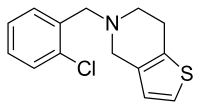
Ticlopidine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Ticlopidine | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 14 ClNS | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 263.79 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
||||||||||||
| boiling point | |||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Ticlopidine is a drug from the group of platelet aggregation inhibitors , so it reduces the ability of blood platelets to clump together .
Substance class
Ticlopidine is an ADP receptor inhibitor from the group of thienopyridine derivatives (see clopidogrel ).
Mode of action
Thienopyridine derivatives bind irreversibly to the P2Y 12 receptor of platelets. Thereby, the increase in activity of activated platelets and activation still inactive platelets by ADP, which is secreted by activated platelets themselves inhibited. The ADP blockade causes, via an intracellular mechanism, an indirect inhibition of the glycoprotein IIb / IIIa complex (cf. GPIIb / IIIa antagonists, tirofiban ), which is responsible for binding fibrinogen , and thus a reduction in the cross-linking of platelets to form thrombi . Thrombi that develop are smaller and structurally looser under treatment with ticlopidine (also clopidogrel), so that they can be more easily dissolved and washed away by the bloodstream. Thrombi observed during therapy were too small to be able to lead to a vascular occlusion .
Ticlopidine and clopidogrel differ in their molecular structure only by one side group, but ticlopidine can be understood as a precursor substance of clopidogrel, which is used much more frequently today.
indication
Ticlopidine can be used to inhibit coagulation after myocardial infarction, with known CAD , after balloon dilation or stent insertion. However, due to the availability of modern substances (e.g. clopidogrel, prasugrel , ticagrelor ) with a lower risk of side effects , the substance has become much less important.
Side effects and restrictions on use
Uncommon : changes in the blood count ( neutropenia in 1% of cases, agranulocytosis ), mouth ulcers, fever, dizziness, headache, weakness, loss of appetite, malaise, ringing in the ears, palpitations, insomnia, depressive mood
Rare : thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, medullary aplasias, leukocytopenia (BB control, bleeding tendency, susceptibility to infection), diarrhea, nausea, allergic reactions, allergic vasculitis, lupus erythematosus, liver dysfunction, increase in cholesterol and triglycerides by approx. 10%.
In the case of regional anesthesia procedures near the spinal cord ( spinal anesthesia or epidural anesthesia ), ticlopidine should be discontinued ten days in advance, but can be given again immediately after the procedure.
Interactions
Reduced concentration in the blood by antacids, increased by cimetidine. Reduction of digoxin concentration when taken at the same time as ticlopidine by 20–30%. Ticlopidine is broken down via the cytochrome P450 system, thus influencing the half-life of all those drugs that are metabolized via the same system (e.g. sedatives , hypnotics, theophylline , phenytoin ).
Contraindications
Children, pregnancy and lactation, known changes in the blood count, hemorrhagic diathesis , acute GI bleeding.
Trade names
Thrombodine (A), Tiklid (A), Tiklyd (D), various generics (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Kuhnert-Brandstätter, M .; Völlenklee, R .: Contribution to the polymorphism of medicinal substances, Part 4: Oxamniquin, Resorantel, Spiperon, Suloctidil, Ticlopidinhydrochlorid, Parsol 1789 and Testosteroncyptonat in Sci. Pharm. 55 (1987) 27-39.
- ↑ Entry on ticlopidine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet Ticlopidine hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on ticlopidine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ Walter, Kerstin; Huppelsberg, Jens: Short textbook physiology . 3. Edition. Thieme, 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-136433-3 , p. 25 .
- ^ Percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI). (PDF) Guidelines of the German Society for Cardiology, 2008, accessed on May 30, 2012 .
- ↑ Wiebke Gogarten, Hugo Van Aken: Perioperative thrombosis prophylaxis - platelet aggregation inhibitors - importance for anesthesia In: AINS - anesthesiology · intensive care medicine · emergency medicine · pain therapy. 47, 2012, pp. 242-252, doi: 10.1055 / s-0032-1310414 .
- ↑ Red List Online, as of September 2009.
- ↑ AGES-PharmMed, as of September 2009.
literature
Küttler: Short textbooks "General Pharmacology and Toxicology" and "Special Pharmacology" , each 18th edition