Cyphenothrin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
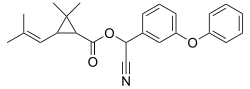
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cyphenothrin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 24 H 25 NO 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish-brownish waxy oil or yellow, waxy solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 375.47 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid / solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.08 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
25 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
154 ° C (13.3 Pa ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1.2 · 10 −4 Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility | |||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Cyphenothrin is an insecticide from the group of pyrethroids . The molecule contains three stereocenters and is used as a mixture of stereoisomers .
It was marketed under the trade name Gokilaht by the Sumitomo company in the late 1980s .
Extraction and presentation
The preparation of cyphenothrin takes place via a multi-stage reaction. Phenol is reacted with m-bromotoluene . The resulting m-phenoxytoluene is then reacted with bromine or N-bromosuccinimide and then with urotropine . The product reacts with hydrochloric acid to form m-phenoxybenzaldehyde and then with sodium cyanide , potassium cyanide or hydrocyanic acid to form m-phenoxycyanobenzyl alcohol (PCBA). This can then be converted into cyphenothrin with chrysanthemum acid .
properties
Cyphenothrin is a yellow to yellow-brown substance with an oily to waxy consistency. It is odorless and almost insoluble in water. The insecticide is not persistent in the soil with a half-life of twelve days.
Mode of action
Like most pyrethroids, cyphenothrin is a contact poison that is absorbed through the body surface and distributed throughout the body. It is one of the neurotoxins whose effect is based on the opening of the sodium channels . As a result, Na + ions flow unhindered into the nerve cell, which leads to uncontrolled nerve impulses. This initially leads to states of excitement with cramps, then to coordination disorders and finally to paralysis. A few minutes after contact with cyphenothrin, the insect is unable to move ( knock-down effect). Death only occurs after a while.
Areas of application
Cyphenothrin breaks down quickly in light. This means that it is of no importance in agriculture . However, it is mainly used in the home for pest control . For example, it is used successfully against infestation by the German cockroach . Cyphenothrin is also used against ticks and fleas in domestic dogs , but these preparations are not approved in Germany.
Trade names
- Plant protection
- Gokilaht-S 5% EC
- Detmol-cap
- Aco.mix C 10 MC
- Veterinary medicine
- Combination preparations
- with Fipronil : Parastar Plus, Fiproguard Max
- with fipronil and methoprene : Frontline Tritak
Individual evidence
- ↑ WHO: d, d, trans-CYPHENOTHRIN. (PDF) Retrieved March 11, 2019 (English).
- ↑ a b c d Entry on cyphenothrin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 16, 2018.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on cyphenothrin in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on March 11, 2019.
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of α-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl 2,2-dimethyl-3- (2-methylprop-1-enyl) cyclopropanecarboxylate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), retrieved on April 16, 2018.
- ↑ Data sheet Cyphenothrin PESTANAL, analytical standard at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 27, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 944 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 938 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Terence Roberts, DH Hutson: Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals . Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge 2007, ISBN 978-1-84755-137-5 .
- ^ Rina Tilak, VK Agrawal, J. Dutta: Field performance of cyphenothrin: an integrated insecticide strategy against German cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blatellidae) . In: Journal of Vector Borne Diseases . tape 42 , no. 2 , June 2005, p. 68-73 , PMID 16161703 .
- ↑ Katharine M. Case, Natalia M. Vega, Ramesh C. Gupta, Michelle A. Lasher, Terry D. Canerdy: Safety Evaluation of Parastar® Plus in Dogs and Assessment of Transferable Residue of Fipronil and Cyphenothrin from Dogs to Humans . In: Frontiers in Veterinary Science . tape 3 , 2016, doi : 10.3389 / fvets.2016.00089 .
- ↑ OM Germant, NI Shashina: [EFFECT OF pyrethroid ON TAIGA TICKS (IXODES persulcatus Ixodidae)] . In: Meditsinskaia Parazitologiia I Parazitarnye Bolezni . No. 1 , January 2016, p. 60-62 , PMID 27029149 .

