Hypericin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
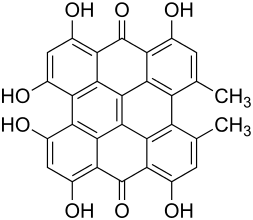
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Hypericin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
1,3,4,6,8,13-hexahydroxy-10,11-dimethylphenanthro [1,10,9,8- opqra ] perylene-7,14-dione ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 30 H 16 O 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 504.44 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
320 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in 1 M sodium hydroxide solution (10 g l −1 ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Hypericin is a red anthraquinone - derivative and one of the essential components of the coloring hypericum , in particular the Real St. John's wort ( Hypericum perforatum ). Hypericin has been used as a drug , mainly as an antidepressant . Phototoxic reactions of the skin , the lens of the eye and the retina were found to be side effects of ingestion ; The latter can lead to macular degeneration . The use of hypericin as an antidepressant is controversial today, as no evidence of the effectiveness of hypericin has been established.
application
In Germany, hypericin is contained in all medicines that contain St. John's herbs.
Side effects
The large chromophore-like system of the molecule means that it can cause a phototoxic reaction in the body if the substance (often used as a "natural" antidepressant in the form of St. John's wort products) is taken in excess or with other photosensitizers (synergetic effect), as hypericin Body photosensitivity increased. After external use of hypericin (baths / foot baths with St. John's wort ), edema can occur when exposed to the sun .
Hypericin activates cytochrome P450 , especially subtype 3A4 , in the liver. Since this is responsible for the metabolism of many medicinal substances, the breakdown of these is promoted. This affects u. a. Contraceptives , which make birth control pills less effective.
Other uses
Since hypericin accumulates preferentially on cancerous tissue , it is used in fluorescence diagnosis as an indicator for cancer cells .
In the research area of photodynamic cancer therapy , hypericin is also used as a photosensitizer because of this accumulation in cancerous tissue . After the administration of the sensitizer, the patient is irradiated with a specific light spectrum which is generated with the aid of lamps or a laser . This exposure leads to a reaction of the sensitizer with oxygen, which leads to the formation of oxygen radicals ; which leads to the death of the irradiated cancer cells. The possibility is also being tested of sensitizing highly resistant bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus strains in festering burns, with hypericin and then killing them with red or IR light.
The antiviral activity is mainly based on the property of hypericin to generate oxygen radicals with light (singlet oxygen, but also other species). These oxygen radicals are toxic and destroy organic material such as the cell wall, genetic information, etc. Because the incubations of hypericin with viral material were usually not protected from light, oxygen radicals inactivate the viruses. In the dark reaction, hypericin usually shows no antiviral activity at all.
St. John's wort ( Hypericum perforatum )
St. John's wort oil containing hypericin ("Johannisöl, Oleum hyperici")
biosynthesis
Hypericin - a fluorescent, cherry-red dye - is biosynthesized from emodin .
Analytics
For the reliable determination of hypericin, the coupling of HPLC with mass spectrometry can be used after adequate sample preparation .
literature
- H. Brockmann , F. Kluge, H. Muxfeldt: Total synthesis of hypericin. In: Chem. Ber. 1957, pp. 2302-2318.
- A. Kubin, F. Wierrani, U. Burner, G. Alth, W. Grünberger: Hypericin - the facts about a controversial agent. In: Current pharmaceutical design. Volume 11, Number 2, 2005, pp. 233-253. PMID 15638760 (Review).
- Heinz Falk : From the photosensitizer hypericin to the photoreceptor stentorin - the chemistry of phenanthroperylene quinones. In: Angew. Chemistry. 111, 1999, pp. 3306-3326.
- M. Waser, H. Falk: Towards Second Generation Hypericin Based Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. 11, 2007, pp. 547-558.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hypericin data sheet (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on December 14, 2010.
- ↑ Data sheet Hypericin from Hypericum perforatum from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 14, 2010 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Hypericin data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 4, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ AR Wielgus et al: Phototoxicity in human retinal pigment epithelial cells promoted by hypericin, a component of St. John's wort. In: Photochem. Phytobiol. 83, 3, 2007, pp. 706-713. PMID 17576381 .
- ↑ H. Schilcher, S. Kammerer: Guide to Phytotherapy. 1st edition. Urban & Fischer, 2000, ISBN 3-437-55340-2 .
- ↑ Alexander Paulke, Manfred Schubert-Zsilavecz, Mario Wurglics: Determination of hypericin and pseudohypericin from Hypericum perforatum in rat brain after oral administration. In: Monthly magazine for chemistry. 139, 2008, p. 489, doi: 10.1007 / s00706-007-0792-1 .
- ↑ Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules. Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich 2006, ISBN 3-906390-29-2 , p. 192.
- ↑ Zuzana Jendželovská, Rastislav Jendželovský, Barbora Kuchárová, Peter Fedoročko: Hypericin in the Light and in the Dark: Two Sides of the Same Coin . In: Frontiers in Plant Science . tape 7 , May 6, 2016, doi : 10.3389 / fpls.2016.00560 , PMID 27200034 , PMC 4859072 (free full text).
- ↑ A. Kubin, F. Wierrani, U. Burner, G. Alth, W. Grunberger: hypericin-the facts about a controversial agent. In: Current pharmaceutical design. Volume 11, Number 2, 2005, pp. 233-253, PMID 15638760 (review).
- ↑ KD Riedel, K. Rieger, M. Martin-Facklam, G. Mikus, WE Haefeli, J. Burhenne: Simultaneous determination of hypericin and hyperforin in human plasma with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. In: J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 813 (1-2), Dec 25, 2004, pp. 27-33. PMID 15556512 .
- ↑ XJ Zhai, F. Chen, C. Chen, CR Zhu, YN Lu: LC-MS / MS based studies on the anti-depressant effect of hypericin in the chronic unpredictable mild stress rat model. In: J Ethnopharmacol. 169, Jul 1, 2015, pp. 363-369. PMID 25957811 .
- ^ F. Liu, C. Pan, P. Drumm, CY Ang: Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry studies of St. John's wort methanol extraction: active constituents and their transformation. In: J Pharm Biomed Anal. 37 (2), Feb 23, 2005, pp. 303-312. PMID 15708671 .


