Nothoscordum
| Nothoscordum | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Nothoscordum | ||||||||||||
| Kunth |
The nothoscordum , sometimes also called bastard onion or bastard flowers, form a genus of plants in the subfamily of the allioideae . The generic name Nothoscordum is derived from the Greek: notho for false and scordum for garlic. The genus includes about 25 species .
Description and ecology

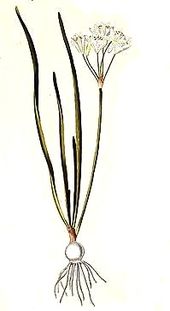
Nothoscordum species are perennial herbaceous plants . The parts of the plant hardly or not smell of garlic or onions. These geophytes form egg-shaped bulbs with a membranous coating and many brood bulbs as persistence organs. The leaves are mostly present during the flowering period. The leaves are alternate and usually arranged spirally in a basal rosette. The sessile, simple, parallel- veined leaves are linear and thread-shaped. The leaf margin is smooth.
The inflorescence shaft is mostly hollow, sometimes solid in individual areas. The originally doldige inflorescence usually contains several flowers. The two membranous bracts protect the buds when they are in bud. The upright flower stalks are different (1 to 5 cm) long. The hermaphroditic, radial symmetry flowers are threefold and often scented. The usually six, in some species eight (exception within the monocot ), almost identical bracts are fused tubular at their base to about a third of their length. The free areas of the bracts are often spread out in a star shape. The colors of the bracts range from white to yellow. There are two circles with three fertile stamens each, they are free from one another, but fused with the base of the bracts and do not protrude beyond them. The stamens are awl-shaped and broadened at their base. The three pistils have become a top permanent ovary grown with some (up to twelve) ovules per ovary chamber. The thread-like stylus ends in a small scar. There are septal nectaries. Pollination occurs by insects ( entomophilia ).
Three-lobed, membranous, loculicidal capsule fruits are formed which contain some seeds. The oil-containing, phytomelane black seeds are angular, flattened to flat.
Systematics and distribution
The genus Nothoscordum was established in 1843 by Karl Sigismund Kunth in Enumeratio Plantarum , 4, p. 457. Type species is Nothoscordum striatum (Jacq.) Kunth. , today a synonym of Nothoscordum bivalve (L.) Britton var. bivalve . A synonym for Nothoscordum Kunth is: Zoellnerallium Crosa .
The genus Nothoscordum belongs to the tribe Ipheieae in the subfamily Gilliesioideae within the family Alliaceae .
Some authors classify some species of the genus Nothoscordum as belonging to the Ipheion , for example Nothoscordum sellowianum or Nothoscordum dialystemon . In most cases, the umbellate inflorescences of the Nothoscordum species contain several flowers and the Ipheion species only one flower, but there are exceptions. Other genera in which some of the Nothoscordum species are classified are: Milla , Tristagma , Brodiaea , Beauverdia .
The genus Nothoscordum is originally widespread in the New World . Most species are found in South America , some are also found in North America. In many countries, some species are invasive plants .


The genus Nothoscordum contains 25 to 85 species:
- Nothoscordum achalense Ravenna : It occurs only in the Argentine province of Córdoba .
- Nothoscordum albitractum Ravenna : It occurs only in the Argentine province of Jujuy .
- Nothoscordum altillanense Ravenna & Biurrun : It occurs only in the Argentine province of La Rioja .
- Nothoscordum andicola Kunth : It is distributed from Peru to north-western Argentina.
- Nothoscordum andinum (Poepp.) Kunth ex Fuentes (Syn .: Nothoscordum strictum Gay , Nothoscordum brevispathum Phil. , Nothoscordum sellowianum var. Brevispathum (Phil.) Fuentes , Nothoscordum poeppigii (Kunth) Fuentes ): It is from Chile to the argentinian provinces Mendoza as well as San Juan common.
- Nothoscordum aparadense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum arenarium Herter
- Nothoscordum auratum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum bahiense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum balaenense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum basalticum Ravenna
-
Nothoscordum bivalve (L.) Britton : There are two varieties:
- Nothoscordum bivalve (L.) Britton var. Bivalve (Syn .: Nothoscordum flavescens Kunth , Nothoscordum ornithogaloides (Walter) Kunth , Nothoscordum sellowianum Kunth , Nothoscordum striatellum (Lindl.) Kunth , Nothoscordum striatum (Jacq.) Kunth , Nothoscordum subbiflorum (Colla) Walp. , Nothoscordum philippianum Kunth & CDBouché , Nothoscordum gramineum Beauverd , Nothoscordum texanum M.E.Jones ): It is distributed in the Neotropics.
- Nothoscordum bivalve var. Nanum (Griseb.) Guagl. : It is common in northeastern Argentina.
- Nothoscordum boliviense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum bonariense (Pers.) Beauverd
- Nothoscordum × borbonicum Kunth
- Nothoscordum calcaense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum calderense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum cambarense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum capivarinum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum carambolense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum catharinense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum clevelandicum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum collinum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum conostylum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum correntinum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum curvipes Ravenna
- Nothoscordum cuyanum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum demissum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum dialystemon (Guagl.) Crosa
- Nothoscordum dynamiandrum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum empedradense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum entrerianum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum exile Ravenna
- Nothoscordum famatinense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum gaudichaudianum Kunth
- Nothoscordum glareosum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum gracile (Aiton) Stearn
- Nothoscordum gracilipes Ravenna
- Nothoscordum ibiramense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum ineanum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum inundatum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum ipacarainum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum itatiense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum izaguirreae Crosa
- Nothoscordum jaibanum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum leptogynum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum luteomajus Ravenna
- Nothoscordum luteominus Ravenna
- Nothoscordum macrantherum (Kuntze) Beauverd
- Nothoscordum mahui Traub
- Nothoscordum moconense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum modestum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum montevidense Beauverd
- Nothoscordum nublense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum nudicaule (loam.) Guagl.
- Nothoscordum nudum Beauverd
- Nothoscordum nutans Ravenna
- Nothoscordum ostenii Beauverd
- Nothoscordum pachyrhizum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum paradoxum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum patricium Ravenna
- Nothoscordum pedersenii Ravenna
- Nothoscordum pernambucanum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum planifolium Ravenna
- Nothoscordum portoalegrense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum pulchellum Kunth
- Nothoscordum punillense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum rigidiscapum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum saltense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum scabridulum Beauverd
- Nothoscordum sengesianum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum serenense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum setaceum (Baker) Ravenna
- Nothoscordum stenandrum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum subtle Ravenna
- Nothoscordum tafiense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum tarijanum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum tenuifolium Ravenna
- Nothoscordum tibaginum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum tricostatum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum tuyutiense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum umburucuyanum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum uruguaianum Ravenna
- Nothoscordum velazcoense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum vernum Phil.
- Nothoscordum vigilense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum yalaense Ravenna
- Nothoscordum yatainum Ravenna
Four South American Nothoscordum species were placed in the reactivated genus Beauverdia Herter in 2014 :
- Nothoscordum dialystemon (Guagl.) Crosa → Beauverdia dyalistemon (Guagl.) Sassone & Guagl.
- Nothoscordum hirtellum (Kunth) Herter → Beauverdia hirtella (Kunth) Herter subsp. hirtella : There are two subspecies:
- Nothoscordum lorentzii (Herter) Ravenna → Beauverdia hirtella subsp. Lorentzii (Herter) Sassone & Guagl.
- Beauverdia sellowiana (Kunth) Herter
- Nothoscordum vittatum (Griseb.) Ravenna → Beauverdia vittata (Griseb.) Herter
use
In the genus Nothoscordum there are a few species that are ornamental plants for the garden.
Nothoscordum gracile onions are eaten raw or cooked; they serve as a substitute for garlic . However, the plants of Nothoscordum gracile do not smell of garlic or onions when injured; this species is rated as an aggressive invasive plant.
swell
- TD Jacobsen, Dale W. McNeal Jr .: Nothoscordum. , P. 276 - the same text online as the printed work , In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Ed.): Flora of North America North of Mexico. Volume 26: Magnoliophyta: Liliidae: Liliales and Orchidales , Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford, 2002. ISBN 0-19-515208-5
- J. Gathe, Leslie Watson: Nothoscordum. in the Western Australian Flora online.
- DC Godden: Nothoscordum. : New South Wales Flora online .
- Agostina B. Sassone, Liliana M. Giussani, Encarnación R. Guaglianone: Beauverdia, a Resurrected Genus of Amaryllidaceae (Allioideae, Gilliesieae). In: Systematic Botany , Volume 39, Issue 3, 2014, pp. 767-775. doi: 10.1600 / 036364414X681527
Individual evidence
- ^ Nothoscordum at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
- ^ A b Nothoscordum in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved October 28, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm Rafaël Govaerts (Ed.): Nothoscordums - Data sheet at World Checklist of Selected Plant Families of the Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved October 28, 2014
- ↑ Entries on Nothoscordum at Plants For A Future
- ↑ Invasive Plant.
Web links
- Nothoscordum at the pacificbulbsociety .
- Nothoscordum at the bulbsociety .