Nitrous tetroxide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
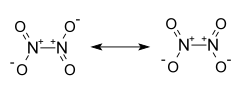
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nitrous tetroxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | N 2 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless gas, reddish brown when heated, with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 92.01 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous (at 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.45 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−11 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
21 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.1 M Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
hydrolyzed in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
11.1 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dinitrogen tetroxide , N 2 O 4 , is a colorless gas at 25 ° C. It is the dimer of nitrogen dioxide , NO 2 , and is in a pressure- and temperature-dependent equilibrium with it.
Dinitrogen tetroxide is used under its common name nitrogen tetroxide , or mostly under the abbreviation NTO (from English nitrogen tetroxide ), in space travel and rocket technology as a hypergolic oxidant (oxidizer) that can be stored without cooling and reacts with hydrazine and its derivatives .
properties
Dinitrogen tetroxide is a caustic and strongly oxidizing gas at a temperature above 21 ° C. The colorless, diamagnetic dinitrogen tetroxide is in equilibrium with the red-brown, paramagnetic nitrogen dioxide . In the gas phase, one molecule of N 2 O 4 breaks down into two molecules of NO 2 .
Depending on the pressure and temperature, there are different proportions of the two gases. Because nitrogen dioxide is a red-brown gas, nitrous oxide is usually colorless. With increasing temperature, the above equilibrium shifts to the right and the brown color deepens. At 800 ° C the disintegration is almost complete. The dissociation constant can be reproduced here using the partial pressures proportional to the concentration :
The value of the dissociation constant depends significantly on the temperature.
| T in ° C | 0 | 8.7 | 25th | 35 | 45 | 50 | 86.5 | 101.5 | 130.8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K d in atm | 0.0177 | 0.0374 | 0.147 | 0.302 | 0.628 | 0.863 | 7.499 | 16.18 | 59.43 |
As it cools down, nitrous oxide condenses and the liquid clears. In the vicinity of the boiling point, the substance shows a brown color due to the nitrogen dioxide still in solution. N 2 O 4 forms colorless crystals and crystallizes in the cubic system (a = 7.77 Å) with six N 2 O 4 groups per unit cell . The variation in pressure also influences the balance. An increase in pressure shifts it to the left, a decrease to the right ( principle of the smallest constraint ). The critical point of N 2 O 4 is 157.85 ° C and 10 MPa .
N 2 O 4 and NO 2 form the mixed anhydride of nitric acid and nitric acid . With alkali hydroxide solutions, nitrates and nitrites are formed , e.g. B:
Manufacturing
Dinitrogen tetroxide is the dimer of nitrogen dioxide, which is formed as an intermediate product in the large-scale synthesis of nitric acid by the air oxidation of nitrogen monoxide NO. Upon cooling, nitrogen dioxide dimerizes to dinitrogen tetroxide and can thus be produced as a by-product in a nitric acid factory.
It can be visualized in the laboratory
- in analogy to technical synthesis
- by reducing concentrated nitric acid with copper
- by heating heavy metal nitrates such as lead nitrate or silver nitrate in a stream of oxygen
- by reacting fuming nitric acid with phosphorus (V) oxide and thermal decomposition of the nitrous pentoxide obtained at 260 ° C:
use
Dinitrogen tetroxide has been used under the common name nitrogen tetroxide in many rockets since the 1950s as an oxidizer that can be stored without cooling. Together with hydrazine as a reducing agent it forms the only with carrier and intercontinental ballistic missiles used hypergolic fuel mixtures. So it was z. B. used together with hydrazine and UDMH as a fuel mixture ( Aerozin 50 ) of the lunar lander and the Apollo spacecraft in the American Apollo program for main and control engines.
First dinitrogen tetroxide was used as a storable oxidizer in the ICBMs second generation as the Titan II was used, thus always fully fueled and ready for their immediate start wait. After that, nitrous tetroxide was used in the launchers derived from these ICBMs and numerous newly developed launchers to this day. Besides MON , nitrous tetroxide is the standard oxidizer of satellites and space probes .
Risk assessment
Dinitrogen tetroxide was included in the EU's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in 2015 in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The causes of the uptake of nitrous oxide were concerns about exposure of workers and the high risk characterization ratio (RCR) as well as the possible dangers of mutagenic and reproductive properties. The reassessment was supposed to be carried out by Latvia , however the reassessment of the substance was withdrawn in 2019 because the risks were assessed as low.
See also
literature
- Ralf Steudel : chemistry of non-metals . 3. Edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2008, ISBN 978-3-11-019448-7 , page 345.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on nitrous oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Dinitrogen tetraoxide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-16.
- ↑ Hans-Dieter Jakubke, Ruth Karcher (Ed.): Lexikon der Chemie . Spectrum Academic Publishing House, Heidelberg, 2001.
- ↑ a b J. Chao, RC Wilhoit, BJ Zwolinski: Gas phase chemical equilibrium in dinitrogen trioxide and dinitrogen tetroxide . In: Thermochim. Acta , 10, 1974, pp. 359-371, doi: 10.1016 / 0040-6031 (74) 87005-X .
- ↑ a b A. Pedler and FH Pollard: Nitrogen (IV) oxide (Dinitrogen Tetroxide) . In: Therald Moeller (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 5 . McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1957, pp. 87-91 (English).
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): dinitrogen tetraoxide , accessed on March 26, 2019.
- ↑ ECHA: Withdrawal , March 19, 2019.








![{\ displaystyle {\ ce {2 N2O5 -> [T] [] 2 N2O4 + O2}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a0fe2c36a1a923e3e51df48539ce44190855224a)