Samoro
| Samoro | ||
|
||
| Data | ||
| surface | 15.34 km² | |
| population | 329 (2015) | |
| Chefe de Suco | Luís Batista de Jesus (election 2009) |
|
| Aldeias | Population (2015) | |
| Uma Querec Leten | 171 | |
| Uma Querec Lor | 158 | |
|
|
||
Samoro is an East Timorese suco in the Soibada administrative office ( Manatuto municipality ). "Samoro" means "green snake" in Tetum .
geography
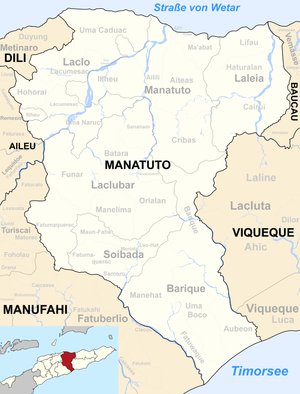
Before the 2015 regional reform, Samoro had an area of 14.35 km². Now there are 15.34 km². The Suco is located in the southeast of the Soibada administrative office. To the northwest is the Suco Fatumaquerec , northeast of the Suco Manlala and east of the Suco Leo-Hat . In the southeast Samoro borders on the administrative office Barique with its Suco Manehat and in the southwest on the administrative office Fatuberlio with its Suco Clacuc belonging to the municipality of Manufahi . The Quic river crosses the Suco before it forms the eastern border river Sáhen with the Bun coming from the north . The country road from Uma Boco to Soibada leads through the north of Samoro . Apart from the northern tip of Samoros, which extends into the town of Soibada and where the administrative headquarters of the administrative office is located, there are no larger settlements in Suco. There is a state primary school for this.
The two aldeias Uma Querec Leten and Uma Querec Lor are located in the Suco .
Residents
The Suco has 329 inhabitants (2015), 179 men and 150 women. The population density is 21.5 inhabitants / km². There are 54 households in the Suco. Over 68% of the population name Tetum Terik as their mother tongue. Almost 13% speak Idaté , almost 10% Tetum Prasa , over 3% Mambai , minorities Midiki , Makasae , Galoli , Habun , Baikeno , Adabe or Lakalei . The former empire of Samoro is considered to be the center of the eastern Tetum ( Tetum Los ).
history
At the beginning of the 18th century, the Dominican Manuel de Santo António proselytized in Samoro and converted the local Liurai to Christianity. When the ruler of Wehale concluded an alliance with the Dutch with the Treaty of Paravicini in 1756 , the kingdoms in Belu that were subordinate to him were also to join the Dutch. But many refused and stuck to the alliance with Portugal . Samoro was one of them.
The kingdom of Samoro is also listed in Portuguese lists from 1769 and 1868. The area of the Samoro Empire was significantly larger than that of today's Sucos. Soibada and the empire of Laclubar also belonged to it.
Governor José Pinto Alcoforado de Azevedo e Sousa (1815–1820) also had oil searched for in the kingdom of Samoro.
The naturalist Henry Ogg Forbes visited Samoro in 1883. Together with the Liurai's son, he was allowed to climb the over 2000 m high Sobale . To Forbes' displeasure, he was not allowed to collect any plant samples there, as the mountain was considered sacred ( lulik ).
politics
In the elections of 2004/2005 was Luís Batista (Baptista?) De Jesus elected Chefe de Suco and in 2009 re-elected.
Web links
- Results of the 2010 census for the Suco Samoro ( tetum ; PDF; 8.3 MB)
- Results of the 2015 census for the Suco Samoro (tetum; PDF)
- Seeds of Life: Suco information sheets Soibada (tetum)
supporting documents
- Geoffrey C. Gunn: History of Timor - Technical University of Lisbon (PDF file; 805 kB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Direcção-Geral de Estatística : Results of the 2015 census , accessed on November 23, 2016.
- ↑ a b Geoffrey Hull : The placenames of East Timor , in: Placenames Australia (ANPS): Newsletter of the Australian National Placenames Survey, June 2006, pp. 6 & 7, ( Memento of the original of February 14, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. accessed on September 28, 2014.
- ↑ Direcção Nacional de Estatística: Population Distribution by Administrative Areas Volume 2 English ( Memento of the original from January 5, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (2010 census; PDF; 22.6 MB)
- ^ Timor-Leste GIS-Portal ( Memento from June 30, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ UNMIT map of the Manatuto district, August 2008 ( Memento of the original from December 3, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 581 kB)
- ↑ Manatuto District Development Plan 2002/2003 ( Memento of the original dated February 3, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 829 kB)
- ↑ Jornal da Républica with the Diploma Ministerial n. 199/09 ( Memento of February 3, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) (Portuguese; PDF; 323 kB)
- ↑ Results of the 2010 census for the Suco Samoro ( tetum ; PDF; 8.3 MB)
- ↑ History of Timor, p. 7
- ^ Artur Teodoro de Matos: D. Frei Manuel de Santo António: missionário e primeiro bispo residente em Timor. Elementos para a sua biografia (1660-1733) ( Memento of the original from May 25, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (Portuguese)
- ↑ TIMOR LORO SAE, Um pouco de história ( Memento of the original dated November 13, 2001 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ East Timor - PORTUGUESE DEPENDENCY OF EAST TIMOR ( Memento of February 21, 2004 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Judith Bovensiepen: Opening and Closing the Land: Land and power in the Idaté highlands , accessed on March 29, 2015.
- ↑ History of Timor, p. 54
- ^ A. McWilliam, L. Palmer and C. Shepherd: Lulik encounters and cultural frictions in East Timor: Past and present , 2014, Aust J Anthropol, 25: pp. 304-320. doi: 10.1111 / taja.12101 ., accessed December 12, 2017.
- ↑ Secretariado Técnico de Administração Eleitoral STAE: Eleições para Liderança Comunitária 2004/2005 - Resultados ( Memento of August 4, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Secretariado Técnico de Administração Eleitoral STAE: Eleições para Liderança Comunitária 2009 - Resultados ( Memento of August 4, 2010 in the Internet Archive )