Salbutamol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
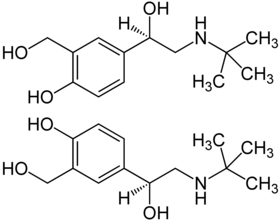
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 1: 1 mixture of ( R ) -Salbutamol (above) and ( S ) -Salbutamol (below) | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Salbutamol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 21 NO 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 239.31 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
151 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Salbutamol is a β 2 sympathomimetic that is used as a bronchospasmolytic in bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis with or without emphysema . When administered by inhalation, salbutamol causes a rapid onset and "long-lasting" relaxation of the smooth muscles in the bronchi . The effect is based on the stimulation of β 2 -adrenoceptors . Salbutamol therefore also belongs to the group of bronchospasmolytics . Overall, salbutamol (half-life 3 - 4 h) and fenoterol (half-life 3 h) are short-acting substances for use in acute asthma attacks.
Dosage forms
As a rule, salbutamol is used by inhalation ( powder inhaler , pressurized gas inhalation, inhalation solution for nebulization), with the effect occurring within seconds; the maximum effect is reached after about 15 minutes. If the effect is to be delayed, prolonged-release tablets or drops for oral use are also used.
doping
Since salbutamol is used as a doping agent due to its spasmolytic and probably also anabolic effects , its medical use by competitive athletes is subject to strict restrictions (1 µg / ml, → doping list ).
Side effects and contraindications
The following side effects can commonly occur with the use of salbutamol:
- Tremor (tremor)
- dizziness
- Palpitations ( palpitations )
- nausea
- sweat
- a headache
- Racing heart ( tachycardia )
Contraindications : In case of hypersensitivity (allergy) to the active ingredient or other components contained in the drug, the drug must not be used.
Special care should be taken when using the drug under certain conditions:
- Hypersensitivity to other sympathomimetics
- if you have severe heart disease
- if you have severe and untreated hypertension (high blood pressure)
- if cardiac glycosides (medicines used to treat heart failure) are already being used
- for aneurysms (pathological widening of the vessel wall)
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- difficult to control diabetes mellitus
- Pheochromocytoma (a disease of the adrenal medulla)
It should not be used during pregnancy , as the active ingredient can pass from the placenta to the unborn child. Salbutamol can also have an anti-labor effect on the body. When used during breastfeeding , it should be taken into account that the active ingredient salbutamol is excreted in breast milk .
Stereoisomerism
Salbutamol is chiral because it contains a stereocenter. There are thus two enantiomers , the ( R ) form and the ( S ) form. The effective enantiomer ( eutomer ) is ( R ) -albutamol. The commercial preparations contain the drug as a racemate (1: 1 mixture of enantiomers). This is mainly due to the fact that the ( S ) -enantiomer blocks the enzymatic degradation path and thereby the metabolism of the ( R ) -enantiomer is delayed. Overall, this results in a prolonged duration of action of the preparation. Pure ( R ) -Salbutamol is commercially available under the international non- proprietary name Levosalbutamol . A more favorable side effect profile of the ( R ) -enantiomer with regard to tachycardia and tachyarrhythmia in cardiac patients could not be proven in studies.
Trade names
Apsomol (D), Broncho-Inhalat (D), Bronchospray (D), Butovent (A), Cyclocaps Salbutamol (D), Dospir (CH), Ecovent (CH), Epaq (D), Novolizer Salbutamol (A), Pädiamol (D), Pentamol (D), Salamol (CH), Salbubronch (D), SalbuHEXAL (D), Sultanol (D, A), Ventilastin (D), Ventolin (B, CH, E, GB, TR, USA) , Ventoline (F), Volmac (D), numerous generics (D, A)
Combivent (A), Dospir (CH), Ipramol (CH), Nebu-Iprasal (A)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on salbutamol in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Data sheet Salbutamol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 8, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ Wehling, Martin: Clinical Pharmacology. 2., update Edition Thieme, Stuttgart 2011, ISBN 978-3-13-126822-8 , pp. 117 .
- ↑ a b c d Package leaflet : Information for the user - Salbutamol-ratiopharm ® N metered dose inhaler 0.1 mg / spray, pressurized inhalation (package insert). (PDF; 400 kB) In: Sanicare .de. Ratiopharm , November 2013, archived from the original on December 29, 2015 ; accessed on March 18, 2020 .
- Jump up ↑ Medicinal Chemistry of the Peripheral Nervous System - Adrenergics and Cholinergic their Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Structure Activity Relationships. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on November 4, 2010 ; accessed on February 17, 2014 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Effects of nebulized bronchodilator therapy on heart rate and arrhythmias in critically ill adult patients . PMID 21960699 .