Flucloxacillin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
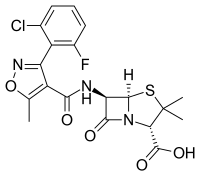
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Flucloxacillin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
(2 S , 5 R , 6 R ) -6 - {[3- (2-chloro-5-fluorophenyl) -5-methyl-oxazole-4-carbonyl] amino} -3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo- 4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 17 FCIN 3 O 5 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Isoxazolyl penicillin |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Cell wall synthesis inhibition, bactericidal |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 453.87 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
2.7 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Flucloxacillin is a penicillinase-resistant β-lactam antibiotic which was developed especially against β-lactamase- forming staphylococci and is therefore also referred to as a staphylococcal penicillin .
It belongs to the group of isoxazolyl antibiotics, which include cloxacillin (none in Germany approved for humans preparations), dicloxacillin and oxacillin belong. The remedy cloxacillin is marked on the list of indispensable drugs of the World Health Organization and, according to the WHO, can be replaced with an agent of the same substance group or the same spectrum of activity. In Germany, this remedy is flucloxacillin or oxacillin. Methicillin , which is also resistant to penicillinase , is only used to test resistance to MRSA and MRSE ; these germs cannot be treated with flucloxacillin either. The active ingredient was patented by Beecham (now GlaxoSmithKline ) in 1968 and is used in the form of various salts; these include the sodium salt, the sodium salt mono hydrate and the magnesium salt octahydrate.
indication
Flucloxacillin is used to treat infections with β-lactamases forming Staphylococci (such as Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis ), but also Streptococcus pyogenes , pneumoniae Klebsiella , Neisseria species, Bacillus anthracis ( anthrax ), Bacillus subtilis , Clostridium and Listeria monocytogenes indicated. Flucloxacillin has good tissue penetration , crosses the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk . It is often used for infections of the skin, mucous membranes and soft tissues - such as boils and abscesses , pyoderma and paronychia - as well as the respiratory tract, bones and bone marrow. Most enterococci are resistant to flucloxacillin.
Trade names
Flanamox (D), Floxapen (A, CH), Staphylex (D), Fluclox (D)
literature
- Sutherland R, Croydon EA, Rolinson GN: Flucloxacillin, a new isoxazolyl penicillin, compared with oxacillin, cloxacillin, and dicloxacillin . In: Br Med J . 4, No. 5733, 1970, pp. 455-460. doi : 10.1136 / bmj.4.5733.455 . PMID 5481218 . PMC 1820086 (free full text).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on Flucloxacillin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 1, 2019.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Thomas Karow, Ruth Lang-Roth: General and special pharmacology and toxicology. Lecture-oriented presentation and clinical guidelines for study and practice 2013 . Self-published, Pulheim 2013.
- ^ A b Franz von Bruchhausen: Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice . Springer DE, 1949, ISBN 3-540-52688-9 , pp. 220–222 ( limited preview in Google Book search).