1,4-dioxane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 1,4-dioxane | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 8 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, flammable, somewhat oily, pleasantly smelling liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 88.11 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.03 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
11.8 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
101 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.422 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
1,4-Dioxane is an alicyclic diether and as such is a heterocyclic organic compound.
Extraction and presentation
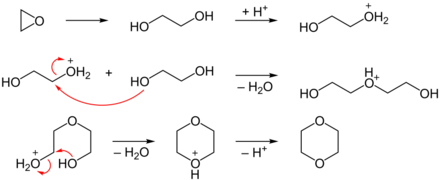
In the first step, ethylene oxide is converted into ethylene glycol (1,2-ethanediol) by acid-catalytic (concentrated sulfuric acid ) ring opening with water as the nucleophile . The second and third step each describe the acid-catalyzed S N 2 substitution, the second of which occurs intramolecularly. Protonation and deprotonation steps were omitted for reasons of space.
Dioxane is also formed very easily as a by-product in all acid-catalyzed reactions of ethylene glycol or diethylene glycol (e.g. esterifications).
properties
Physical Properties
1,4-Dioxane is a colorless and low-viscosity liquid that boils at 101 ° C under normal pressure. According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 4.58135, B = 1570.093 and C = −31.297 in the temperature range from 293 to 378 K. In the solid phase there are two different crystal forms. At 0 ° C, Form II converts to Form I, which melts at 11 ° C. The heat of transformation is 2.351 kJ mol −1 , the heat of fusion 12.845 kJ mol −1 . The cyclic diether can be mixed with water as required.
Like cyclohexane or pyranoses, the molecule is mainly in the inversely symmetrical chair form . For the dipole moment of 0.45 D (for comparison: tetrahydrofuran has a dipole moment of 1.63 D) other conformers, especially the shape of the tub, are responsible.
Dioxane is easily miscible with most organic solvents and water. At normal pressure, an azeotropic boiling point of 87.6 ° C. is observed in the binary system dioxane / water at 82.1 mass percent dioxane .
Vapor pressure function of 1,4-dioxane
Binary phase diagram of the 1,4-dioxane / water system
Safety-related parameters
Dioxane forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of 11 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.4% by volume (51 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 22.5% by volume (820 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL). A correlation of the explosion limits with the vapor pressure function results in a lower explosion point of 9 ° C and an upper explosion point of 58 ° C. The maximum explosion pressure is 9.1 bar. The limit gap width was determined to be 0.7 mm. This results in an assignment to explosion group IIB. The ignition temperature is 375 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2. The electrical conductivity is very low at 5 · 10 −13 S · m −1 .
use
Since it is relatively inert and easily miscible with other solvents, 1,4-dioxane is used as a solvent .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on 1,4-dioxane. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 26, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l Entry on 1,4-dioxane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 3, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet 1,4-Dioxane from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 5, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on 1,4-dioxane in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 123-91-1 or 1,4-dioxane ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ JL Crenshaw, AC Cope, N. Finkelstein, R. Rogan: The Dioxanates of the Mercuric Halides. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 60, 1938, pp. 2308-2311, doi : 10.1021 / ja01277a010 .
- ^ A b C. J. Jacobs, GS Parks: Thermal data on organic compounds. XIV. Some heat capacity, entropy and free energy data for cyclic substances. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 56, 1934, pp. 1513-1517, doi : 10.1021 / ja01322a020 .
- ^ CH Schneider, CC Lynch: The Ternary System: Dioxane-Ethanol-Water. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 65 (6), 1943, pp. 1063-1066, doi : 10.1021 / ja01246a015 .
- ↑ a b c E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters. Volume 1: Flammable Liquids and Gases. Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ↑ Technical rule for hazardous substances TRGS 727, BG RCI leaflet T033 Avoidance of ignition hazards due to electrostatic charges , status August 2016, Jedermann-Verlag Heidelberg, ISBN 978-3-86825-103-6 , PDF download .