Potassium oxide
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ K + __ O 2− | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium oxide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | K 2 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
hygroscopic, colorless and odorless crystals |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 94,20 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
2.32 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | |||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
violent decomposition in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Potassium oxide (K 2 O) is a chemical compound from the group of alkali metal oxides and is a white solid.
Extraction and presentation
Potassium oxide can be obtained through the reaction of oxygen and potassium , whereby potassium peroxide K 2 O 2 and, through the reaction with further potassium, then potassium oxide is formed.
Alternatively, potassium oxide can be created by heating potassium nitrate with potassium:
properties
Physical Properties
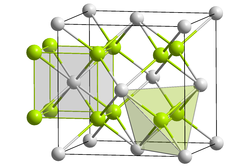
Potassium oxide has a antifluorite - crystal structure . In this structure, the anions and cations exchange their positions compared to that of calcium fluoride .
The standard enthalpy of formation of potassium oxide is ΔH f 0 = −363 kJ / mol.
Chemical properties
Like other alkali metal oxides, potassium oxide forms a hydroxide on contact with water , in this case potassium hydroxide (KOH), which dissolves in water to form potassium hydroxide .
Potassium oxide is the anhydride in potassium hydroxide. In the air it reacts with the humidity to form potassium hydroxide and with carbon dioxide to form potassium carbonate .
Potash lye is a strong lye that, like caustic soda , attacks fats , base metals and glass , among other things . With strong acids , rapid, sometimes vigorous neutralization occurs . The reaction is slower with weak or very dilute acids . It formed potassium salts .
use
Potassium oxide itself is not used as a fertilizer (PK / NPK fertilizer), but is used there as a unit of measurement for the proportion of potassium (e.g. in the form of potassium sulfate , potassium formate , potassium nitrate or potassium chloride ) in the fertilizer.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on POTASSIUM OXIDE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 4, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on potassium oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ^ AF Holleman , N. Wiberg : Inorganische Chemie . 103rd edition. Volume 1: Basics and main group elements. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / Boston 2016, ISBN 978-3-11-049585-0 , p. 1515 (reading sample: Part A - Basics of the chemistry of hydrogen. Google book search ).
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1285.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1286.
- ↑ Federal Ministry of Justice: Ordinance on the placing on the market of fertilizers, soil additives, growing media and plant additives (Fertilizer Ordinance - DüMV) §6 (definition of fertilizer types)




