Löcknitz (Elbe)
| Löcknitz | ||
|
Löcknitz near Polz |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | EN : 5932 | |
| location | Ludwigslust-Parchim district , Prignitz , Neuhaus district | |
| River system | Elbe | |
| Drain over | Elbe → North Sea | |
| River basin district | Elbe | |
| source |
Ziegendorf near Parchim 53 ° 18 ′ 35 ″ N , 11 ° 49 ′ 55 ″ E |
|
| Source height | approx. 53 m | |
| muzzle | At Wehningen in the Elbe coordinates: 53 ° 10 '3 " N , 11 ° 9' 21" E 53 ° 10 '3 " N , 11 ° 9' 21" E |
|
| Mouth height | 11.5 m | |
| Height difference | approx. 41.5 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 0.63 ‰ | |
| length | 66 km | |
| Catchment area | 937 km² | |
| Discharge at the Gadow A Eo gauge : 464 km² Location: 42.9 km above the mouth |
NNQ (July 25, 1963) MNQ 1956–2014 MQ 1956–2014 Mq 1956–2014 MHQ 1956–2014 HHQ (March 4, 1956) |
50 l / s 439 l / s 2.31 m³ / s 5 l / (s km²) 10.6 m³ / s 22.2 m³ / s |
| Drain |
MQ |
4.6 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | u. a. Karwe, main trench | |
| Right tributaries | u. a. Löcknitz-Mühlbach, Tarnitz , Alte Elde | |
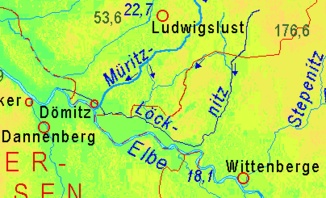
The Löcknitz is a right tributary of the Elbe . It flows through Mecklenburg and Brandenburg to Lower Saxony , 43 of the 66 river kilometers run in Brandenburg. The catchment area of the Löcknitz covers 937 km², of which 460 km² are in Brandenburg.
course
The headwaters of the Löcknitz are located in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania in the Ludwigslust-Parchim district northeast of Ziegendorf on the western foothills of the Ruhner Mountains .
The Löcknitz flows south from its source. The Brandsöhler Bach flows into it at the level of Balow . Around Streesow , the Tarnitz flows on the right into the Löcknitz, which crosses the border to Brandenburg ( Prignitz district ) there, shortly afterwards the Karwe flows on the left . To the west of Karstädt, federal road 5 crosses the Löcknitz, which continues to flow between extensive forest areas. From Karstädt the Löcknitz reaches a width of 10-14 meters and an average water depth between 0.7 and 1.3 meters. The weir systems reach a depth of up to two meters.

The Löcknitz crosses the Gadower Forest, at Bernheide the Schmaldiemen flows from the east . Here the river bends west and flows parallel to the Elbe, a few kilometers away, to the small town of Lenzen . At Baekern, the Löcknitz is up to 70 meters wide and up to four meters deep. The Alte Elde flows into Seedorf . In the further course to the west, the Löcknitz delimits the Lenzer Wische , which historically was often flooded by the Elbe and Löcknitz. To the west of Polz , the Löcknitz forms the border between Brandenburg and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania for a short section. Until 1973, Klein Schmölen where it flows into the Elbe.
New Löcknitz
In order to improve its drainage into the Elbe, which has a steeper gradient, for flood protection, the Löcknitz was lengthened parallel to the Elbe by about ten kilometers. This Neue Löcknitz bends in Dömitz , about a kilometer before the old mouth, north of the Löcknitz and then flows west to Dömitz. There it is passed under the Elde Canal by means of a culvert and then passed north of the city. Six kilometers northwest of Dömitz, the river has flowed into the Elbe at Wehningen (river kilometer 513) since 1973 . When the Elbe floods, the Wehningen weir can be closed, thus preventing Elbe water from flowing into the Löcknitz. As a result of the reintegration of the Neuhaus office into Lower Saxony in 1993, the Löcknitz estuary has been in this state since then.
history
Until around 1900 the course of the river was regarded as that of the Alte Elde after the union of the Alte Elde with the Löcknitz near Seedorf. Only then was this piece called Löcknitz.
nature
The Löcknitz is important for the irrigation and drainage of agricultural areas, but also important for nature conservation. The lower reaches of the Löcknitz are located in the Löcknitztal-Altlauf nature reserve . Near Ziegendorf there is the largest river mussel population in the Löcknitz with the highest number of young mussels in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. Especially in the upper reaches there were water engineering interventions, several built-in weirs dam the water for the irrigation of adjacent agricultural areas. These stretches of water are mostly meliorated and without wood fringes. Heavy vegetation with aquatic plants forms in the fully exposed parts. In the Löcknitz Valley, due to the occurrence of numerous species of amphibians, birds, butterflies and dragonflies, some parts are classified as ecologically "valuable" or "particularly valuable". In the lower reaches, e.g. B. in the area of the Gandower Schweinweide and the Lenzer Wische , the Löcknitz with its tributaries, oxbow lakes and ponds forms a highly branched water system, there are remains of broken and alluvial forests, large areas of reed beds, bank breaks, sandbanks as well as impact and sliding slopes. This landscape offers a habitat for many protected plant species as well as for animal species such as beavers , bats and various rare birds, including sea eagles , as well as numerous insects including dragonfly species, such as the southern damsel and the southern rush damsel . The river is also an important connecting water for the migration of the otter . In the Löcknitz there are numerous species of fish, especially lead, roach, bream, aland, tench, carp, pike, trout, eel, perch and pikeperch.
Individual evidence
- ^ German Hydrological Yearbook Elbe Region, Part III 2014. (PDF) ISSN 0949-3654. Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, Hamburg Port Authority, p. 133 , accessed on October 4, 2017 (German, at: dgj.de).
- ^ Keyword Elde in: Meyers Konversationslexikon , 4th edition, 1885-1892
- ^ Gustav Hempel : Geographical-statistical-historical handbook of the Meklenburger Land , Frege, 1837
- ↑ various maps, example
- ^ Keyword Elde in: Meyers Großes Konversationslexikon , 6th edition, 1905–1909
- ↑ various maps, example