Strontium fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
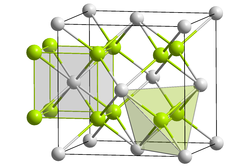
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Sr 2+ __ F - | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system | ||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Strontium fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | SrF 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 125.62 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
4.24 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1473 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
2489 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very heavy in water (0.12 g l −1 at 27 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4380 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1217 kJ mol −1 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Strontium fluoride (also strontium (II) fluoride ) is the fluoride of the alkaline earth metal strontium . It is a white, crystalline, brittle solid that becomes liquid at 1473 ° C and eventually evaporates at 2489 ° C.
Occurrence
The only known, naturally occurring compound so far is strontiofluorite , which was recognized as a mineral in 2009 , which has so far only been found at its type locality Koaschwa in the Russian Chibinen (Kola Peninsula).
presentation
Strontium fluoride can be produced by the reaction of strontium chloride (SrCl 2 ) with fluorine .
Alternatively, it can be obtained by reacting hydrofluoric acid with strontium carbonate (SrCO 3 ).
properties
The solid crystallizes in the cubic crystal system in the fluorite structure . The lattice parameter is a = 579.96 pm , the refractive index of the crystals is 1.439 at 580 nm. In the vapor phase the bond angle between F – Sr – F is approximately 120 °, which is an exception to the VSEPR model , which predicts a linear structure would. Calculations were used to show that influences of the shell, which is directly below the valence shell , cause this effect. Another assumption is that the polarization of the electron nucleus of the strontium atom causes an approximately tetrahedral charge distribution , which interacts with the Sr – F bond and thus leads to the setting of this angle.
Strontium fluoride is almost insoluble in water at 0.12 g / l. It irritates both skin and eyes and is harmful if inhaled or swallowed.
At elevated temperatures, strontium fluoride acts as an ion conductor , so it can transport electrical charges via ions and thus conducts the electrical current.
The connection is translucent in the light spectrum , i.e. the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum and a little beyond that. Its optical properties are between those of calcium fluoride and barium fluoride. This makes it interesting for applications in the optical sector (see usage).
use
Strontium fluoride is used as a coating for lenses to reduce reflections and increase transmission . It is also used as a crystal in thermoluminescent dosimeters . It is also used as a carrier for the isotope 90 Sr, which is used in radionuclide batteries .
Web links
- Product description at Crystran (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on strontium fluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 14, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c data sheet strontium fluoride from AlfaAesar, accessed on August 15, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ^ H. Kojima, SG Whiteway, CR Masson: Melting points of inorganic fluorides . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 46 (18), 1968, pp. 2968-2971, doi : 10.1139 / v68-494 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-248.
- ^ AF Holleman , N. Wiberg : Inorganische Chemie . 103rd edition. Volume 1: Basics and main group elements. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / Boston 2016, ISBN 978-3-11-049585-0 , p. 1460 (reading sample: Part A - Basics of the chemistry of hydrogen. Google book search ).
- ↑ Mineral Atlas: Strontiofluorite (IMA 2009-014)
- ↑ Entry in Strontium fluoride (SrF 2 ) at korth.de, accessed on February 25, 2018.
- ↑ Ian Bytheway, Ronald J. Gillespie, Ting-Hua Tang, Richard FW Bader: Core Distortions and Geometries of the Difluorides and Dihydrides of Ca, Sr, and Ba , in: Inorg. Chem. , 1995 , 34 (9), pp. 2407-2414; doi : 10.1021 / ic00113a023 .
- ↑ Strontium fluoride data sheet from AlfaAesar, accessed on December 15, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Newmet homepage ( Memento of 29 September 2007 at the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Crystran Ltd. Optical Component Materials: Strontium Fluoride (SrF2) , accessed April 14, 2013.


