Diethyl zinc
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
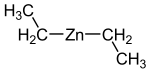
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diethyl zinc | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 10 Zn | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 123.51 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.21 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−28 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
117 ° C (1013 h Pa ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
27.7 hPa (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
reacts extremely violently with water |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4936 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Diethyl zinc , also known as zinc diethyl or DEZ , is an organometallic compound that consists of two ethyl groups bonded to zinc .
history
The chemist Edward Frankland (1825–1899) first produced diethyl zinc in 1848 from zinc and ethyl iodide . Frankland was working as a guest in Robert Bunsen's Marburg laboratory . At that time, carbon dioxide was used as a protective gas, which can be generated in the Kipp apparatus . In many publications this is described as the first synthesis of an organometallic compound. However, there had been other syntheses of organometallic compounds before, such as the synthesis of diethyl tellurium by Friedrich Wöhler in 1840 or that of the cacodyl by Louis Claude Cadet de Gassicourt in 1760 . However, the elements tellurium or arsenic contained in these compounds are not typical metals, but semi-metals. Frankland later improved the synthesis by replacing the ethyl iodide with diethylmercury .
Presentation and extraction
Diethylzinc is synthesized by a transalkylation of triethylaluminum using zinc chloride , and the desired product can be separated from the by-product diethylaluminum chloride by distillation .
Another way of producing diethyl zinc is the classic synthesis from ethyl iodide or ethyl bromide with a zinc-copper pair (activated zinc).
properties
Diethyl zinc is a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It reacts violently with water and is pyrophoric in air . Handling must therefore take place under a protective gas , for example nitrogen or argon .
structure
The crystal structure of diethylzinc shows a tetragonal body- centered unit cell ( space group I 4 1 md (space group no. 109) ). The molecules form a polar crystal packing, with the two ethyl groups arranged in the cis position. The Zn – C bonds are 194.8 (5) pm long, while the C – Zn – C angle is slightly bent at 176.2 (4) °. The zinc atoms are linearly coordinated in the gas phase . The Zn – C bonds here are 195.0 (2) pm.
use
Diethyl zinc is used in a wide variety of ways in organic synthesis, as it can be used to produce highly functionalized substances that are important starting materials for the production of pharmaceuticals , natural product derivatives , polymers and many other compounds. In contrast to many other organometallic compounds, diethylzinc tolerates a large number of functional groups . Another advantage over other organometallic compounds is that diethylzinc often reacts stereo- and regioselectively with organic compounds in the presence of suitable catalysts .
Diethyl zinc is currently used in large quantities in the solar industry for the production of TCO layers from zinc oxide for thin-film solar cells.
Diethyl zinc acts as a nucleophilic ethyl synthon in addition reactions of carbonyl groups . With diiodomethane it forms the reactive agent in the Simmons-Smith reaction .
In a project by the Library of Congress in Washington, DC , DEZ was used for many years as a mass deacidification agent to protect valuable books and other documents from acid degradation. After an accident in which DEZ residues reacted with moisture in a preparation chamber and led to a detonation , the project was ended.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on diethyl zinc in the GESTIS material database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Datasheet Diethylzinc from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 17, 2010 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Roth / Weller dangerous chemical reactions , ecomed Sicherheit-Verlag, 59th supplement 11/2009.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-172.
- ↑ Entry on Diethylzinc in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ E. Frankland, In: Liebigs Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie , 71/1849, p. 213.
- ^ E. Frankland, On the isolation of the organic radicals. In: J. Chem. Soc. , 2/1850, p. 263.
- ^ Max Bodenstein: Robert Wilhelm Bunsen's position on organic chemistry . In: Natural Sciences . tape 24 , no. March 13 , 1936, p. 193-196 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01491303 .
- ^ Friedrich Wöhler: Diethylzink . In: Liebig's annals of chemistry and pharmacy . tape 35 , 1840, pp. 111 .
- ^ E. Frankland, BF Duppa: On a new reaction for the production of the zinc compounds of the alkyl radical . In: J. Chem. Soc. tape 17 , 1864, p. 29-36 , doi : 10.1039 / JS8641700029 .
- ↑ Michael J. Krause, Frank Orlandi, Alfred T. Saurage, Joseph R. Zietz Jr .: Aluminum Compounds, Organic . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley-VCH , Weinheim 2005, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a01_543 .
- ↑ CR Noller: Diethyl Zinc In: Organic Syntheses . 12, 1932, p. 86, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.012.0086 ; Coll. Vol. 2, 1943, p. 184 ( PDF ).
- ↑ P. Bolze, Organometallic Chemistry (PDF file; 204 kB), University of Marburg.
- ↑ John Bacsa, Felix Hanke, Sarah Hindley, Rajesh Odedra, George R. Darling, Anthony C. Jones and Alexander Steiner: The Solid State Structures of Dimethylzinc and Diethylzinc . In: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. . 50, 2011, pp. 11685-11687. doi : 10.1002 / anie.201105099 .
- ^ A. Haaland, JC Green, GS McGrady, AJ Downs, E. Gullo, MJ Lyall, J. Timberlake, AV Tutukin, HV Volden, K.-A. Østby: The length, strength and polarity of metal – carbon bonds: dialkylzinc compounds studied by density functional theory calculations, gas electron diffraction and photoelectron spectroscopy . In: Dalton Trans . 2003, pp. 4356-4366. doi : 10.1039 / B306840B .
- ↑ Klaus Stingl, Jürgen Martens : Synthesis of chiral Catalysts for the enantioselective Addition of Diethylzinc to aromatic Aldehydes . In: Synth. Commun. tape May 22 , 1992, pp. 2745-2756 , doi : 10.1080 / 00397919208021539 .
- ^ Sabine Wallbaum, Jürgen Martens: Catalytic Enantioselective Addition of Diethylzinc to Aldehydes: Application of a new Bicyclic Catalyst . In: Tetrahedron: Asymmetry . tape 4 , no. 4 , April 1993, pp. 637-640 , doi : 10.1016 / S0957-4166 (00) 80167-6 .
- ↑ Thomas Mehler, Jürgen Martens: New Thioether Derivatives as Catalysts for the Enantioselective Addition of Diethylzinc to Benzaldehyde . In: Tetrahedron: Asymmetry . tape 5 , no. 2 , 1994, p. 207-210 , doi : 10.1016 / S0957-4166 (00) 86174-1 .
- ↑ Patent WO2007020298A1 : Highly reactive form of zinc, process for their production and use of the highly reactive form of zinc. Registered on August 21, 2006 , published on February 22, 2007 , applicant: Chemetall GmbH, inventors: Sebastian Lang, Alexander Murso, Ulrich Wietelmann.
- ^ AB Charette, H. Lebel: (2S, 3S) - (+) - (3-phenylcyclopropyl) methanol In: Organic Syntheses . 76, 1999, p. 86, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.076.0086 ; Coll. Vol. 10, 2004, p. 613 ( PDF ).
- ^ Y. Ito: One-Carbon Ring Expansion of Cycloalkanones to Conjugated Cycloalkenones: 2-Cyclohepten-1-one In: Organic Syntheses . 59, 1979, p. 113, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.059.0113 ; Coll. Vol. 6, 1988, p. 327 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Nicholson Baker: Double Fold . Libraries and the Assault on Paper. Vintage ,, 2002, ISBN 0-375-72621-7 .
literature
- MH Abraham, JA Hill, Organometallic Compounds 3. The acidolysis of some symmetrical - and unsymmetrical - dialkyl zincs by primary amines. In: Journal of Organometallic Chemistry , 7/1967, pp. 23-33; doi: 10.1016 / S0022-328X (00) 90822-2 .
- Michael J. Rozema, Duddu Rajagopal, Charles E. Tucker, Paul Knochel, Preparation of polyfunctional diorganomercurials and their transmetallation to diorganozincs. Applications for the preparation of optically active secon. In: Journal of Organometallic Chemistry , 438/1992, pp. 11-27; doi: 10.1016 / 0022-328X (92) 88002-Z .
- AG Davies, Studies of Homolytic Organometallic Reactions. In: Journal of Organometallic Chemistry , 200/1980, pp. 87-99; doi: 10.1016 / S0022-328X (00) 88639-8 .
- J. Boersma, Zinc and Cadmium. In: Journal of Organometallic Chemistry , 147/1978, pp. 1-16.



