Fluazinam
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
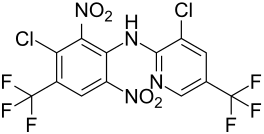
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fluazinam | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 4 Cl 2 F 6 N 4 O 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow, odorless crystals |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 465.09 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.76 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
116-117 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
7.5 mPa (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very sparingly soluble in water (0.135 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Fluazinam is a chemical compound from the group of 2,6- dinitroanilines and pyridines . The compound was developed by Ishihara Sangyō and introduced as a fungicide in 1990 .
Extraction and presentation
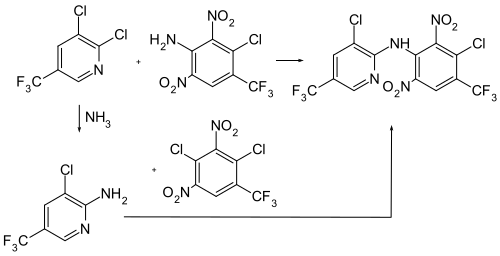
Fluazinam can be obtained by reacting 5,6-dichloro-3-trifluoromethylpyridine with 2,6-dinitro-3-chloro-4-trifluoromethylaniline . Alternatively, 5,6-dichloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine can also be reacted first with ammonia and then with 2,6-dinitro-3-chloro-4-trifluoromethylchlorobenzene . 5,6-dichloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine is produced by chlorination and fluorination of 3-methylpyridine .
use
Fluazinam is a non-systemic fungicide that works by disrupting oxidative phosphorylation . It is sold under the trade names Shirlan as Fusarium stain and against late blight used.
Admission
In 2008 the EU Commission included Fluazinam in the list of active ingredients of plant protection products permitted in the EU. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, plant protection products with the active ingredient fluazinam are approved.
toxicology
Fluazinam is one of the strongest known decouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. Compared to Dinocap and Binapacryl , however, Fluazinam is significantly less toxic.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Bahadir, Parlar, Spiteller: Springer Umweltlexikon . Springer, 2000, ISBN 3-540-23480-2 , pp. 445 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c data sheet from Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha (PDF; 403 kB)
- ↑ Entry on fluazinam in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 17, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ entry on fluazinam (ISO); 3-chloro-N- [3-chloro-2,6-dinitro-4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl] -5- (trifluoromethyl) pyridin-2-amine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on 1 August 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can extend the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Fluazinam data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 17, 2020 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 865 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Commission Directive 2008/108 / EC of November 26, 2008 (PDF) amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substances flutolanil, benfluralin, fluazinam, fuberidazole and mepiquat.
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on fluazinam in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved February 19, 2016.
- ↑ Ze-jian Guo, Hideto Miyoshi, Terumasa Komyoji, Takahiro Haga, Toshio Fujita: Uncoupling activity of a newly developed fungicide, fluazinam [3-chloro-N- (3-chloro-2,6-dinitro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl) - 5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridinamine] . In: Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics . 1056, No. 1, 1991, pp. 89-92. doi : 10.1016 / S0005-2728 (05) 80077-5 .