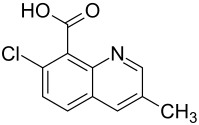
Quinmerac
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Quinmerac | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 8 ClNO 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, odorless powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 221.64 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.49 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
244-246 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
416 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very sparingly soluble in water (0.223 g l −1 ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Quinmerac is a chemical compound from the group of quinolines and carboxylic acids and a systemic herbicide introduced by BASF in 1993 .
Extraction and presentation
Quinmerac can be obtained by reacting 7-chloro-3,8-dimethylquinoline with N -bromo succinimide , sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid .
use
Quinmerac is used as a soil herbicide against problem weeds such as burdock bedstraw , speedwell species and dead nettles in cereal, rapeseed and sugar beet cultivation. Quinmerac is a synthetic auxin that induces ACC synthase . This primarily leads to an accumulation of the plant hormone abscisic acid in the plant tissue . This leads to the death of the sensitive plant via leaf epinasty , growth inhibition of the roots and increased perspiration.
Admission
In Germany, Austria and other EU countries as well as in Switzerland, plant protection products with quinmerac as an active ingredient are approved.
literature
- Britt Leps: Anti-Quinmerac: Single Chain Antibody Expression in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Dissertation, Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg, 2003. urn : nbn: de: gbv: 3-000005961
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on 7-chloro-3-methyl-8-quinolinecarboxylic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 31, 2020 (JavaScript required)
- ↑ a b SAFETY DATA SHEET Quinmerac. (PDF) In: HPC Standards GmbH. April 9, 2019, accessed July 31, 2020 .
- ↑ a b Entry on Quinmerac. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 21, 2014.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 593 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Florene Scheltrup, Klaus Grossmann: Abscisic Acid is a Causative Factor in the Mode of Action of the Auxinic Herbicide Quinmerac in Cleaver (Galium aparine L.) . In: Journal of Plant Physiology . tape 147 , no. 1 , January 1995, p. 118–126 , doi : 10.1016 / s0176-1617 (11) 81423-9 ( PDF ).
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Quinmerac in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 7, 2019.
