Coagulation factor VIII
| Coagulation factor VIII | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
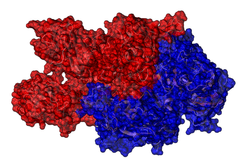
| Ribbon or surface model of factor VIII (without B chain) according to PDB 3CDZ . The light chain is marked in red, the heavy chain in blue. | ||
|
Available structural data : 1cfg , 1d7p , 1iqd , 1fac , 2r7e , 3cdz |
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 265 kDa / 2332 AS | |
| Cofactor | Von Willebrand factor | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | F8 ; AHF; DXS1253E; F8 protein; F8B; F8C; FVIII; HEMA | |
| External IDs | ||
| Drug information | ||
| ATC code | B02 BD02 | |
| DrugBank | DB00025 | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Coagulation factor 5 | |
| Parent taxon | Euteleostomi | |
Blood coagulation factor VIII (coagulation factor VIII, factor VIII, F8) , also antihemophilic globulin A , is a glycoprotein and a coagulation factor in vertebrates . An acute deficiency or absence of the coagulation factor in humans leads to haemophilia A (so-called hemophilia ). The cause is always a mutation in the F8 gene , which codes for factor VIII . An intravenous supply of this blood coagulation factor is therefore the only therapy for hemophiliacs. Until the end of the 1980s, factor VIII was obtained exclusively from donated human blood plasma, today several genetically engineered preparations are also available.
Increases in factor VIII activity to values above 150% are also disease-related and lead to an increased risk of thrombosis , e.g. B. Studies found this increased activity in around 20% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome .
In the 1980s, factor VIII was at the center of one of the biggest drug scandals in Germany and worldwide, the so-called " blood (er) scandal ", in which - largely deliberately - contaminated factor VIII preparations were distributed and administered, even though those responsible in the pharmaceutical industry were responsible , Medicine and politics knew early on that these drugs would cause HIV and hepatitis infections.
biosynthesis
The place of synthesis of factor VIII has not yet been fully clarified. In addition to the liver sinusoids , the vascular endothelium and thrombocytes are also discussed as synthesis sites , with the latter probably being the main synthesis site according to recent studies on knockout mice . The breakdown takes place in the liver and kidneys.
The F8 gene spans 187,000 base pairs in 26 exons . The transcribed mRNA is 9029 bases long and is translated into a protein with 2351 amino acids , from which a further 19 amino acids are removed by post-translational modification .
The factor VIII molecule is modified at 31 amino acid side chains with complex sugar molecules (25 × N -glycosylation, 6 × O -glycosylation), the amino acid chain is finally cut at two points by specific proteases. The finished molecule consists of two chains, a 200 kDa heavy chain and an 80 kDa light chain.
Biological function
Factor VIII, together with calcium and phospholipids (resulting from injuries) are cofactors for factor IXa , which is necessary to factor X to be activated. This reaction step is essential for blood coagulation, because factor Xa activates in complex with factor Va prothrombin to thrombin and this releases fibrin from fibrinogen .
pharmacology
The substitution of factor VIII (intravenous application) is the therapy of choice for haemophilia A patients. Until 1992, factor VIII was produced exclusively from human blood plasma. Genetically engineered factor concentrates such as octocog-alfa are now available in addition to those obtained from plasma .
Manufactured from plasma
Factor VIII is obtained from human plasma by cold precipitation (cryoprecipitation) and then purified by chromatography. An important goal in production is the inactivation of potential pathogens (e.g. viruses). In addition to the selection of the donors and the testing of the processed plasma, inactivating production steps such as solvent and detergent treatment (S / D process, inactivation of enveloped viruses), heat and / or nanofiltration are part of today's safety standard.
Octocog alfa
Octocog alfa ( INN ) is recombinantly produced human factor VIII , which as a medicinal substance has identical areas of application to factor VIII produced from plasma. Chemically, it differs only slightly from this one. The following statements therefore also apply to octocog alfa.
Octocog alfa is not extracted from human blood plasma , but is produced using recombinant DNA technology : It is produced by a cell into which a gene has been introduced that enables it to express human coagulation factor VIII (see also pharmaceutical biotechnology ).
Dosis, kind and Time of the Use
The dosage and frequency of use depends on whether factor VIII is used for the treatment of bleeding, for the prophylaxis of bleeding or as part of a surgical procedure. The dosage is also adjusted depending on the severity of the bleeding and the type of surgical intervention.
Contraindications
All analgesics that inhibit platelet aggregation are contraindicated, especially acetylsalicylic acid . For example, dextropropoxyphene, tilidine + naloxone , pentetocin, buprenorphine , paracetamol , diclofenac are indicated .
unwanted effects
Patients with haemophilia A can form antibodies (inhibitors) against factor VIII, which completely or partially inactivates it. This leads to what is known as "inhibitor hemophilia", a bleeding despite the use of the usual factor doses. Patients with such inhibitors are divided into low responders and high responders . Inhibitors can regress spontaneously, more so in low responders than in high responders. Treatment of acute bleeding is symptomatic. The causal treatment consists in the elimination or reduction of the inhibitors by creating an immune tolerance (immune tolerance induction, ITI) and should always be aimed for. Since February 2018, the bispecific antibody emicizumab has been available in Europe as a new therapy option for secondary inhibitor hemophilia in hemophilia A patients.
Both in the symptomatic treatment of acute bleeding and in the elimination of inhibitors, factor concentrates must be administered in high doses.
Genetic blood coagulation factor VIII is available on the market in different variants. These are divided into a 1st, 2nd and 3rd generation. Octocog alfa belongs to the 2nd generation. In the RODIN study published in 2013, treatment with preparations of the 2nd generation was associated with a more frequent formation of inhibitory antibodies compared to treatment with preparations of the 3rd generation. The Pharmacovigilance Committee of the European Medicines Agency, on the other hand, did not find sufficient evidence for a different frequency of antibody formation, but nevertheless recommended that the product information be adjusted to reflect the results of the study.
In the event of an allergic reaction after the start of the infusion, the infusion must be stopped and switched to another preparation. In the event of an anaphylactic reaction, the usual emergency treatment measures apply.
"Blood (er) scandal" in the 1980s
In the 1980s, contaminated donor blood led to HIV and hepatitis infections in haemophiles around the world - initially due to ignorance, later mainly due to negligence, consciously ignoring warnings and addiction to profit. In Germany at that time over 43% of all haemophiles were infected with HIV. In some countries this became known as a " blood (er) scandal ", because the pharmaceutical industry and politics withheld the known contaminants and the associated risks from the public and thus caused one of the largest medical scandals - besides the Contergan case - worldwide at least 10,000 hemophiles infected with HIV at the time died by the mid-2000s alone. Although there were technical warnings about contaminated preparations as early as March 1983 and, for example, those responsible at the responsible subsidiary of Bayer AG had already advised in January 1983 in internal correspondence against the transmission of contaminated factor VIII blood preparations, infectious preparations were made at least until the summer of 1985 expelled and administered accordingly.
In Germany in 1993, around ten years later, the German Bundestag set up a specific committee of inquiry on “HIV infections through blood and blood products”. In October 1993 the then President of the Federal Health Office Dieter Großklaus was dismissed and the office itself was dissolved at the end of June 1994. At that time, more than 400 of the hemophiles infected during the period in question had died of HIV infection. Other persons involved in the scandal from the pharmaceutical industry, medicine and politics were not prosecuted in Germany. In 2013 this scandal was dealt with by ZDF in the fictional television film Blutgeld and a related documentary. In addition, the feature film “Unter der Haut” (2015), with Friedrich Mücke in the lead role, also addresses the negligent behavior with which the pharmaceutical industry approved of the risk of illness.
See also
Web links
- Public assessment report (EPAR) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for: octocog alpha
Individual evidence
- ^ CJ Glueck, P. Wang, N. Goldenberg, L. Sieve: Pregnancy loss, polycystic ovary syndrome, thrombophilia, hypofibrinolysis, enoxaparin, metformin. In: Clinical and applied thrombosis / hemostasis. Volume 10, Number 4, October 2004, pp. 323-334. PMID 15497018 .
- ^ SA Fahs, MT Hille, Q. Shi, H. Weiler, RR Montgomery: A conditional knockout mouse model reveals endothelial cells as the principal and possibly exclusive source of plasma factor VIII. In: Blood. Volume 123, Number 24, June 2014, pp. 3706-3713. PMID 24705491 .
- ↑ Charité: Determination of parameters in the blood ( Memento from February 11, 2013 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ Blood coagulation factor VIII. In: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man . (English).
- ↑ AOK on factor VIII blood level
- ↑ ENSEMBL entry
- ↑ Roche Pharma AG: EU approval for routine prophylaxis of haemophilia A with inhibitors against coagulation factor VIII - press releases. Retrieved on May 22, 2018 (German).
- ↑ Samantha C. Gouw, Johanna G. van der Bom, Rolf Ljung, Carmen Escuriola, Ana R. Cid, S gol ne Claeyssens-Donadel, Christel van Geet, Gili Kenet, Anne M kipernaa, Angelo Claudio Molinari, Wolfgang Muntean, Rainer Kobelt, George Rivard, Elena Santagostino, Angela Thomas, H. Marijke van den Berg: Factor VIII Products and Inhibitor Development in Severe Hemophilia A. In: New England Journal of Medicine. 368, 2013, pp. 231-239, doi: 10.1056 / NEJMoa1208024 .
- ↑ EMA: PRAC considers benefits of Kogenate Bayer / Helixate NexGen outweigh risks in previously untreated patients .
- ↑ Advate: European Public Assessment Report / Product Information. European Medicines Agency, November 10, 2005, archived from the original on November 20, 2006 ; Retrieved December 7, 2016 .
- ↑ Barbara Möller: TV film "Blutgeld": "All acting people are fictitious". In: The world . , October 28, 2013, accessed December 7, 2016.
- ↑ Walt Bogdanich, Eric Koli: 2 Paths of Bayer Drug in 80's: Riskier One Steered Overseas . In: The New York Times . May 22, 2003. Retrieved January 17, 2014.
- ↑ AIDS scandals around the world . In: BBC News . August 9, 2001.
- ↑ AIDS Scandal: Deadly Cocktail . In: Focus . 31, August 1, 1994, pp. 40-43, accessed December 7, 2016.
-
↑ The history of the blood AIDS scandal in Germany. Interest group haemophiles e. V., May 9, 2000, archived from the original on November 14, 2011 ; Retrieved December 7, 2016 . Wolfgang Hoffmann: Seehofer remains stubborn . In: time online . January 28, 1999, accessed December 7, 2016.
- ↑ Michael Hanfeld: AIDS disease through drugs. In: Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung . December 2, 2015, accessed May 29, 2016 .