.2.1] hept-2-yl acetate |
| Structural formula |  |

|
| CAS number | 5655-61-8 | 20347-65-3 |
| 76-49-3 (racemate) | ||
| EC number | 227-101-4 | 243-750-6 |
| 200-964-4 (racemate) | ||
| ECHA info card | 100,024,638 | 100,039,757 |
| 100,000,878 (racemate) | ||
| PubChem | 442460 | 6950274 |
| 6448 (racemate) | ||
| Wikidata | Q27105264 | Q27284125 |
| Q780165 (racemate) | ||
Occurrence

The ester belongs to the drug family of essential oils and is found in many plants available such as in the, conifers fir ( Abies ), pine ( Pinus ), spruce ( Picea ) and larch ( Laryx ), but also in chaste tree ( Vitex agnus- castus ), musk yarrow ( Achillea moschata ), magnolias ( Magnolia ) and wild flowers ( Tanacetum ).
Properties and appearance
Bornyl acetate is a white, crystalline substance that gives the pine and spruce needle oil its characteristic odor. As a pure substance, the compound smells very strongly of spruce or pine and has a burning taste. The characteristic odor can already be perceived in a concentration of 75 ppb or more. Bornyl acetate melts at 25 to 29 ° C to a colorless liquid and can be produced industrially from borneol and acetic acid.
use
Balsam fir needle oil ( Abietis balsameae aetherloeum ) and spruce needle oil ( Piceae aetheroleum ) contain up to 23%, Canada balsam ( Balsamum canadense ) between 4 and 11% bornyl acetate. These essential oils are used for rubbing in, pure bornyl acetate and its isomer isobornyl acetate as an odor component in bath preparations, sprays and soaps , baked goods, puddings and beverages and as a component of pharmaceuticals ( Lindofluid N ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on bornyl acetate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 26, 2014.
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia , Deutscher Apotheker Verlag Stuttgart, 6th edition, 2008, p. 545, ISBN 978-3-7692-3962-1 .
- ↑ a b c Hermann Ammon (Ed.): Hunnius Pharmaceutical Dictionary . 8th edition, de Gruyter, Berlin 2004, ISBN 3-11-015792-6 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g G.A. Burdock: Fenaroli's Handbook Of Flavor Ingredients , 2004, CRC Press , ISBN 0-8493-3034-3 .
- ↑ Bornyl acetate data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 30, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ U. Schwabe, D. Paffrath: Drug Ordinance Report 2003 , Springer-Verlag , ISBN 3-540-40188-1 .
