Pipe grasses
| Pipe grasses | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
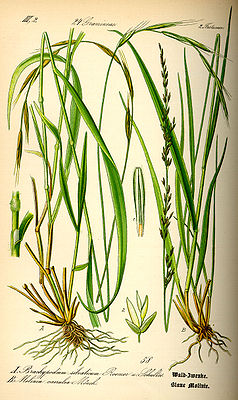
Illustration: Right: Blue pipe grass ( Molinia caerulea ), left Brachypodium sylvaticum |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Molinia | ||||||||||||
| closet |
The pipe grasses ( Molinia ) are a genus of the sweet grass family (Poaceae). There are four species in this genus, two of which occur in Central Europe. There are occurrences in Europe, Africa, in the temperate climate in Asia and in North America. Among them are grasses typical of meadows.
The botanical genus name is derived from Juan Ignacio Molina (1737-1829), a Jesuit and botanist living in Chile . The German trivial name is derived from the use of the hard stalks with a few knots as a pipe cleaner.
description
The Molinia species are perennial, herbaceous plants . The pipe grasses are hemicryptophytes : the dense clumps of the foliage protect the renewal buds that are near the surface of the earth in winter. At most they form short rhizomes . The upright stalks are 15 to 120 cm long, depending on the species. The ligule consists of a hairline. The narrow, rough leaves, mostly blue-gray in color, reach a length of 30 to 90 cm. Their striking autumn color ranges from yellow to yellow-brown to red-brown tones.
The paniculate inflorescence is composed of individually standing, 4 to 15 mm long spikelets. The fertile spikelets are stalked and contain one to six fertile flowers , depending on the species . There are also sterile flowers. The glumes are keeled or keeled. The membranous lemma is keeled and wingless with three to five nerves. The palea is about the same length as the awn with two nerves. The two cavernous bodies (Lodiculae) are fleshy. There are three stamens and two cicatricial branches.
The caryopses are obovate. The hilum is the same length as the achene.
Use as an ornamental plant

With their many varieties, pipe grass species offer a wide range of uses. They are suitable in gardens as a solitary shrub , but also for group planting. They are often used in near-natural perennial plantings. The 'Variegata' variety is suitable for the rock garden . It finds a location corresponding to its natural occurrence in heather gardens or on the edge of woody plantations. The flower heads and seed heads are often used in flower making.
The dry seed heads also remain on the plant until spring and form a decorative winter decoration in the garden. Like many perennials , pipe grass can easily be multiplied by dividing it, but it also grows out of its own accord.
Systematics
The genus Molinia belongs to the tribe Arundineae of the subfamily Arundinoideae. Synonyms for Molinia cabinet are: Amblytes Dulac , Enodium Pers. ex Gaudin , Moliniopsis Hayata , Monilia Gray orth.var.
There are two to four species in the genus Molinia :
- Pipe mermaid ( Molinia arundinacea cabinet , syn .: Molinia litoralis host , Molinia altissima link )
- Blue pipegrass ( Molinia caerulea (L.) Moench ): The distribution ranges from Europe to Asia.
- Japanese pipe grass ( Molinia japonica Hackel , Syn .: Moliniopsis japonica (Hackel) Hayata ): Home is northeast Asia from Sakhalin to Japan and from the Chinese provinces of Anhui and Zhejiang to Korea.
No longer belong to the genus:
- Molinia maxima Hartm. ⇒ Glyceria maxima (Hartm.) Holmb.
- Molinia squarrosa Trin. ⇒ Kengia squarrosa (Trin.) Packer
literature
- WD Clayton, KT Harman & H. Williamson: Molinia : Online, 2008 at GrassBase - The Online World Grass Flora.
- R. Schubert, W. Rothmaler: Excursion flora from Germany - Volume 2: Vascular plants . 15th edition, Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena Stuttgart 1994, ISBN 3-334-60828-X
- Helmut Genaust: Etymological dictionary of botanical plant names. 3rd, completely revised and expanded edition. Nikol, Hamburg 2005, ISBN 3-937872-16-7 (reprint from 1996).
- F. Röber, D. Fritz, W.-D. Naumann: The new garden dictionary . Volume 3, Mosaikverlag, Munich 1996, ISBN 3-576-10653-7
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Molinia in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
- ↑ Rafaël Govaerts (ed.): Molinia. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved November 17, 2016.
