Difenoconazole
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Basic structural formula (stereocenters are marked with an * ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Difenoconazole | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 17 Cl 2 N 3 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 406.26 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.39 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
82-83 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
3.32 10 −8 Pa (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
1.1 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Difenoconazole is a mixture of several isomeric chemical compounds from the group of triazoles and conazoles . It is used as a fungicide .
properties
Difenoconazole is a white odorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. The technical product is yellowish with a slightly sweet odor. The compound is stable to photolysis and hydrolysis at pH values of 5, 7 and 9.
Stereoisomers
Due to the two stereocenters on the acetal five-membered ring, difenoconazole forms a cis - trans pair of racemic diastereomers , the mixture thus consists of four stereoisomers the ( R , R ) -, ( S , S ) -, ( R , S ) - and the ( S , R ) shape. The ratio of the diastereoisomers after preparation is about 60% of the cis isomers [( R , S ) - and ( S , R ) form] and about 40% of the trans isomers [( R , R ) - and ( S , S ) form].
| Difenoconazole (4 stereoisomers) |
|
|---|---|
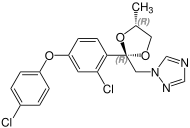 ( R, R ) configuration |
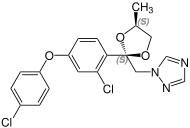 ( S, S ) configuration |
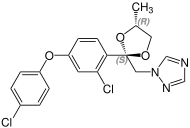 ( S, R ) configuration |
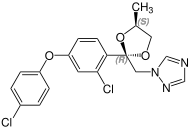 ( R, S ) configuration |
Extraction and presentation
Difenoconazole can be obtained by etherification of 2,4-dichloroacetophenone with 4-chlorophenol , subsequent bromination of the intermediate product with elemental bromine and subsequent acetalization with 1,2-propanediol and nuclophilic substitution with 1,2,4-triazole .
use
Difenoconazole is a systemic triazole fungicide that is used in a number of plant diseases on fruits, vegetables and ornamentals, e.g. B. is used by Ascomycetes , Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes . It influences the ergosterol biosynthesis in the fungi by inhibiting the C-14 demethylation of sterols , which leads to morphological and functional changes in the fungal cell membrane . The compound was launched in 1989.
Legal position
In the European Union, the substance was included in Directive 2008/69 / EC in Annex I of Directive 91/414 / EEC on the placing of plant protection products on the market.
In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, plant protection products with this active ingredient are approved.
In Switzerland a. for basil and parsley a relatively high maximum residue level of 10 milligrams difenoconazole per kilogram.
Web links
- Review report for the active substance difenoconazole (SANCO / 830/08 - rev. 1) (PDF; 50 kB) EU General Directorate Health and Consumers , March 10, 2008
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h FAO: Difenoconazole (PDF; 1.0 MB).
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Difenoconazole, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 19, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Patent US9462807 : Difenoconazole sterepospmeric composition with reduced phytotoxicity. Registered on February 4, 2013 , published on January 27, 2014 , inventors: JR Godwin, AM Heming, C. Lothschuetz, P. Schneiter, W. Stutz.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide synthesis handbook . 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5 , pp. 691 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Reasoned opinion on the modification of the existing MRLs for difenoconazole in various crops. In: EFSA Journal. 11, 2013, p. 3149, doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2013.3149 .
- ^ Horst Börner, Klaus Schlueter: Plant diseases and plant protection . Springer, 2009, ISBN 3-540-49068-X , pp. 496 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Commission Directive 2008/69 / EC of July 1, 2008 (PDF) amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substances clofentezine, dicamba, difenoconazole, diflubenzuron, imazaquin, lenacil, oxadiazon, picloram and pyriproxyfen.
- ↑ Directive 91/414 / EEC (PDF) of the Council of July 15, 1991 on the placing of plant protection products on the market.
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on difenoconazole in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 18, 2016.
- ↑ Ordinance of the EDI on the maximum levels for pesticide residues in or on products of plant and animal origin. In: admin.ch . Retrieved February 6, 2020 .


