Selenous acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
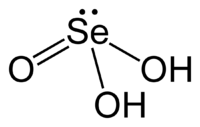
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Selenous acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Dihydrogen selenite ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 2 SeO 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, hygroscopic crystals |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 128.97 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.004 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
Decomposes above 70 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
0.02 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Selenous acid is a water-soluble crystalline solid with the empirical formula H 2 SeO 3 . It is a biprotonic acid of selenium . Their salts are called selenites . Selenous acid is poisonous.
Extraction and presentation
Selenious acid can be obtained from the reaction of selenium dioxide and water or nitric acid with selenium.
Chemical properties
Selenous acid is very soluble in water and has a very hygroscopic effect . In water dissolved it reacts strongly acidic ( pK s value of the first protolysis : 2.62 and the second protolysis: 8.32).
It is a weaker acid than sulphurous acid , but in contrast to this it can be isolated in the form of crystals. It shows practically no reducing properties. It is reduced to red selenium by sulfur dioxide , hydrogen sulfide , hydrogen iodide and hydrazine .
It is oxidized to selenic acid by hydrogen peroxide , potassium permanganate or chloric acid.
use
Selenous acid is used as a catalyst for the synthesis of 1,2- dialdehydes .
In industry it is used to change the color of metallic materials. In the arms industry in particular , a process known as "blueing" is known with which steel surfaces are colored. The chemical industry uses similar processes to discolour surfaces, for example of copper . There are drug tests in the United States , the key reagent of which is selenious acid.
Biological importance
Like many selenium compounds, selenium acid is toxic to the human body. According to German water law , the connection is marked with water hazard class 3. The mean lethal concentration for fish is 6.61 g · m −3 . There is evidence of a possible carcinogenic effect of the compound. The biological limit value is 150 µg · l −1 .
safety instructions
Selenous acid is very irritating to the skin, respiratory tract and mucous membranes. It is able to destroy living tissue in high concentrations ( corrosion ). Long-term exposure to the compound can cause severe physiological damage. Selenous acid is highly toxic even in the smallest quantities. In the event of poisoning with selenium compounds, permanent damage must be expected.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Entry on selenium acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on October 25, 2012 (JavaScript required)
- ↑ Data sheet Selenous acid, 99.999% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 25, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on Selenous Acid in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed October 25, 2012.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 .
- ↑ M. Binnewies et alii: Allgemeine und Anorganische Chemie . 2nd Edition. Spectrum, 2011, ISBN 3-8274-2533-6 , pp. 567 .
- ↑ E. Riedel, Christoph Janiak: Inorganic Chemistry . 8th edition. de Gruyter, 2011, ISBN 3-11-022566-2 , p. 458 .
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Vol. 1, Academic Press 1963, pp. 432-3.
- ↑ Anthony R. Ronzio and TD Waugh: Glyoxal Bisulfite In: Organic Syntheses . 24, 1944, p. 61, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.024.0061 ; Coll. Vol. 3, 1955, p. 438 ( PDF ).
- ^ R. Angier: Firearm Blueing and Browning , Stackpole Co., Harrisburg, 1936.
- ^ Poisons Information Monograph (PIM) for Selenium , accessed December 9, 2014.
- ↑ Sirchie Fingerprint Laboratories, Inc. May, 2006.
- ↑ Info sheet from the United States Department of Justice : (PDF; 135 kB) .
- ↑ Study by the European Food Safety Authority ( PDF )
- ↑ W. Forth, D. Henschler, W. Rummel, K. Starke: General and special pharmacology and toxicology 7th ed .; Spectrum Akademischer Verlag GmbH, Heidelberg 1996.
- ^ Robert M. Russell (for the German edition: Hans-Joachim F. Zunft). Vitamins and trace elements - deficiency and excess. In: Manfred Dietel, Joachim Dudenhausen, Norbert Suttorp (eds.) Harrison's internal medicine , Berlin 2003, ISBN 3-936072-10-8 .








