Cantharidin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
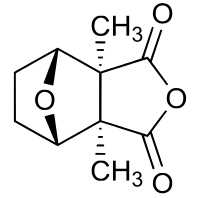
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cantharidin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 12 O 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, orthorhombic platelets |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 196.20 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
218 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Cantharidin , also cantharidin , is a natural substance and belongs to the group of terpenoids . It is a monoterpene which is said to have an aphrodisiac effect, but which is above all a strong irritant .
Occurrence
Cantharidin is an ingredient in various species of beetles . It was named after the genus Cantharis , now partially Lytta . Cantharidin was first described as an ingredient in the Spanish fly ( Lytta vesicatoria ).
history
Cantharidin was first isolated by Pierre-Jean Robiquet in 1810 . According to war reports, the aphrodisiac effects of the cantharidine are said to have already been fatal to Napoleon's troops during the Egyptian campaign , who caught and ate frogs in the swamps of the Egyptian Nile Delta . They mainly fed on the said beetles and stored the cantharidin without being damaged themselves. The first descriptions of its use in medicine come from ancient times, for example by Hippocrates and Pliny the Elder . It is reported that Livia Drusilla , the wife of the later Roman emperor Augustus , added the drug to the meals of the other members of the imperial family in order to encourage them to sexual debauchery, which could later be used against them.
properties
Chemical properties
Cantharidin is a monoterpene that crystallizes in colorless, orthorhombic platelets. It has a melting temperature of 218 ° C. It is insoluble in water , soluble in chloroform , acetone and ethanol . It is readily soluble in acids and alkalis .
Biochemical properties
Cantharidin has a high affinity for binding to proteins , which are accordingly referred to as cantharidin-binding proteins (CBP). Some analogous molecules, such as the herbicide Endothal, have the same property . The heterodimeric protein consists of an α and a shorter β chain. This CDB is obviously identical to the protein phosphatase 2A, which occurs as an enzyme in plants and animals. The various toxic effects are therefore probably caused by a blockage of this enzyme in its function in phosphorylation and dephosphorylation .
Biological importance
Cantharidin is in the hemolymph contain a number of beetle species, especially in the oil beetles (Meloidae), even after the effect of cantharidin on human skin "blister beetle" called the fire beetles (Pyrochroidae) and representatives of the family of oedemeridae (Oedemeridae) . The biological meaning is different. The oil beetles use the toxin primarily as defense secretion , which is squeezed out in the form of drops at the leg joints in the event of a potential threat ( reflex bleeding ). In the fire beetles, cantharidin is primarily a lure pheromone that makes the males attractive to the females. On the other hand, cantharidin has a deterrent effect on most other insects, only the flower beetles (Anthicidae) are also attracted, as they can find the corpses of oil beetles in this way. Cantharidin also plays a role in mating with them: before mating, the females check the cantharidin content of the storage containers under the wings of the males and make their willingness to mate dependent on this. However, the beetles cannot produce the substance themselves, but take it from the oil beetles. Cantharidin is also attractive to some species of midges (Ceratopogonida), a group of mosquitoes that suckle beetles containing cantharidin.
Cantharidin is a strong irritant and neurotoxin , which makes it very effective as a defense secretion. It has a strong irritative effect on the skin and especially on the mucous membranes. In humans and other vertebrates, it triggers the formation of blisters and sometimes deep necrosis . It also leads to inflammation and especially severe damage to the kidneys . The latter occurs especially in the event of abuse, such as excessive ingestion as an aphrodisiac .
Sequestration
Some animal species have specialized in consuming oil beetles and storing their poison in their tissues in order to protect themselves or other species from predators . This includes the spur-winged goose ( Plectropterus gambensis ), one of the few poison birds whose meat is inedible therefore for people.
Application by humans
Cantharidin was considered a potency-increasing agent that is supposed to bring about a long-lasting erection in men . The application is controversial, especially since the erection can be very painful, the dosage is very difficult and on the other hand a painful permanent erection can lead to permanent impotence. It should be achieved by rubbing the genitals or ingesting dissolved cantharidin, whereby the Spanish fly ( Lytta vesicatoria ) is usually ground up.
Cantharidin was mainly used in skin irritation therapy and as a means to remove warts , often in the form of a transdermal patch ( Canthariden patch ). Due to its highly irritating effect on the skin, cantharidin is used experimentally in pharmacology for skin blister tests (cantharidin test). Here, cantharidin creates a skin blister , in the liquid of which the concentration of medicinal substances can be measured. Due to its effect in the event of an overdose , it should only be used after consulting a doctor.
The lowest fatal dose LD Lo for humans is around 0.5 mg / kg body weight. In ancient Greece , the poison was used next to the hemlock cup to carry out death sentences.
literature
- Friedrich Eiden : Cantharidin. Wedding gift, protective and attractant, bladder puller and enzyme inhibitor , Chemistry in our time , Volume 40, 2006, pp. 12-19.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on Cantharidin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 11, 2014.
- ↑ a b c data sheet Cantharidin (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on December 12, 2007.
- ↑ a b Entry on cantharidin in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b data sheet cantharidin from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 15, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Toxicon. Vol. 23, p. 36, 1985.
- ^ Stefan Bartram, Wilhelm Boland: Chemistry and ecology of toxic birds. In: ChemBioChem 2, No. 11, November 2001, pp. 809-811, doi : 10.1002 / 1439-7633 (20011105) 2:11 <809 :: AID-CBIC809> 3.0.CO; 2-C .
- ↑ Karem Ghoneim: Cantharidin toxicosis to animal and human in the world: A review. In: Standard Res. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci 1, 2013, pp. 001-022.


