Neotropic
Neotropic is a term from biogeography . It is used in both animal geography and plant geography (as one of the flora kingdoms ). It stands for South America (from a botanical point of view, the southernmost Andean region is no longer part of the Neotropic, but of the Antarctic ), Central America , the West Indies , the southern part of Mexico and the southern tip of Florida . The zoological region of the Neotropics includes South America, Central America and the West Indies. Central America represents a transition area to the Nearctic .
The Neotropic was separated from North America for a long time , so a very independent fauna and flora could develop there, which is more similar to the Gondwanian elements of the Antarctic and Australis .
Subregions
There are several sub-regions within the Neotropics. These are primarily the West Indies, which have a very distinct fauna, and Central America. In South America itself there is a distinction between an Andean - Patagonian and a Guiana-Brazilian fauna. The former includes the Andes region as well as the cooler pampas regions and the Patagonian steppes, the latter the tropical lowland forests and savannas. After all, the Galapagos Islands form a clearly delimited unit within the region.
flora
The most important forms of vegetation include the tropical rainforests . These cover a large part of the Amazon lowlands as well as large areas of Central America. Isolated from this one finds the so-called Mata Atlântica , the Atlantic rainforest belt , on the south east coast . This is separated from the Amazon rainforests by savannahs and dry forests ( Cerrado , Gran Chaco ). In the north of the Amazon forests there is another savannah region, the Llanos . The western flank of South America is dominated by the huge mountain range of the Andes, on the slopes of which the mountain rainforests rise in the tropics and then turn into highland steppes. To the west of the tropical Andes lies the arid Atacama Desert. These arid areas merge in a southerly direction over Mediterranean bush areas into temperate deciduous forests that extend to Tierra del Fuego. In the east of the southern Andes, the Pampas grasslands and the Patagonian steppes extend .
Particularly characteristic families of plants are the Cactaceae and the Bromeliaceae , but also the Tropaeolaceae ; as genera agave and yucca as well as several genera of the pantropical palms family ( Euterpe , Sabal , Jubaea ). Other families are Cannaceae , Cyclanthaceae and Marcgraviaceae .
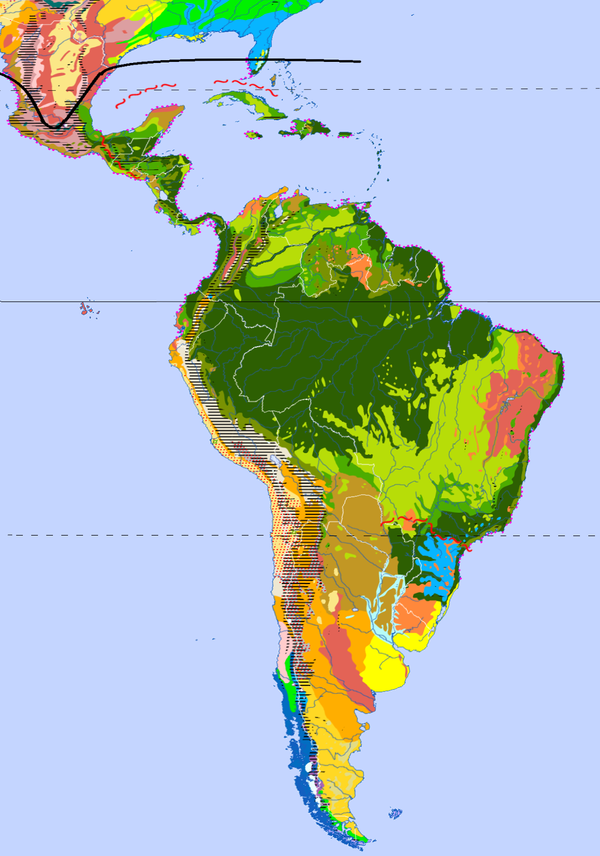
| Ice sheets and glaciers | Evergreen boreal coniferous forest | Winter-cold semi-deserts | Dry savannahs |
| Cold desert | Mountain coniferous forests | Winter cold deserts | Thorn bush and cactus savannas |
| Lichen and Moostundra | Temperate coastal rainforests | Hard foliage vegetation | Tropical dry forests |
| Dwarf shrub and meadow tundra | Deciduous and mixed coniferous forests | Hot semi-deserts | Rain-green moist savannahs |
| Mountain tundra, alpine meadows and heaths | Temperate deciduous and floodplain forests | Hot deserts | Tropical and ʅ subtropical rain-green wet forests |
| Hardwood forest tundra and boreal floodplains | Mixed forest steppes | Highland steppes and deserts | Tropical and ʅ subtropical rainforests |
| Softwood forest tundra | Grass steppes and salt marshes | Subtropical dry forests | Tropical mountain rainforests and cloud forests |
| Deciduous boreal coniferous forest | Shrub and dry steppes | Subtropical wet forests | Sedge swamps and flowing water plants |
| ≡ = mountain ranges | ::: = desert regions without vegetation | : ¤ : = oasis vegetation (partly with delimitation) | ••• = mangrove coasts |

fauna
South America was isolated from the other continents for most of the Earth's Modern Age. At that time, unique mammal forms emerged, some of which are still characteristic of South America today. These include various marsupials, the armadillos, anteaters and sloths. The New World monkeys and guinea pig relatives also came to the continent very early as island hops. Today's mammalian fauna in the Neotropical region consists for the most part of groups that immigrated from North America in the course of the great American fauna exchange in the Pliocene. When the Central American land bridge was formed about three million years ago, even-toed ungulates ( deer , camels , umbilical pigs ), odd-toed ungulates (tapirs), hares, predators (cats, dogs, martens, bears, small bears), insect eaters and the rodent families of the New World mice and squirrels arrived from North America to South America. At that time, trunk animals and horses also immigrated, but they later disappeared again.

The marsupials are represented in South America by opossum rats , mouse opossums and the Microbiotheriidae . The Beutler are limited to the Neotropic except for the northern opossum , which also occurs in the Nearctic. In addition to climbing forms ( Didelphis , Marmosa ) there are also semi-aquatic forms ( Lutreolina , Chironectes ). The Mausopossums are limited to relic areas of the Andean region.
The variety of armadillos ranges from the mole-like belt mole to the giant armadillo . They inhabit forests and arid areas alike. A single species, the nine-banded armadillo, also occurs in the Nearctic. The anteaters are represented by the giant anteater , tamandua and pygmy anteater . The sloths are only represented by tree forms, while large ground-living forms also existed until the Pleistocene. Anteaters and sloths are now restricted to the Neotropical region. But they also occur here in Central America. The same is true of the New World monkeys , which are endemic to the Neotropics but inhabit both South and Central America. In contrast to the Old World monkeys, the New World monkeys did not produce soil forms. They can be divided into capuchin-like monkeys , spider-tailed monkeys, night monkeys, sakia monkeys and marmosets .
The American continent's guinea pig relatives are almost exclusively restricted to the Neotropical region. Only the tree prickers are at home with the Urson in the Nearctic. The capybaras were there until the late Pleistocene, but are now limited to the Neotropic. Further families of the guinea pig relatives are the truss-like (Octodontoidea), the ground-dwelling Cavioidea , Chinchilloidea and Dinomyoidea . The latter are only represented by the Pakarana . In addition, the swimming Myocastoridae (swamp beavers) occur. The second important group of rodents are the New World mice , which inhabit the entire region with the exception of the Amazon basin and are distributed in a wide variety of forms from Tierra del Fuego and the slopes of the Andes to Mexico. Other rodents are the pocket rats , which occur mainly in Central America, and the pocket mice , which can be found in the north of South America. In addition, there are squirrels ( Sciurus , Sciurillus and Microsciurus ). Hares are represented by two genera ( Lepus and Sylvilagus ) in the Neotropical region.
The shrews are found in Central America and northern South America, while they are represented by opossums in the south. The only genus of shrews found in South America itself is Cryptotis , apparently a very young immigrant. The slot weevils occur in Cuba and Haiti. The Nesophontids became extinct in the Holocene in the Greater Antilles. The bats are only represented by bats (Microchiroptera). These occur in several families.
The artifacts are represented by camels (guanaco, vicuna), various types of deer ( white-tailed deer , pampas deer , swamp deer , fork deer , pudus , mazamas ) and three species of peccary. The collared peccary also penetrates the southern areas of the Nearctic, while the white-bearded peccary and Chaco peccary are restricted to the Neotropic. The white-tailed deer even penetrates as far as Canada in the Nearctic. All other cloven-hoofed species are entirely restricted to the Neotropics. The vicuna is a typical high-mountain inhabitant of the Andes, while the guanaco populates the arid regions of the south. The deer are represented by at least one species in most habitats. While horses in South and North America became extinct around 10,000 years ago at the end of the Pleistocene, the tapirs survived and are the largest land animals on the continent, the Central American tapir. The other two species are the lowland tapir and the mountain tapir . Tapirs are absent in the Nearctic region.
The predators are represented in the Neotropic by skunks and martens, small bears, big bears, cats and dogs. The tayra stands out among the martens. Other forms are weasels , grisons and otters, of which the giant otter is the largest species. The small bears are typical of the Neotropics. These include coatis , raccoons , maci bears and wrapped bears . The Central American cat fret occurs at least in the north of the region. The big bears are now only represented by the spectacled bear , which is restricted to the Andes. The spectacled bear is the last representative of the Tremarctinae . Various representatives of this bear subfamily existed in North and South America during the Pleistocene. The maned wolf is the largest species among dogs . There are also numerous smaller species such as the short-eared fox , forest dog , Maikong and various Lycalopex species. The gray fox, which is otherwise widespread in the Nearctic, reaches at least Venezuela. The largest cat and also the second largest predator of the Neotropics after the spectacled bear is the jaguar . It naturally reached the southern areas of the Nearctic. The puma is a bit smaller and was once widespread across North and South America. He originally inhabited almost the entire Neotropical region. Other smaller cats in the region are ocelots, long-tailed cats, tiger cats, jaguarundi and Andean cats. Manatees and river dolphins live in the rivers of the Neotropical region. Several seal species, such as live on the coasts of the region elephant seal that Mähnenrobbe and the Galapagos sea lion. The Caribbean monk seal , on the other hand, has become extinct.
Among the birds that are particularly diverse in the Neotropical region, the following groups are characteristic: rheas , cocktails , toucans , sawbacks , glossy birds , hummingbirds , tyrants ( Tyrannidae ), hokko chickens , defensive birds , hoatzin . Some tyrant and hummingbird species also occur in the Nearctic.
literature
- HJ Müller: Ecology . 2nd edition, G. Fischer, Stuttgart 1991, p. 135. ISBN 3-334-00398-1
- H. Walter, S.-W. Breckle: Ecology of the Earth. Volume 1: Basics. 2nd edition, Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart 1991. ISBN 3-437-20454-8
- Erich Thenius : Basics of the fauna and distribution history of mammals . A historical animal geography. 2nd, completely revised edition. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart 1980, ISBN 3-437-30312-0 (first edition under the title: Basic features of the history of the spread of mammals ). Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena 1972.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ J. Illies: Tiergeographie . 2nd improved edition. Georg Westermann Verlag, Braunschweig 1972, ISBN 3-14-160285-9 (Edwin Fels, Ernst Weigt, Herbert Wilhelmy; original version: 1970).




