Indaziflam
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
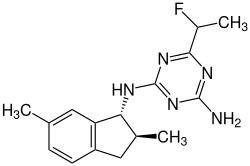
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without complete stereochemistry - mixture of diastereomers - |
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Indaziflam | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
2-Amino-4 - [(1 R , 2 S ) -2,6-dimethyl-indan-1-ylamino] -6 - [(1 RS ) -1-fluoroethyl] -1,3,5-triazine |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 20 FN 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
beige-colored, powdery solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 301.36 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.23 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
183 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.5 · 10 −8 Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility | |||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Indaziflam is a synthetic herbicide from the fluoroalkyltriazine class of substances . It was launched in the United States in 2010 by Bayer CropScience .
presentation
2,6-Dimethyl-1-indanone is catalyzed by a ruthenium (II) complex and reduced stereospecifically to cis - 2,6-dimethyl-indan-1-ol . This intermediate product reacts by means of diphenylphosphoryl azide to form trans - 1-amino-2-methylindane ( Staudinger reaction ). With dicyandiamide in the presence of aluminum triisopropoxide and subsequent ring closure with methyl 2-fluoropropanoate under basic conditions, diastereomeric indaziflam is formed.
Properties and structure
Indaziflam is a beige, powdery solid. It is not very volatile and only sparingly soluble in water. It is very persistent in the soil with half-lives of over 150 days. In shallow waters it photolyzes relatively quickly with a half-life of 5 days.
Stereoisomers
The molecule has three stereocenters . Eight different isomers are therefore possible. The active ingredient is a mixture of two isomers, the
- (1 R , 2 S , 1 R ) form and the
- (1 R , 2 S , 1 S ) shape.
Mode of action
Indaziflam is the most powerful cellulose biosynthesis inhibitor known to date . By inhibiting the formation of cellulose, the cell growth of the plants is disturbed. For this reason, Indaziflam is not suitable for mature plants, but works particularly well on plants in the development or growth phase. It acts on both monocotyledons and dicotyledons . The effect sets in quickly after application (within an hour) and it has a broad spectrum of activity. One study found that plants with resistance to other cellulose biosynthesis inhibitors such as isoxaben are not resistant to indaziflam. This suggests that indaziflam has a different mechanism of action.
use
Indaziflam is used to control weeds on lawns in domestic gardens and sports fields and as a pre-emergence herbicide in the cultivation of stone and pome fruit, citrus fruits, wine, coffee and olives. It is primarily aimed at annual grasses such as Indian fingergrass ( Eleusine indica ), annual bluegrass , lolch and goosefoot plants as well as broad-leaved weeds.
toxicology
Indaziflam is not acutely toxic after oral, dermal or inhalation ingestion. In addition, it does not irritate the eyes or the skin and does not cause skin sensitization. In two-year studies on rats and mice, no carcinogenic or genotoxic effects were observed. For this reason, the US Environmental Protection Agency classifies the substance as probably not carcinogenic .
Admission
In the European Union and Switzerland do not have pesticides approved with the drug Indaziflam. Worldwide, however, it is used in some countries, e.g. Used in the United States , Canada , Mexico, and Japan . The active ingredient is also being sold on the Brazilian market.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on Indaziflam in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on August 5, 2019.
- ↑ a b Datasheet Indaziflam from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on August 5, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Peter Jeschke, Matthias Witschel, Wolfgang Krämer, Ulrich Schirmer: Modern Crop Protection Compounds . John Wiley & Sons, 2019, ISBN 978-3-527-34089-7 ( limited preview in Google Book Search [accessed August 5, 2019]).
- ↑ Jyri Kaapro, John Hall: INDAZIFLAM - A NEW HERBICIDE FOR PRE-EMERGENT CONTROL OF WEEDS IN TURF, FORESTRY, INDUSTRIAL VEGETATION AND ORNAMENTALS . In: Pakistan Journal of Weed Science Research . tape 18 , Special Issue, December 1, 2011, p. 267-270 (English, org.pk ).
- ↑ Seth DeBolt, Michael Barrett, Jozsef Stork, Ying Gu, Lei Lei: Indaziflam Herbicidal Action: A Potent Cellulose Biosynthesis Inhibitor . In: Plant Physiology . tape 166 , no. 3 , November 1, 2014, ISSN 0032-0889 , p. 1177–1185 , doi : 10.1104 / pp.114.241950 , PMID 25077797 , PMC 4226351 (free full text) - ( plantphysiol.org [accessed August 5, 2019]).
- ↑ Pesticide Fact Sheet - Indaziflam. (PDF) In: USEPA. July 26, 2010, accessed August 5, 2019 .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on indaziflam in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on April 25, 2020.
- Jump up ↑ Benjamin Luig, Fran Paula de Castro and Alan Tygel (both Campanha Permanente Contra os Agrotóxicos e Pela Vida), Lena Luig (INKOTA network), Simphiwe Dada (Khanyisa), Sarah Schneider (MISEREOR) and Jan Urhahn (Rosa-Luxemburg- Foundation): Dangerous pesticides. (PDF; 2.4 MB) from Bayer and BASF - a global business with double standards. Rosa Luxemburg Foundation , INKOTA network , Episcopal Aid Organization Misereor u. a., April 2020, accessed on April 25, 2020 .
