2-chloropropionic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
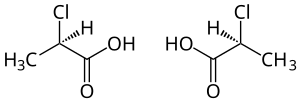
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| ( R ) shape (left) and ( S ) shape (right) | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-chloropropionic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
α-chloropropionic acid |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 5 ClO 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish, almost odorless liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 108.52 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.26 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−12 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
186 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.31 mbar (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
2.8 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4380 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−522.5 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
2-chloropropionic acid is a chemical compound from the group of propionic acid derivatives .
If "2-chloropropionic acid" is mentioned in this text or in the scientific literature without any additional name ( prefix ), racemic 2-chloropropionic acid is [synonyms: DL -2-chloropropionic acid, (±) -2-chloropropionic acid and ( RS ) -2 -Chlorpropionic acid] means a 1: 1 mixture of the two enantiomers .
Extraction and presentation
2-Chloropropionic acid can be obtained by chlorinating propionic acid with PCl 3 , S 2 Cl 2 or chlorosulfonic acid. The L - enantiomer is made from D - lactic acid and thionyl chloride .
properties
2-chloropropionic acid is a colorless to yellowish, almost odorless liquid. Above 60 ° C it begins to decompose, producing hydrogen chloride , carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide .
use
2-chloropropionic acid is used in the manufacture of dyes, medicines and herbicides . The phenoxypropionic acid derivatives such as clodinafop , fenoxaprop , fluazifop , haloxyfop , isoxapyrifop , quizalofop and phenoxycarboxylic acids dichlorprop , fenoprop , flamprop , mecoprop and acetylalanine benalaxyl be illustrated starting from 2-chloropropionic acid.
The reduction of ( S ) -2-chloropropionic acid with lithium aluminum hydride gives ( S ) -2-chloropropanol, the simplest chlorine alcohol, which further reacts with potassium hydroxide to ( R ) - methyl oxirane .
Related links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on 2-chloropropionic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Bernd Engels, Carsten jewelry, Tanja Schirmeister, Reinhold Fink: Chemistry for medical professionals . Pearson Deutschland GmbH, 2008, ISBN 3-8273-7286-0 , p. 553 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c Toxicological assessment of α-chloropropionic acid and sodium α-chloropropionate (PDF) at the professional association for raw materials and chemical industry (BG RCI), accessed on August 22, 2012.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-112.
- ↑ Entry on 2-chloropropionic acid in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-23.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 1030 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Koppenhoefer, B. and Schurig, V .: (R) -Alkyloxiranes of High Enantiomeric Purity from (S) -2-Chloroalkanoic Acids via (S) -2-Chloro-1-Alkanols: (R) -Methyloxiranes In: Organic Syntheses . 66, 1988, p. 160, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.066.0160 ; Coll. Vol. 8, 1993, p. 434 ( PDF ).


