Nitrogen (II) fluoride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nitrogen (II) fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | N 2 F 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless gas |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 104.01 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
4.6 kg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−164.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−73 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.40 M Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
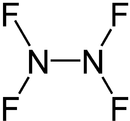
Nitrogen (II) fluoride , also called dinitrogen tetrafluoride , is a chemical compound of the elements nitrogen and fluorine with the empirical formula N 2 F 4 . Here nitrogen has the oxidation state +2. The compound belongs to the group of nitrogen halides .
presentation
Nitrogen (II) fluoride can be prepared by reduction of nitrogen trifluoride synthesized are. For this purpose, it is converted in a redox reaction at an elevated temperature with a metal , for example copper , which is oxidized to copper (I) fluoride .
properties
At room temperature it is a colorless gas that condenses at −73 ° C and solidifies at −164.5 ° C.
Two conformers exist in equilibrium , the gauche and the trans form. Analogous to hydrazine , the trans form, in which the fluorine atoms are on a gap, is energetically more favorable - in this case by about 2 k J mol −1 . The inversion barrier between the two conformations is 12.5 kJ mol −1 .
The bond length between the nitrogen atoms is 148 pm , the NF bond length 139 pm.
Nitrogen (II) fluoride is very reactive and a powerful fluorinating agent . The NN single bond can easily be cleaved by radicals due to the -I effects due to the fluorine substituents. It can react violently with flammable substances such as hydrogen . Hydrolytically it is less stable than nitrogen trifluoride.
use
Nitrogen (II) fluoride oxidizes elemental lithium to lithium fluoride and nitride .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d e f A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 .
- ^ Nitrogen (II) fluoride at webelements.com
- ↑ Entry on dinitrogen tetrafluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 28, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.


