SStB - Bavaria
| SStB - Bavaria | |
|---|---|
|
SStB - Bavaria
|
|
| Numbering: | SB 897 |
| Number: | 1 |
| Manufacturer: | Maffei |
| Year of construction (s): | 1851 |
| Axis formula : | B'B '+ Ct n2 |
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) |
| Fixed wheelbase: | 2,970 mm |
| Total wheelbase: | 10,964 mm |
| Service mass with tender: | 73.0 t |
| Friction mass: | 73.0 t |
| Driving wheel diameter: | 1,067 mm |
| Number of cylinders: | 2 |
| Cylinder diameter: | 508 mm |
| Piston stroke: | 764 mm |
| Boiler overpressure: | 8.5 atm |
| Number of heating pipes: | 229 |
| Heating pipe length: | 4424 mm |
| Grate area: | 2.3 m² |
| Tubular heating surface: | 175.0 m² |
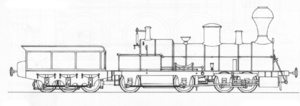
The steam locomotive "BAVARIA" was a freight locomotive of the Imperial and Royal Southern State Railways . It was built by the Maffei locomotive factory in Munich on the occasion of the Semmering competition in 1851 . The other three locomotives that took part in this competition for the right locomotive for the Semmering Railway were the “ SERAING ”, the “ NEUSTADT ” and the “ VINDOBONA ”.
The "BAVARIA" had four axles , the front two of which were stored in a bogie . The wheels of the bogie and the wheels of the three-axle tender were connected by coupling rods. From behind the firebox arranged driving axle , the tender axes were within the frame driven horizontal chain wheels and a chain. The axles of the bogie were also connected to the coupling axle in front of the fire box. So the total weight of the locomotive and the tender could be used as an adhesive weight.
In the performance tests carried out in the course of the competition, the locomotive far exceeded the prescribed performance parameters and landed in first place. The vehicle was bought by the state for 20,000 ducats.
During further test drives (between January 12th and April 28th, 1852) it turned out that the chains required for the drive only withstood the load for a few days. Without these chains, however, the performance of the "BAVARIA" would have been equivalent to that of a double-coupled machine, which means that it would not have been suitable for operation on the Semmering .
Because of the above-mentioned defects, the machine was soon shut down and eventually scrapped. Its powerful boiler still supplied steam as a stationary boiler in the Graz operations workshop of the Southern State Railroad until the mid-1860s .
literature
- Ad. Schmid: Railway over the Semmering . (Part One). In: Georg Winiwarter (Red.): Journal of the Austrian Engineering Association . Issue 17.1851 (3rd year), ZDB -ID 2534635-0 . Seidel, Vienna 1851, pp. 131–136, route profile (two maps). - Text online (PDF; 7.0 MB) ,
- -. (Part II). Issue 18.1851, pp. 137-144. - Text online (PDF; 1.1 MB) ,
- -. (Part III). Issue 19.1851, pp. 145–152. - Text online (PDF; 2.3 MB) ,
- -. (Part IV). Issue 20.1851, pp. 153-159. - Text online (PDF; 1.0 MB) ,
- -. (Part V). Issue 21.1851, pp. 162–168, two construction plans (Loks Bavaria , Wr Neustadt ). - Text online (PDF; 4.4 MB) ,
- -. (Part VI). Issue 22.1851, pp. 169–176, two construction plans (Loks Seraing , Vindobona ). - Text online (PDF; 3.0 MB) ,
- -. (Part VII, conclusion). Issue 23.1851, pp. 177-184. - Text online (PDF; 3.0 MB) .
- Rudolf Sanzin : The influence of the construction of the Semmering Railway on the development of the mountain locomotive . In: Conrad Matschoss (ed.): Contributions to the history of technology and industry . Volume 4. Springer, Berlin 1912, ZDB -ID 2238668-3 , pp. 333-357. - Full text online .
- Karl Gölsdorf : Locomotive construction in old Austria 1837–1918 . International Archive for Locomotive History , Volume 26, ZDB -ID 256348-4 . Slezak publishing house , Vienna 1978, ISBN 3-900134-40-5 .
- Herbert Dietrich (ed.), Hermann Heless (contributions): The southern railway and its precursors . Bohmann-Verlag, Vienna 1994, ISBN 3-7002-0871-5 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Sanzin: The influence of the construction of the Semmering Railway , p. 341.