Dextromoramide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Dextromoramide | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
(3 R ) -3-methyl-4- (morpholin-4-yl) -2,2-diphenyl-1- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) butan-1-one ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 392.53 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
180-184 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dextromoramide is a strong synthetic pain reliever with an opiate-like effect. The drug was launched in 1957 by Janssen Pharmaceutica under the tradename Palfium .
The substance is a derivative of 3,3-diphenylpropylamine and belongs to the methadone group. In contrast to methadone, the molecule contains a morpholine and a pyrrolidine ring.
Extraction and presentation
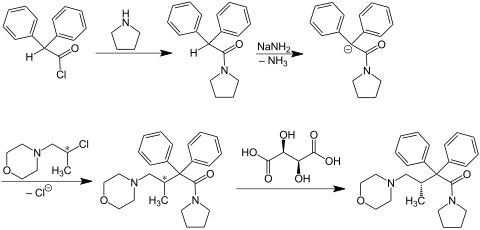
The synthesis of dextromoramide starts from diphenylacetyl chloride, which is first converted into the corresponding acid amide with pyrrolidine. After reaction with sodium amide and 4- (2-chloropropyl) morpholine, this gives the racemic (±) -moramid (racemoramid). A racemate resolution using D - tartaric acid leads to the enantiomerically pure target compound:
The (3 S ) -enantiomer levomoramide obtained in the resolution is pharmacologically inactive.
Legal situation
According to the Narcotics Act in the Federal Republic of Germany, dextromoramide has been a marketable, but not a prescription, narcotic drug since 1993 .
literature
- HJ Bochnik: Development of addiction and severe withdrawal symptoms after use of dextromoramide (Jetrium, MCP 875, Palfium, R 875, Errecalme, Pyrrolamidol). In: Archiv für Toxikologie , Vol. 18 (No. 3), 1960, pp. 170-176.
- HJ Roth and H. Fenner: Medicines. Thieme, Stuttgart and New York 1988, pp. 336-343.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on dextromoramide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 16, 2014.
- ↑ a b Janssen, PAJ; Janssen, JC: A New Series of Potent Analgesics in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 78 (1956) 3862-3862, doi: 10.1021 / ja01596a087 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c d e f A. Kleemann , J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances - Synthesis, Patents, Applications , 4th Edition, Thieme-Verlag, Stuttgart 2000, ISBN 978-1-58890- 031-9 .
- ↑ Patents BE 544 757, DE 1 117 126, GB 822 055 (Janssen 1956).
- ↑ Paul AJ Janssen, Anton H. Jageneau: A New Series of Potent Analgesics: DEXTRO 2: 2-Diphenyl-3-methyl-4-morpholinobutyrylpyrrolidine and Related Amides Part I. Chemical Structure and Pharmacological Activity . In: Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology . tape 9 , no. 1 , September 1957, p. 381-400 , doi : 10.1111 / j.2042-7158.1957.tb12290.x .
- ↑ Fourth Amendment to Narcotics Law - 4th BtMÄndV, of December 23, 1992 .
Trade names
Jetrium (D - no longer available), Palfium (D - no longer available, NL ), Palface (NL)