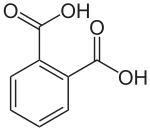
Phthalic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phthalic acid (more precisely ortho- phthalic acid ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phthalic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 6 O 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
monoclinic, colorless tablets, needles or scales |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 166.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.59 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
191 ° C (closed capillary) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
decomposes when heated |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 5 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Phthalic acid [ ˈftaːl… ] is a chemical which in chemistry is one of the carboxylic acids , more precisely the dicarboxylic acids . Phthalic acid is usually used to denote orthophthalic acid, which, along with terephthalic acid, has the greatest technical importance. The bulk of phthalic acids in terms of quantity is used in the manufacture of synthetic resins or synthetic fibers. The salts and esters of phthalic acids are called phthalates .
As a term, phthalic acid comprises the group of three positionally isomeric benzene dicarboxylic acids , which differ in the arrangement of the two carboxylic acid groups. In detail these are:
- 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid ( ortho -phthalic acid, o -phthalic acid)
- 1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid ( isophthalic acid , m -phthalic acid)
- 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid ( terephthalic acid , p -phthalic acid)
history
o -phthalic acid was discovered by Auguste Laurent in 1836 during the oxidation of 1,2,3,4-tetrachloro-1,2,3,4- tetrahydronaphthalene with nitric acid, so it got its name from this hydrocarbon.
Manufacturing
For a long time, o- phthalic acid was only produced by oxidizing naphthalene with oleum using a process developed by Eugen Sapper ; today, however, o- xylene is by far the predominant raw material used. Isophthalic acid is also produced from m -Xylene and terephthalic acid from p -Xylene .
properties
o -phthalic acid is a colorless, crystalline solid. The acid is slightly soluble in water.
It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system in the space group C 2 / c (space group no. 15) with the lattice parameters a = 500 pm , b = 1420 pm, c = 960 pm and β = 93.5 °. In the unit cell contains four formula units .
use
o -Phthalic acid is a raw material for the production of polyester resins. The phthalic acid or mostly its anhydride with polyhydric alcohols , eg. B. glycerin , esterified. By boiling polyunsaturated vegetable oils such as linseed oil with phthalic acid and polyhydric alcohols, alkyd resins are produced by transesterification. Phthalic acid is also the starting material for the production of many dyes , color pigments and plasticizers . Some of the phthalic acid esters used as plasticizers are controversial as hazardous to health ( endocrine disruptors ). The thermally very stable phthalocyanines can be produced via the intermediate stage phthalic acid dinitrile or phthalic anhydride . From the phthalic anhydride, the Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene leads to anthraquinone , from which vat dyes can be produced.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on phthalic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on phthalic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 23, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ chem.wisc.edu: pKa Data , Compiled by R. Williams (PDF, 78 kB).
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 88-99-3 or phthalic acid ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ^ Paul Karrer, Textbook of Organic Chemistry, Georg Thieme Verlag, 1941.
- ↑ Entry on isophthalic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on terephthalic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ^ TGD van Schalkwyk: The Crystal Structure of Phthalic Acid , in: Acta Cryst. , 1954, 7 , p. 775; doi : 10.1107 / S0365110X54002344 .

