Nozon
| Nozon | ||
|
Cascade du Dard near Croy |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | CH : 246 | |
| location | Switzerland | |
| River system | Rhine | |
| Drain over | Talent → Thielle → Zihl Canal → Aare → Rhine → North Sea | |
| source | at the foot of a rock face in the so-called Cul du Nozon southwest of the village of Vaulion 46 ° 40 ′ 39 ″ N , 6 ° 22 ′ 55 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 995 m above sea level M. | |
| muzzle | east of Orbe in the Talent Coordinates: 46 ° 43 ′ 51 ″ N , 6 ° 33 ′ 33 ″ E ; CH1903: 532 776 / 175896 46 ° 43 '51 " N , 6 ° 33' 33" O |
|
| Mouth height | 436 m above sea level M. | |
| Height difference | 559 m | |
| Bottom slope | 23 ‰ | |
| length | 24 km | |
| Catchment area | 58.15 km² | |
| Drain at the mouth |
MQ |
910 l / s |
The Nozon is an approximately 24 km long right tributary of the Talent in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland . It drains a section of the Vaud Jura and the western edge of the Vaud Central Plateau and belongs to the catchment area of the Rhine .
geography
course
The Nozon rises as a karst spring at about 1000 m above sea level. M. at the foot of a rock face in the so-called Cul du Nozon southwest of the village of Vaulion . Geologically, the area lies in a syncline between the Jura ranges of the Mollendruz and the Dent de Vaulion . A little north of the karst spring are the two caves Grotte du Gros-Fort and Grotte de la Pernon .
First, the Nozon flows northeast through the Vaulion basin. Then it turns to the east and overcomes a height difference of almost 300 m over a distance of 6 km in the valley sunk deep between the heights of Sur Grati and Chalet Dernier . At Romainmôtier he leaves the actual Jura heights and now reaches the Jura foot plateau. In the course of time, the Nozon has sunk into the limestone layers of this plateau an erosion valley, usually around 100 m deep .
In the area of the village of Croy , the course of the river curves to the south. With the Cascade du Dard waterfall , a gorge-like section begins along a fault zone in the Jura Arc. The Nozon approaches the Venoge , which is part of the catchment area of the Rhone , up to a distance of 1.5 km . Over a distance of 4 km both streams flow parallel to the east, being separated from each other only by the heights of Les Aleveys and Mormont ; the lowest point of the watershed is 455 m above sea level. M. (in the Entreroches Gorge).
At the village of Orny, northeast of La Sarraz , the Nozon enters the agriculturally intensively used Orbe plain , turns to the north and has practically no gradient for the last 7 km. In the plain east of the town of Orbe it flows at 440 m above sea level. M. in the talent that flows together with the Orbe shortly afterwards .
Catchment area
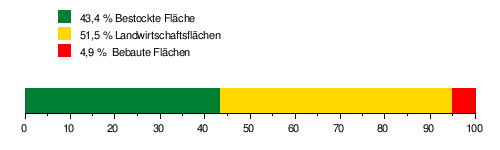
The catchment area of the Nozon is 58.15 km² and consists of 43.4% forest land , 51.5% agricultural land and 4.9% settlement area .
The mean height of the catchment area is 826 m above sea level. M. , the minimum height is 436 m above sea level. M. and the maximum height at 1482 m above sea level. M.
Tributaries
- Le Ruisseau de Chatrey ( left )
- Le Ruisseau de Rochey ( left )
- La Gay ( right )
- La Diey ( right )
- Le Bief de Romainmôtier ( left fork )
- Le Ruisseau du Bec à l'Aigle ( right )
- Le Ruisseau de la Vallée d'Engens ( right )
- Le Bief de l'Augine ( right fork )
- Le Bief ( right )
Hydrology
At the confluence of the Nozon in the Talent, its modeled mean flow rate (MQ) is 0.91 m³ / s and its flow regime type is pluvial jurassia .
The flow rate of the Nozon fluctuates relatively strongly over the course of the year. The highest water levels were determined for the months of February to April. The flow rate reaches its peak in April at 1.46 m³ / s. After that, the discharge falls noticeably in May, then sinks month by month and reaches its lowest level in August at 0.44 m³ / s, and then starts to rise steadily from September onwards, month after month.
The modeled monthly mean discharge (MQ) of the Nozon in m³ / s

character
Since the Nozon flows through an area with calcareous subsoil, in which the fallen rainwater quickly seeps away, it has only a few insignificant side streams. Above Romainmôtier, it gets its water from the karst spring Source de la Diey . The upper and middle reaches of the Nozon are largely natural to near-natural. However, the lower reaches of the Orbe plain were channeled and straightened.
history
The Nozon was first mentioned in a document in 642 under the name Novisonum fluviolum ; The name Noisonem fluviolum has been handed down from 1049 . The name is made up of the Gallic word noviis (new) and the suffix onno (water).
The area of the Nozon, in particular the area between Romainmôtier and Pompaples, was already settled in Roman times. Here, ore deposits were mined in various places and processed in iron smelting furnaces. The Benedictine monastery Romainmôtier was founded in the valley of the Nozon in the 5th century AD .
The Nozon's hydropower has been used to power mills, sawmills and forges since the Middle Ages . In the 16th century a mill was built near Pompaples on the valley watershed between the catchment areas of the Rhône and the Rhine ( Moulin Bornu ). For this, part of the water from the Nozon was diverted into a canal and led to the mill. The canal divides below the mill: one part flows back to the Nozon, the other, however, flows south to the Venoge and thus to the Rhône. Since then the place has been called Milieu du Monde (Middle of the World). In the Orbe plain, water from the Nozon is used to irrigate the vegetable crops.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Geoserver of the Swiss Federal Administration ( information )
- ↑ a b c d Topographical catchment areas of Swiss waters: Nozon
- ↑ "Hidden behind the mean values" - the variability of the discharge regime , p. 7
