Lead (II) fluoride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
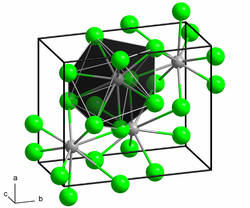
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Pb 2+ __ F - | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lead (II) fluoride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Lead fluoride |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | PbF 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 245.20 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
824 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
1293 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very heavy in water (0.67 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.767 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Lead (II) fluoride is a chemical compound of lead from the group of fluorides .
presentation
Lead (II) fluoride can be produced by various methods, for example by treating lead (II) hydroxide or lead (II) salts (e.g. lead (II) carbonate ) with hydrogen fluoride :
The reaction of potassium fluoride with a lead (II) nitrate solution is also possible.
properties
Lead (II) fluoride is a colorless, odorless, non-flammable solid that is very sparingly soluble in water. In the presence of nitric acid or nitrates , the solubility is greater. The compound occurs in two different crystal forms . The orthorhombic α-form (lead chloride type ) transforms into the cubic β-form ( fluorspar type ) above 316 ° C.
use
Lead (II) fluoride is used in low-melting glasses , in mirror coatings to reflect infrared radiation and as a catalyst for the production of picoline .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on lead (II) fluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Y. Chergui, N. Nehaoua u. a .: The structural properties of PbF2 by molecular dynamics. In: The European Physical Journal Applied Physics. 51, 2010, p. 20502, doi : 10.1051 / epjap / 2010096 .
- ↑ NIST data review 1980
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-247.
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the specified labeling it falls under the group entry lead compounds with the exception of those named in this annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on December 14, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 232.





