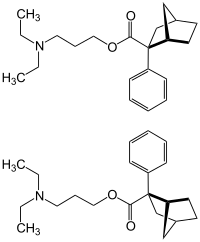
Bornaprine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture of stereoisomers - 1: 1 mixture of the ( S ) -form (top) and the ( R ) -form (bottom) | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Bornaprine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
( RS ) -3-Diethylaminopropyl-2-phenyl-8,9,10-trinorbonane-2-carboxylate ( IUPAC ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | |||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | |||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Bornaprin (trade name Sormodren, manufacturer Abbott ) is a synthetically produced chemical compound from the group of norbornane derivatives. It is used as a drug in the group of anticholinergics in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and excessive sweating ( hyperhidrosis ). The substance was developed and patented in 1956 at Knoll AG ; Bornaprine hydrochloride , which is more soluble in water, is used in drug production.
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Approved areas of application for Bornaprin are:
- tremor-dominant Parkinson's syndromes ,
- extrapyramidal symptoms caused by neuroleptics such as B. Tongue, throat and gaze cramps, akathisia and Parkinsonoid ,
- Hyperhidrosis.
There are no indications for use in children.
Contraindications and restrictions on use
Contraindications for therapy with Bornaprine include hypersensitivity to the active ingredient, glaucoma , mechanical constrictions in the gastrointestinal tract, megacolons , intestinal obstruction and memory disorders.
Particular caution is required in the case of benign prostatic hyperplasia , diseases in which there is a risk of atrial fibrillation and coronary insufficiency .
Drug interactions
An increase in side effects can occur with the simultaneous administration of other anticholinergic drugs such. B. Psychotropic drugs , other Parkinson drugs, antihistamines and antispasmodics . There are further interactions with quinidine (enhancement of the cardiovascular effect, especially on the AV conduction ); Levodopa (aggravation of dyskinesia ); Pethidine (enhancement of the central nervous effects); Alcohol; Metoclopramide (cancellation of the effect); Tricyclic antidepressants (severe anticholinergic effects such as paralytic ileus , hyperpyrexia ).
Adverse effects (side effects)
Side effects occur particularly at the beginning of treatment and when the dose is increased too quickly. These can include hypersensitivity reactions, psychiatric disorders (restlessness, agitation, confusion, delirium , hallucinations , nervousness, sleep disorders) and disorders of the nervous system (dizziness, drowsiness, memory disorders, headache, dyskinesia). Furthermore, accommodation disorders , mydriasis , photophobia , narrow-angle glaucoma, dry mouth, stomach pain, constipation, reduced perspiration, micturition disorders , urinary retention , fatigue and increased heart rate were observed; the frequencies are unknown.
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
After absorption into the body and passage through the blood-brain barrier, bornaprine has an antagonistic effect on the muscarinic receptors , i.e. H. it occupies them and so prevents acetylcholine from binding to them. The effects of the drug are based on this mechanism.
Absorption and distribution in the body (pharmacokinetics)
Bornaprine is effective orally. After ingestion, it is absorbed quickly and well, and plasma protein binding is 96% in vitro . The metabolites and the small amounts of unchanged substance are mainly excreted renally - about 80% of the ingested dose within five days.
toxicology
An acute overdose of bornaprine is manifested by the same symptoms that can occur as side effects. In the event of convulsions , the usual emergency medications can be used. The use of beta blockers can be considered. Experiments on animals have shown that reversible effects on liver metabolism only occurred at high doses (up to 250 mg / kg body weight in rats and 8 mg / kg body weight in dogs) . No significant indications of a toxic effect could be observed.
Other Information
Medicines containing bornaprine are only available from pharmacies and require a prescription .
See also
Atropine , anticholinergic , Parkinson's medication
Trade names
Monopreparations : Sormodren D, A, CH, I
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Rote Liste 2013. Rote Liste Service GmbH, Frankfurt / Main, 2013.
- ^ Sormodren at Onmeda, accessed on March 4, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Entry on Bornaprine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 5, 2014.
- ↑ a b Federal Gazette No. 136 ( Memento of March 5, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) of July 25, 1990, accessed on March 4, 2014 (DOC).
- ↑ a b Sormodren tablet (PDF; 43 kB) from Abbot, accessed on March 5, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on Bornaprine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
- ↑ a b Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapy . Vol. 128, p. 204, 1960.
- ↑ a b c d e f Specialist information from Sormodren (PDF; 24 kB) , accessed on March 4, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on Bornaprin in Flexikon , a wiki of the DocCheck company , accessed on March 4, 2014.