Diazinon
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
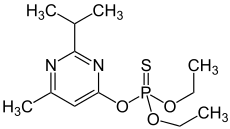
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diazinon | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 21 N 2 O 3 PS | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish liquid with a weak ester-like odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 304.35 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.12 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
<25 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
<0.1 Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very poor in water (40–47 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) (slow decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4922 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 0.1 mg m −3 (measured as inhalable dust ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Diazinon is a thiophosphoric acid ester that is used as a non-systemic insecticide and acaricide . Diazinon was developed in 1952 by H. Gysin at the Swiss company Geigy , which later became part of Novartis and then Syngenta .
history
Diazinon was intended by Geigy as a successor to DDT . In 1953, DDT production in the Schweizerhalle plant near Basel was temporarily discontinued from 1955 onwards, because the capacity for Diazinon was required. In the production of Diazinon, the risk of fire and explosion was higher than that of DDT, and the unpleasant smell and the toxic effects for the workers were greater. Until the end of the 1970s, commercially available diazinon also contained toxic impurities and decomposition products. They were later removed by separation processes or their formation prevented by the addition of stabilizers .
use
Pest Control
Diazinon is used against leaf and soil insects, but does not have a species-specific effect, but attacks all insects. The main areas of application are the control of cockroaches , silverfish , ants and fleas in living areas that are not used for food storage or preparation. The toxic effect is based on the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase .
In accordance with European legislation (Directive 98/8 / EC on the placing of biocidal products on the market) and with the resolution of February 8, 2010, a decision has been made not to include the active ingredient diazinon in the corresponding list (Annex I / IA of Directive 98/8 / EG) for biocidal products (product type 18). The sale of biocidal products that contain the active ingredient diazinon is therefore no longer permitted in the EU (Switzerland has adopted this provision) for insecticides from March 1, 2011.
Plant protection
Diazinon is no longer approved as an active ingredient in plant protection products as a result of a decision by the EU Commission on June 6, 2007. In Switzerland, on May 15, 2011, Diazinon was removed from the appendix to the approved active ingredients. Diazinon is still approved in the USA, but is one of the particularly restricted crop protection products. Its use has decreased significantly over the past 20 years.
Vermin collar for cats and dogs
Diazinon is used as an active ingredient in collars for external use in case of infestation of dogs and cats with ectoparasites such as dog fleas ( Ctenocephalides canis ), cat fleas ( Ctenophalides felis ), ticks ( Ixodes ricinus ) and brown dog ticks ( Rhipizephalus sanguinis ), for example Optipet ad us. vet. (CH).
toxicology
Diazinon has a relatively high toxicity to vertebrates. It is also absorbed through the skin. Symptoms of intoxication correspond to those of other inhibitors of cholinesterases: colic , nausea , diarrhea and vomiting , dizziness , headache , blurred vision ( accommodation disorders ), contracted and unresponsive pupils ( miosis ), bradycardia , drop in blood pressure up to cramps and apnea occur.
The oral LD 50 for rats is 66 mg / kg; for mice 17 mg / kg the lowest known toxic dose (TD Lo ) for humans is 214 mg / kg after oral intake. It has the water hazard class 3 (highly hazardous to water).
An evaluation by the IARC in March 2015 came to the conclusion that there was limited human evidence of the carcinogenic potential of diazinon, while there was convincing evidence of the substance's DNA or chromosome-damaging effects. IARC therefore classifies Diazinon in category 2A (probably carcinogenic for humans, probably carcinogenic to humans ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on diazinon in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 6, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on Diazinon in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-140.
- ↑ Entry on Diazinon in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 333-41-5 or Diazinon ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b Clinical Toxicology . Vol. 12, p. 435, 1978.
- ↑ a b Down to Earth. Vol. 35, p. 25, 1979.
- ↑ a b Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. Food Hygiene Journal. Vol. 24, p. 268, 1983.
- ↑ R. Gasser: About a new insecticide with a broad spectrum of activity. In: Journal of Nature Research B . 8, 1953, pp. 225-232 ( online ).
- ^ Christian Simon , DDT - cultural history of a chemical compound , Christoph Merian Verlag, pp. 76-77, Basel, 1999, ISBN 3-85616-114-7 .
- ↑ Directive 98/8 / EC on the placing of biocidal products on the market . In: Official Journal of the European Communities . L, No. 123, August 24, 2008, pp. 1-63.
- ↑ Decision on the non-inclusion of diazinon in Annex I of Directive 98/8 / EC on the placing of biocidal products on the market . In: Official Journal of the European Communities. L, No. 36, February 9, 2010, pp. 34-35.
- ↑ a b Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Diazinon in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 14, 2016.
- ↑ Decision of the Commission of 6 June 2007 on the non-inclusion of diazinon in Annex I of the Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and the revocation of the authorizations for plant protection products with this active substance (2007/393 / EC)
- ↑ Federal Department of Economic Affairs : Ordinance on the placing of plant protection products on the market (Plant Protection Products Ordinance, PSMV), amendment of April 21, 2011 (PDF; 496 kB).
- ^ IARC press release of March 20, 2015 IARC Monographs Volume 112: evaluation of five organophosphate inscecticides and herbicides , accessed on March 23, 2015.


