Phenylacetylene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
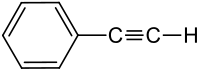
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phenylacetylene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 102.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.93 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−44.8 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
142–144 ° C (1013 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.7 hPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
0.46 g l −1 in water (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5494 (at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Phenylacetylene is the simplest aromatic alkyne . It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a flash point of 27 ° C. In research it is sometimes used as an analogue of acetylene , as a liquid it is easier to handle than gaseous acetylene.
Manufacturing
In the laboratory, phenylacetylene, by elimination of hydrogen bromide from 1,2-Dibromphenylethan (also incorrectly referred to as Styroldibromid) with sodium in liquid ammonia can be obtained:
It can also be made by eliminating hydrogen bromide from 1- or 2-bromophenylethene (common names 1- or 2-bromostyrene) with molten potassium hydroxide .
properties
Like acetylene , its ethynyl group (–C≡C – H) reacts to very strong bases (such as NaNH 2 ) as an acid and shows other reactions typical of alkynes, such as electrophilic additions , hydrogenation or polymerizations . Phenylacetylene fumes are flammable. The flash point is 27 ° C.
Reactions
- Phenylacetylene can be reduced ( hydrogenated ) to styrene by hydrogen over the Lindlar catalyst .
- It trimerizes with metal catalysis to 1,2,4- (97%) and 1,3,5-triphenylbenzene (3%):
- It adds water under catalysis by sodium tetrachloroaurate . The enol initially formed tautomerizes spontaneously to acetophenone :
However, this reaction is of no practical importance, since acetophenone can be prepared by a simple Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with acetyl chloride and Lewis acids .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Phenylacetylene data sheet (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 19, 2011.
- ↑ Robert A. Benkeser, Richard A. Hickner: The Stereochemistry of the addition of Silicochloroform to Acetylenes . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 80 , no. October 19 , 1958, p. 5298–5300 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01552a072 .
- ↑ Kenneth N. Campbell, Barbara K. Campbell: Phenylacetylene In: Organic Syntheses . 30, 1950, p. 72, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.030.0072 ; Coll. Vol. 4, 1963, p. 763 ( PDF ).
- ↑ John C. Hessler: Phenylacetylene In: Organic Syntheses . 2, 1922, p. 67, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.002.0067 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 438 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Phenylacetylene data sheet at AlfaAesar, accessed on May 20, 2016 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Gerhard Hilt, Thomas Vogler, Wilfried Hess, Fabrizio Galbiati: In A simple cobalt catalyst system for the efficient and regioselective cyclotrimerization of alkynes Chemical Communications , 2005 , 11 , pp. 1474-1475.





