Sigma
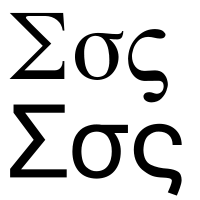 Sigma |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pronunciation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| antique | [ s, z ] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| modern | [ s ] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equivalents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Latin | Ss | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyrillic | Сс | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hebrew | ס | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arabic | ﺱ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phoenician | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| transcription | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| From the ancient world | s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| From the modern | s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 at the end of the word |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Greek letter Sigma ( Greek neuter Σίγμα , majuscule Min , minuscule in the word σ , minuscule at the end of the word ς ) is the 18th letter of the Greek alphabet and, according to the Milesian system, has the numerical value 200. In the Greek language it is called the voiceless “ S " spoken.
Origin and derivatives
The Phoenician alphabet had four letters for sibilants . The Greeks adopted two of them for their S-sound, but they never appeared at the same time in one of the different ancient Greek alphabets. The letter Samech was used in the Ionic alphabet as X with the sound value ksi . His name, however, was transferred in a slightly modified form to the Phoenician letter "Sin", which was now called Sigma in Greek.
In Hellenistic times , the letter in manuscripts to today as was lunares Sigma (lunar " crescent-shaped ") simplified form designated (originally only as Majuskel Σ for Unziale , from the minuscule ς ), which in late antiquity and the Byzantine Empire to most used form and is still common today in the ecclesiastical context ( Orthodox churches ). Both the Coptic semma ( Ⲥ / ⲥ ) and the Cyrillic Es ( С / с ) are derived from this letter form , while the Latin S is derived from the common capitals via the Etruscan form .
use
- as a small sigma σ
- in quality management Six Sigma (3.4 errors per million possible errors)
- in physics
- for surface tension
- for the yield stress
- for the surface electrical charge density
- for the Stefan-Boltzmann constant
- for the specific electrical conductivity of a material
- for the Pauli matrices
- for the cross section
- for mechanical tension
- in materials science
- a very brittle phase in the Fe-Cr system
- the tension
- in computer science
- to denote the selection in relational algebra
- to designate the selectivity of a database query
- in math
- in the statistics for the standard deviation of the population
- in mathematical number theory for a partial sum
- in functional analysis for the spectrum of a linear operator
- in measure theory that a property or axiom extends from finite to countable index sets .
- for number walls as a designation for the number of basic cells
- in chemistry
- for naming a molecular orbital bond
- to name the sigma complex
- as a sign of the volume concentration
- in biology
- for a protein which is necessary for the initiation of transcription by binding to the RNA polymerase (see sigma factor )
- in phonology
- for one syllable
- in microeconomics
- as a sign of the elasticity of substitution
- in structural geology
- to name a clast type (see Sigma-Klast )
- as a capital sigma Σ
- Identifier in physics for a Σ-baryon .
- Symbol in physics for a frame of reference .
- Symbol in mathematics for sum or signature .
- Symbol in statistics for the covariance matrix
- Symbol in theoretical computer science for an alphabet
- In astronomy , the sigma is the speed at which the stars move at the very edge of a galaxy .
- as a word sigma
- Use in ecology and vegetation: sigma sociology (synsociology), d. H. the recording of vegetation complexes
- Abbreviation in medicine for the S-shaped part of the large intestine ( Colon sigmoideum ).
Examples
- Socrates ( Σωκράτης , ancient Greek pronunciation Sōkrátēs , today's Greek Sokrátis )
- Lunar Sigma:
Detail of the Nomos inscription on the back of the monumental statues , Nemrut Dağı
Entrance to the Greek Orthodox monastery Μετοχιον Γεθσημανης Metochion Gethsimanis , Church of the Holy Sepulcher in Jerusalem
Apse painting Jesus Christ as Pantocrator with the letters "IC" and "XC" for Jesus Christ, Beuron Art School , St. Remigius (Bliesen)
Unicode output of the variants
In addition to the normal form specified in the above info block , the lunar sigma is also coded as a symbol in the Unicode block Greek and Coptic :
- Majuskel Σ (Unicode U + 03F9: "GREEK CAPITAL lunate SIGMA SYMBOL")
- Minuscule ϲ (Unicode U + 03F2: "GREEK LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL")
There is also a dotted version of this:
- Majuskel Ͼ (Unicode U + 03Fe: "GREEK CAPITAL DOTTED lunate SIGMA SYMBOL")
- Minuscule ͼ (Unicode U + 037C: "GREEK SMALL DOTTED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL")
In addition , the antisigma developed by the Roman emperor Claudius as part of his writing reform is also defined, as is a dotted version of it:
- Majuskel Ͻ (Unicode U + 03FD "GREEK CAPITAL REVERSED lunate SIGMA SYMBOL")
- Minuscule ͻ (Unicode U + 037B: "GREEK SMALL REVERSED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL")
- Majuskel Ͽ (Unicode U + 03FF "GREEK CAPITAL REVERSED DOTTED lunate SIGMA SYMBOL")
- Minuscule ͽ (Unicode U + 037D: "GREEK SMALL REVERSED DOTTED LUNATE SIGMA SYMBOL")