Hair mermaids
| Hair mermaids | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
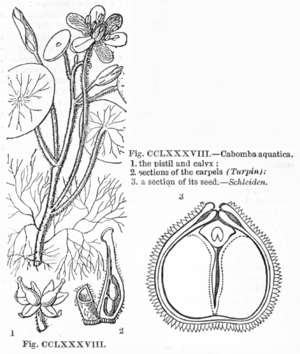
Cabomba aquatica |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Cabomba | ||||||||||||
| Aubl. |
The hair mermaids ( Cabomba ) are a genus of plants from the family of the hair mermaid family (Cabombaceae). Few species are used as aquarium plants .
description
Vegetative characteristics
Most of the species of hair mermaid are slender, stem and rhizome-forming , mucus-bearing, herbaceous plants that grow below the water level . Young vegetative parts of plants often have rust-colored hair. The leaves can be monotonous or multiform. Leaves that grow submerged are opposite or whorled and have long stalks, the leaf blade is divided into five to nine trichotomous or dichotomous branched segments, the last subdivision being more or less linear. If there are floating leaves, they are alternate, forked with a shield-like and linear-elliptical to ovoid leaf blade. The leaf stalks are long to short.
Generative characteristics
The flowers are single, axillary on long flower stalks and swim at least at the end of the flowering period on the water surface. The hermaphroditic flowers are whorled and threefold. Both the three sepals and the three petals are slightly conical in shape at the base and white to yellow or purple in color. The petals are nailed and have nectar-carrying ears. The three to six stamens have slender stamens , the anthers protrude beyond the crown. The one to four upper carpels are free, in each there are usually three (one to five) hanging ovules . The rarely one, usually two to four free styles are longer than the head-shaped scars . Pollination occurs by insects ( entomophilia ).
When ripe, the carpels grow apart. Usually three seeds develop in each elongated pear-shaped fruit . The more or less egg-shaped seed has a surface with small bumps and contains a tiny embryo , which is surrounded by a thin layer of endosperm and abundant perisperm . The two cotyledons ( cotyledons ) are fleshy.
Systematics and distribution
The genus Cabomba was founded in 1775 by Jean Baptiste Christophe Fusée Aublet in Hist. Pl. Guiane , page 321 published. The name Cabomba probably goes back to a Guyanese name.
The Cabomba species are common in the New World .
There are five types:
- Giant hair mermaid ( Cabomba aquatica Aubl. ): It is distributed in South America in Colombia , Brazil , Guiana , Venezuela , Suriname and French Guiana .
-
North American hair mermaid ( Cabomba caroliniana A. Gray ): There are two varieties:
- Florida hair mermaid ( Cabomba caroliniana var. Caroliniana , Syn .: Cabomba caroliniana var. Pulcherrima R.M. Harper ): It is distributed in eastern Canada , in the eastern to central United States and in Brazil, Argentina , Paraguay and Uruguay .
- Cabomba caroliniana var. Flavida Ørgaard : It occurs in Brazil, Argentina and Paraguay.
- Forked hair mermaid ( Cabomba furcata Schult. & Schult.f. ): It occurs in Colombia , Ecuador , Brazil, Bolivia , Peru , Venezuela, Suriname, Guiana, French Guiana, Costa Rica , Cuba , Trinidad and Tobago .
- Cabomba haynesii Wiersema : It occurs in El Salvador , Honduras , Nicaragua , Panama , Cuba, Jamaica , Puerto Rico , the Dominican Republic, Venezuela, Brazil, Colombia and Ecuador.
- Mexican hair mermaid ( Cabomba palaeformis Fassett ): It occurs in Mexico via Belize and Guatemala to Nicaragua. In Florida she is a neophyte .
literature
- John. H. Wiersema: Cabombaceae in der Flora of North America , Volume 3: Cabomba - same text online as the printed work , In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Ed.): Flora of North America North of Mexico , Volume 3 - Magnoliidae and Hamamelidae , Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford 1997, ISBN 0-19-511246-6 .
- Dezhi Fu, John H. Wiersema: Cabombaceae in der Flora of China , Volume 6, p. 119: Cabomba - online with the same text as the printed work , Wu Zhengyi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (ed.): Flora of China , Volume 6 - Caryophyllaceae through Lardizabalaceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2001, ISBN 1-930723-05-9 .
- JA Duke: Nymphaeacea . In: Robert E. Woodson, Jr. and Robert W. Schery (Ed.): Flora of Panama , Part IV, Fascicle 5, Missouri Botanical Garden, May 1963. Pages 137-143.
- Walter Erhardt et al .: The big pikeperch. Encyclopedia of Plant Names. Volume 2. Verlag Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8001-5406-7 .
- Christel Kasselmann : aquarium plants. Ulmer Verlag, Stuttgart 1999, ISBN 3-8001-7454-5 , pp. 155-162.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Marian Ørgaar: The genus Cabomba (Cabombaceae) - a taxonomic study. In: Nordic Journal of Botany , Volume 11, Issue 2, June 1991, pages 179-203. doi : 10.1111 / j.1756-1051.1991.tb01819.x
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Cabomba in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
