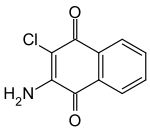
Quinoclamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Quinoclamine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
2-amino-3-chloro-1,4-naphthoquinone |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 6 ClNO 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 207.61 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.55 g cm −3 (bulk density) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
202 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
348 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
7.0 10 −3 mPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility | ||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Quinoclamine is a chemical compound from the quinone group that is used as a herbicide .
Extraction and presentation
Quinoclamine can be obtained by reacting 2,3-dichloro-1,4-naphthoquinone with ammonia by nucleophilic substitution .
properties
Quinoclamine is a yellow solid that is practically insoluble in water.
use
Quinoclamine is used as a herbicide and algicide . The effect is based on the inhibition of photosynthesis.
Admission
The active ingredient quinoclamine was approved in Germany in 1998. In the European Union it was approved for use as a herbicide with effect from January 1, 2009. However, the approval has since expired.
In Switzerland, plant protection products (e.g. Mogeton) with this active ingredient are approved.
Web links
- Review report for the active substance quinoclamine , March 14, 2008
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j data sheet Quinoclamine at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 21, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Quinoclamine in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed July 31, 2013.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide synthesis handbook . 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5 , pp. 968 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ pesticide info : Quinoclamine - toxicity, ecological toxicity and regulatory information
- ↑ Peter Brandt: Reports on Plant Protection Products 2009: Active Ingredients in Plant Protection Products ; Approval history and regulations of the Plant Protection Application Ordinance . Springer DE, 2010, ISBN 3-0348-0028-2 , pp. 25 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Directive 2008/66 / EC of the Commission of 30 June 2008 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substances bifenox, diflufenican, fenoxaprop-P, fenpropidin and quinoclamine (PDF) .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Quinoclamine in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 6, 2019.


