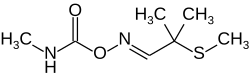
Aldicarb
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Aldicarb | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 14 N 2 O 2 S | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, crystalline solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 190.27 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.195 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
99-100 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
225 ° C (6.7 mbar) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.013 Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
sparingly soluble in water (6 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Aldicarb is a crop protection active compound from the family of carbamates , which as insecticide , acaricide and nematicide is used. The highly toxic compound is used to decontaminate the soil .
history
Aldicarb was developed by Union Carbide in 1962 .
Extraction and presentation
Aldicarb can be obtained starting from isobutylene by reaction with nitrosyl chloride or sodium nitrite and further reaction of the intermediate product formed with sodium methanethiolate and then with methyl isocyanate .
properties
Aldicarb is a crystalline, white solid.
use
Aldicarb comes in the form of 5, 10 or 15% granules . The most important areas of application are in the cultivation of cotton , soy and peanuts .
Admission
Aldicarb is not on the list of plant protection products authorized in the European Union. As a result, no pesticides containing aldicarb are permitted in the EU countries including Germany and Austria.
In Switzerland, the use of aldicarb-containing pesticides was limited to controlling the beetroot in sugar beet cultivation. Today, no pesticides containing aldicarb are permitted in Switzerland either.
toxicology
Aldicarb inhibits the enzyme cholinesterase and in this way increases the cholinergic impulse conduction between nerve cells, with the symptoms of strong parasympathetic activity as a result. The substance is highly toxic when ingested or in contact with the skin. The toxic effect occurs quickly and lasts between 4 and 12 hours. The LD 50 in rodents is 0.5 to 1.5 mg / kg body weight when the aldicarb was administered in water or oil. For dry granules, the LD 50 is around 7 mg / kg body weight. There is no evidence of a teratogenic , mutagenic or carcinogenic effect.
literature
- Ronald L. Baron: A carbamate insecticide: a case study of aldicarb , Environmental Health Perspectives , Vol. 102, December 11, 1994, pp. 23-27; PMC 1566767 (free full text, PDF).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on Aldicarb in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Extoxnet: Aldicarb , as of June 1996.
- ↑ Entry on Aldicarb in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry on Aldicarb in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), accessed on December 16, 2009.
- ↑ Entry on Aldicarb. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 27, 2014.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide synthesis handbook . 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5 , pp. 135 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Aldicarb in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 11, 2016.

