Transmission system operator
Transmission System Operator ( TSO , Eng. Transmission System Operator , shortly TSO ) are service companies that the infrastructure of the national power grids operate electrical transmission operative for need-based maintenance and dimensioning ensure and provide electricity traders / suppliers non-discriminatory access to these networks. In addition, they have the task of procuring control power when required and making it available to the system in order to keep network fluctuations as low as possible , which result from a disproportion between electrical energy generated and consumed at a given point in time . The transmission or transport networks are connected via substations to the more closely meshed and lower-voltage networks of the distribution network operators (DSOs), which usually ensure the supply of end customers, usually in low-voltage networks. Individual major customers such as energy-intensive industrial companies can also be connected directly to the transmission network.
Transmission grids are natural monopolies and their operators are generally subject to state supervision.
Technology of power transmission
Transmission system operators operate transmission or transport networks with three-phase high-voltage transmission , in Europe with a network frequency of 50 Hz and in North America with 60 Hz. Three-phase transmission networks are usually designed in the topology of a mesh network . The voltage levels of the transmission networks in Germany are 220 kV and 380 kV. In special areas of application such as submarine cables or over very long distances, high-voltage direct current transmissions between two end points are also used.
National characteristics
State regulation
In Germany, the “regulated network access” model came into force in 2005 with the second amendment to the Energy Industry Act (EnWG). It empowers the Federal Network Agency to regulate transmission system operators. The provisions of the third EU internal market package , which became legally valid with the amendment of the EnWG in November 2010 and which had to be implemented by March 2012 at the latest, resulted in extensive unbundling requirements , which required the conversion of integrated network operators to so-called "ownership unbundled transport network operators" ( ownership unbundled ) or “independent transmission operators ” ( ITO) with non-discriminatory network access for all market participants. This also included the requirement to completely differentiate oneself in name and image from the trading activities of the parent company. In practice, these provisions in Germany led to extensive sales by the network operators by the integrated electricity companies (E.ON, RWE and Vattenfall). This enables competition at the other stages of the value chain, since every market participant can receive network access and there is a transmission competition in the electricity network.
In Austria, E-Control is the regulatory authority for transmission system operators.
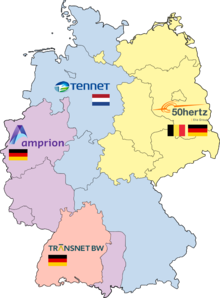
Transmission system operator in Germany and Europe
There are four transmission system operators in Germany:
The network area of Stadtwerke Flensburg is a special case in Germany. Because of the direct connection to the Danish power grid at the 60 kV and 150 kV level, it is technically part of the control area of the Danish transmission system operator energinet.dk and not of the control area of northwest Germany responsible transmission system operator TenneT TSO. The connection to the German power grid, which has a phase shift of 180 degrees compared to the Danish power grid, is made by a helical regulating transformer with galvanic isolation (combination of series control (usually step switch ) and cross control (with a phase shift transformer )). Flensburg is thus a virtual control area in Denmark, but participates in the market rules in Germany. Stadtwerke Flensburg has been assigned the market roles of a transmission system operator and a balance sheet coordinator for market communication .
At the European level, the transmission system operators have joined forces in the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) .
In 2018, ENTSO-E represents 43 transmission system operators from 36 European countries; the Turkish transmission system operator has the status of an observer.
See also
- Union for the Co-ordination of Transmission of Electricity (UCTE)
- Association of European Transmission System Operators (here also a complete list of transmission system operators in Europe)
- Distribution network operator (DSO)
- Transmission system operator in the gas sector
literature
- Tobias Strobel: The investment planning and investment obligations of the transmission system operator. In particular historical development, implementation and entrepreneurial personal responsibility . Nomos Verlagsgesellschaft, Baden-Baden 2017, ISBN 978-3-8452-8417-0 (also dissertation, University of Bayreuth, 2017).
Individual evidence
- ^ Tasks of the Federal Network Agency ( Memento of March 28, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Stadtwerke Flensburg ,: market communication, information on business processes. Retrieved May 13, 2020 .
- ↑ Code allocation portal of Energie Codes und Services GmbH - on behalf of BDEW. Retrieved May 12, 2020 .
- ↑ ENTSO-E Member Companies. In: entsoe.eu. Retrieved October 20, 2018 .
- ↑ Power Statistics. Inventory of transmission. Database query for the year 2017. In: entsoe.eu. Retrieved October 19, 2018 .