Iprovalicarb
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| Mixture of two diastereomers ( S, R ) -form (top) and ( S, S ) -form (bottom) |
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Iprovalicarb | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 28 N 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 320.43 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.11 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point | ||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Iprovalicarb is a mixture of two isomeric chemical compounds from the group of carbamates .
Extraction and presentation
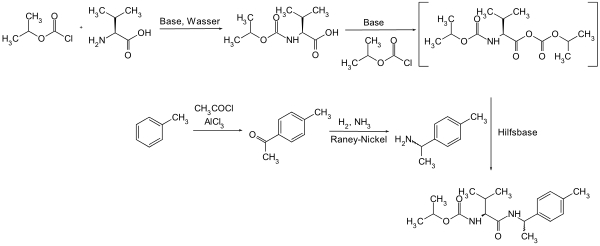
Iprovalicarb can be obtained by a multistage reaction of isopropyl chloroformate with L- valine in a sodium hydroxide solution and then again with isopropyl chloroformate under basic conditions in a toluene solution. The resulting intermediate is reacted with p -methylphenylethylamine to form iprovalicarb .
Stereochemistry
Iprovalicarb has two stereocenters which are both determined by the synthesis. By using L -Valin [( S ) -Valin] this stereocenter is firmly fixed, ie enantiomerically pure . However, the synthesis of p -methylphenylethylamine leads to the racemate (1: 1 mixture of both enantiomers). For ipovalicarb, this means that it is formed as a mixture of two diastereomers .
properties
Iprovalicarb is a flammable white solid that is very sparingly soluble in water. It is stable to hydrolysis at pH 5 to 9 at 25 ° C.
use
Iprovalicarb is used as an active ingredient in crop protection products. It is used as a fungicide on potatoes and grapevines. On March 30, 1998, Bayer AG applied to the EU to include the connection in Annex I of Directive 91/414 / EEC. It was the first fungicide from the amino acid amide class and occurs in four stereoisomeric forms. It was first approved in Indonesia in 1998 . It is often used as a combination preparation with other crop protection products such as Tolylfluanid , Mancozeb , Folpet and Propineb . The effect is based on the inhibition of cellulose synthase.
Admission
Since July 2002, plant protection products with iprovalicarb can be approved in the states of the European Union. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, plant protection products (e.g. Melody Combi ) containing this active ingredient are approved.
literature
- Britta Delvos: Studies of the effects of iprovalicarb and dimethomorph on the cell wall of Phytophthora infestans, urn : nbn: de: hbz: 061-20090722-070741-2
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on iprovalicarb in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 4, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h EU: Review report for the active substance iprovalicarb (PDF file; 294 kB), July 2, 2002
- ↑ a b Wolfgang Krämer, Ulrich Schirmer, Peter Jeschke, Matthias Witschel: Modern Crop Protection Compounds . Wiley-VCH, 2011, ISBN 978-3-527-32965-6 , pp. 812 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Directive 2002/48 / EC of the Commission of May 30, 2002 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and including the active substances Iprovalicarb, Prosulfuron and Sulfosulfuron (PDF)
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Iprovalicarb in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 13, 2016.