Tolcapone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Tolcapone | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
3,4-dihydroxy-4'-methyl-5-nitrobenzophenone |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 11 NO 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 273.25 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
144-145 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tolcapone is the international non-proprietary name (INN) of an active ingredient for the treatment of Parkinson's disease . From a chemical point of view, the active ingredient is a substituted benzophenone . Tolcapon was awarded the PZ Innovation Prize in 1998.
presentation
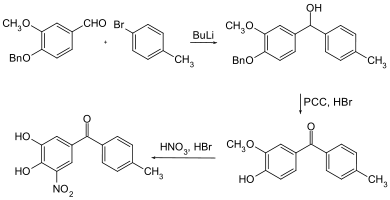
A benzyl- protected aromatic aldehyde serves as the starting compound . This is reacted with butyllithium and 4-bromotoluene. The secondary alcohol obtained in this way is then first oxidized with PCC and then the benzyl radical is split off with hydrobromic acid . Nitric acid nitration and cleavage of the methyl ether with hydrobromic acid gives the tolcapone.
Mode of action
Parkinson's disease is caused by the destruction of dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra , which triggers a dopamine deficiency and thus a predominantly cholinergic and glutaminergic excitation mechanism in the basal ganglia . Administering the missing dopamine as a medication does not achieve the goal because it cannot cross the blood-brain barrier. However, this is possible with the dopamine precursor ( prodrug ) L-Dopa (dihydroxyphenylalanine), for which there is an active transporter in the blood-brain barrier. L-dopa is, however, rapidly metabolized to 3- O- methyldopa (3-OMD) through the enzymatic reaction of catechol- O- methyltransferase (COMT) .
This is where the effect of tolcapone begins; it inhibits ("inhibits") the enzyme COMT and is the first active ingredient for which this effect has been described. In this way, like other therapeutic approaches, it helps to restore the balance of the impulse transmission that is disturbed in Parkinson's patients. Tolcapone prevents the breakdown of L-dopa not only peripherally, but also centrally, as it can cross the blood-brain barrier . This quadruples the half-life of L-Dopa in plasma . As a result, the bioavailability of dopamine in the central nervous system (CNS) and its concentration in the brain increase, but not in the peripheral plasma level. The combination with L-Dopa as a comedication significantly reduces the motor fluctuations. At an early stage of the disease, in combination with L-Dopa and a decarboxylase inhibitor , the time without complications is significantly increased. Central effects are also discussed, but their clinical relevance is still unclear.
Side effects
The most common undesirable effects are: dyskinesias (involuntary movements), dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty sleeping, increased sweating, decreased appetite, diarrhea, fainting, headache, dizziness when standing, constipation, chest pain, respiratory infections, drowsiness, confusion and hallucinations. Liver dysfunction; severe hepatitis has been observed in isolated cases .
Admission
In 1997, the Hoffmann-La Roche company approved tolcapone as Tasmar across Europe for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Only one year later, the European approval authority ordered the approval to be suspended after severe hepatotoxic side effects occurred. Tasmar (pharmaceutical company Meda AB ) has been licensed again since 2004, subject to strict conditions (liver function controls). The field of application is the additional treatment of Parkinson's disease in combination with L-dopa / benserazide or L-dopa / carbidopa .
The following liver monitoring procedure is required for treatment with tolcaprone:
| EMEA | FDA | |
|---|---|---|
| Liver monitoring | Every 2 weeks for a year, then every 4 weeks for 6 months, then every 8 weeks | Every 2–4 weeks for 6 months, then at the medical discretion |
| Suspending medication | GOT / GPT > ULN * | GOT / GPT> 2 * ULN * |
* ULN = upper limit of normal (upper limit of the normal range)
Trade names
- Tasmar (D)
Web links
- Francois Didereich, Christian Lerner: Chemical building block in the fight against Parkinson's. (PDF; 2.8 MB); In: Bulletin; Magazine of the Swiss Federal Technical University of Zurich. 282, 2001, pp. 14-17.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Datasheet Tolcapone, ≥ 98% (HPLC) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 7, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ^ Govi-Verlag Pharmazeutischer Verlag: Pharmazeutische Zeitung online: Drug development: tops and flops of the last 20 years. Retrieved August 24, 2015 .
- ^ Hermann Hager: Hagers Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice. Springer, 1999, ISBN 978-3-540-62646-6 , p. 663 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ^ Govi-Verlag Pharmazeutischer Verlag: Pharmazeutische Zeitung online: Tolcapon – Tasmar ® –70–1997. Retrieved August 24, 2015 .
- ↑ Package insert
- ↑ a b Universimed ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ ROTE LISTE 2017, Verlag Rote Liste Service GmbH, Frankfurt am Main, ISBN 978-3-946057-10-9 , p. 222.