6-thioguanine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 6-thioguanine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 5 N 5 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 167.2 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
> 360 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
6-thioguanine ( tioguanine ( INN ), ( 6-TG ) (trade name: Lanvis, manufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline )) is an analogue of the nucleobase guanine and a drug that is used as a cytostatic agent in chemotherapy to treat cancer . 6-thioguanine belongs to the group of antimetabolites .
properties
The compound is a pale yellow, crystalline powder with no inherent odor. 6-thioguanine is a thio analogue of the naturally occurring purine base guanine .
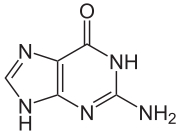
|

|
| Guanine | Thioguanine |
Mechanism of action
6-thioguanine competes with hypoxanthine and guanine for the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRTase). HGPRTase converts 6-thioguanine into 6-thioguanyl phosphate (TGMP). High concentrations of TGMP are accumulated intracellularly and hinder the synthesis of guanine nucleotides in several places. The purine biosynthesis is disturbed by an inhibition of the enzyme glutamine-5-phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase. TGMP also blocks the conversion of inosine phosphate to xanthine phosphate by competing for the enzyme inosine phosphate dehydrogenase.
Thioguanyl phosphate (TGMP) is converted to di- and triphosphates by phosphorylation : thioguanine diphosphate (TGDP) and thioguanine triphosphate (TGTP). At the same time, 2-deoxyribosyl analogs are also formed by the same enzymes that metabolize the guanine nucleotides. The thioguanine nucleotides are then incorporated into the DNA and RNA via phosphodiester compounds. Here they act as the “wrong” nucleotide and interfere with DNA replication .
In summary, 6-thioguanine acts by inhibiting purine biosynthesis, by inhibiting the conversion of purine nucleotides and by incorporating it into DNA and RNA in the sense of a “sequential” blockade of the synthesis and utilization of the purine nucleotides. Thioguanine acts specifically in the S phase of the cell cycle ; 6-thioguanine does not work in resting cells (G1 phase of the cell cycle).
An additional effect arises from the incorporation of 6-thioguanine into the RNA . This results in a modified RNA strand that can no longer be read by the ribosomes . This eliminates the production (synthesis) of the protein originally encoded by the thus modified RNA.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
A single oral dose of 6-thioguanine is only absorbed very incompletely and with high interindividual variability. The bioavailability of 6-thioguanine averages 30% (range 14–46%). The maximum concentration in plasma after a single oral dose is reached after 8 hours.
6-thioguanine is incorporated into the DNA and RNA of human bone marrow cells. Studies with radioactively labeled 6-thioguanine showed that 5 daily doses of 6-thioguanine resulted in a 100-fold higher accumulation of 6-thioguanine in DNA and RNA than a single daily dose of 6-thioguanine. At 5 daily doses of 6-thioguanine, 50% to almost 100% of all guanine nucleotides are replaced by 6-thioguanine. According to the current state of knowledge, 6-thioguanine itself can not cross the blood-brain barrier . 6-thioguanine could not be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid (nerve fluid ), just as the structurally closely related substance 6-mercaptopurine cannot penetrate the brain.
The plasma half-life of 6-thioguanine is very short. The reason for this is the rapid absorption of 6-thioguanine into the cells as well as the rapid introduction of 6-thioguanine into the metabolic pathways of purines . The metabolites of 6-thioguanine can therefore also be detected when 6-thioguanine is eliminated from the plasma.
6-Thioguanine is mainly excreted in the urine via the kidneys. However, there is hardly any unchanged 6-thioguanine in the urine; rather, 2-amino-6-methylthiopurine can be detected as a metabolite of 6-thioguanine. The median plasma half-life of 6-thioguanine is given as 80 minutes (with a range of 25 to 240 minutes).
6-thioguanine is metabolized in two ways. One route of degradation is deamination by guanase to 6-thioxanthine , which has only minimal antineoplastic activity. This metabolic pathway does not depend on the effectiveness of xanthine oxidase , so that allopurinol, as an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, does not block the breakdown of 6-thioguanine as it does with mercaptopurine. Another way of degradation is the methylation of 6-thioguanine to 2-amino-6-methylthiopurine, which is minimally antineoplastic and significantly less toxic than 6-thioguanine. This degradation path is also independent of the enzyme activity of xanthine oxidase.
Interactions
6-thioguanine is cross-resistant with mercaptopurine. Cancers that do not respond to treatment with mercaptopurine also do not respond to thioguanine.
If busulfan is used at the same time , there is increased hepatotoxicity in the form of liver damage, esophageal varices and portal hypertension (severe liver damage). The mechanism for this is unknown.
In contrast to mercaptopurine, the breakdown of 6-thioguanine is not hindered by allopurinol .
Application areas)
Adults
Children and young people
administration
6-thioguanine is administered orally (as a tablet).
Contraindications
Side effects
- Leukopenia and neutropenia (simultaneously)
- Thrombopenia
- anemia
- Liver toxicity: liver necrosis and veno-occlusive disease (VOD)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
literature
- Gertrude B. Elion, George H. Hitchings: The Synthesis of 6-Thioguanine ; J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1955, 77 (6), pp. 1676-1676; doi: 10.1021 / ja01611a082 .
- Tohru Ueda, Kazunobu Miura, Tsuguo Kasai: Synthesis of 6-Thioguanine and 2, 6-Diaminopurine Nucleosides and Nucleotides from Adenine Counterparts via a Facile Rearrangement in the Base Portion (Nucleosides and Nucleotides. XIX) ; Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin ; 1978, 26 (7), pp. 2122-2127; doi: 10.1248 / cpb.26.2122 .
- Pashna N. Munshi, Martin Lubin, Joseph R. Bertino: 6-Thioguanine: A Drug With Unrealized Potential for Cancer Therapy ; The Oncologist , 2014, 19 (7), pp. 760-765; doi: 10.1634 / theoncologist.2014-0178 .
Web links
- Information from the British Columbia Cancer Agency on thioguanine Comprehensive, clinically oriented monograph on thioguanine. As of March 1, 2007, freely accessible.
- ch.oddb.org: Technical information on thioguanine freely accessible.
- US package insert ( Memento January 18, 2009 on the Internet Archive ), freely accessible.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Data sheet 6-thioguanine from AlfaAesar, accessed on March 19, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet 6-Thioguanine from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 19, 2019 ( PDF ).