Adder tongue family
| Adder tongue family | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Moon rue ( Botrychium lunaria , right) and |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the order | ||||||||||||
| Ophioglossales | ||||||||||||
| link | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Ophioglossaceae | ||||||||||||
| Martinov |
The adder tongue plants (Ophioglossaceae) are a family of plants from the order adder tongue-like (Ophioglossales), which belongs to the class Psilotopsida of the ferns . It includes a total of about 80 isospore species.
description
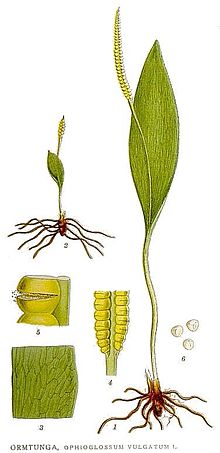

The buds are nodding. The growth does not take place with a crown cell , but with a group of initial cells. The rhizome and petioles are fleshy. Root hairs are missing. Usually only one leaf frond is formed per year, which is not rolled up during growth. The leaf is a three-dimensional space duster and consists of a fertile (yellow) and a sterile (green) part. The fertile part consists of a single sporophore which arises at the base, or along the trophophyll stalk and at the base of the trophophyll blade. The sporangia are large, have no annulus, and the walls consist of two layers of cells (eusporangiat). The spores are round to tetrahedral. Over 1000 spores are formed per sporangium.
The prothallia are greatly reduced, live underground without chlorophyll and feed on myco-heterotrophic fungi. The prothallium can live a few years. The antheridia and archegonia are sunk into the prothallium. In some species, the embryo can also survive underground for a few years.
The basic chromosome number is x = mostly 30, 45, 94, rarely 44 or 46.
Occurrence
The species are mostly terrestrial, less often epiphytic . They occur mainly in the temperate and boreal zones, some species also pantropically.
Systematics and distribution
The Ophioglossaceae family was founded in 1820 by Ivan Ivanovič Martinov in Tekhno-Botanicheskīĭ Slovar ': na latinskom i rossīĭskom iazykakh. Sanktpeterburgie , p. 438. Type genus is Ophioglossum L. Synonyms for Ophioglossaceae Martinov are: Botrychiaceae Horan. , Helminthostachyaceae Ching .
The family Ophioglossaceae is distributed almost worldwide. In China there are three genus with about 22 species, two of them only there.
In the family Ophioglossaceae there are only five (rarely four to nine are mentioned) genera with about 80 species:
- Botrychium , also called moonwort ( Botrychium Sw. , Syn .: Botrypus Michx. , Japanobotrychum Masamune , Sceptridium Lyon ): There are about 50 species worldwide.
- Cheiroglossa C.Presl : There are about three ways.
-
Helminthostachys Kaulf. (Syn .: Ophiala Desv. ) It includes only one species:
- Helminthostachys zeylanica (L.) Hook. ( Helminthostachys dulcis Kaulf. Nom. Illeg.): It is widespread from the subtropics to the tropics of the Old World and occurs in India , Sri Lanka , Thailand , Indonesia , Malaysia , Taiwan , China , Queensland and New Caledonia .
-
Mankyua B.Y.Sun, MHKim, CHKim : There is only one kind:
- Mankyua chejuensis B.Y.Sun et al. : This endemic wasfirst describedin 2001 from the Korean island of Cheju .
- Adder tongues ( Ophioglossum L. , Syn .: Ophioderma flower ): There are 25 to 50 species worldwide, mainly in the northern hemisphere .
literature
- Peter Sitte , Elmar Weiler , Joachim W. Kadereit , Andreas Bresinsky , Christian Körner : Textbook of botany for universities . Founded by Eduard Strasburger . 35th edition. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2002, ISBN 3-8274-1010-X .
- Maarten JM Christenhusz, XC Zhang, Harald Schneider: A linear sequence of extant families and genera of lycophytes and ferns. In: Phytotaxa , Volume 19, 2011, pp. 7-54. Full text PDF. (Section systematics)
- Alan R. Smith, Kathleen M. Pryer, Eric Schuettpelz, Petra Korall, Harald Schneider, Paul G. Wolf: A classification for extant ferns. In: Taxon. Volume 55, No. 3, 2006, ISSN 0040-0262 , pp. 705-731, abstract, PDF file .
- Zhang Xianchun, Quanru Liu, Norio Sahashi: Ophioglossaceae , pp. 73-79 - online with the same text as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (eds.): Flora of China. Volume 2-3: Lycopodiaceae through Polypodiaceae. Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2013, ISBN 978-1-935641-11-7 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Zhang Xianchun, Quanru Liu, Norio Sahashi: Ophioglossaceae , pp. 73-79 - same text online as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (ed.): Flora of China. Volume 2-3: Lycopodiaceae through Polypodiaceae. Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2013, ISBN 978-1-935641-11-7 .
- ^ Ophioglossaceae at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, accessed July 17, 2016.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Maarten JM Christenhusz, XC Zhang, Harald Schneider: A linear sequence of extant families and genera of lycophytes and ferns. In: Phytotaxa , Volume 19, 2011, pp. 7-54. Full text PDF.
- ↑ a b Ophioglossaceae at Tropicos.org. In: Flora Mesoamericana . Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
- ↑ Helminthostachys in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved February 15, 2019.
Web links
- Ophioglossaceae at Tropicos.org. In: Catalog of the Vascular Plants of Madagascar . Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
- Ophioglossaceae at Tropicos.org. In: IPCN Chromosome Reports . Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis

