Domperidone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
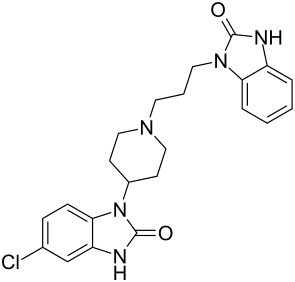
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Domperidone | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 22 H 24 ClN 5 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to almost white powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Dopamine antagonist |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 425.91 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
242.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
7.9 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water , soluble in DMF , sparingly soluble in ethanol 96%, sparingly soluble in methanol |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Domperidone is a drug that is used to relieve symptoms such as nausea and vomiting ( an anti-emetic ). The European Medicines Agency does not see a positive risk-benefit ratio for use in other indications (e.g. bloating , upper abdominal pain; vary slightly in the various EU member states) .
Domperidone is one of the dopamine receptor - antagonists .
chemistry
Domperidone is a piperidine - derivative and related to pimozide and the butyrophenones benperidol and droperidol , also belongs to the class of Benzimidazolones .
Mode of action
The neurotransmitter dopamine can cause central nausea and nausea. Domperidone prevents dopamine to the associated D 2 - dopamine receptor can bind, because it covers it and thus blocked. Peripheral disorders of the gastrointestinal motor system ( motility disorders ) are also remedied by domperidone, the mechanism of action is unclear. In addition, domperidone acts as an agonist on 5-HT4 receptors .
Since, in contrast to metoclopramide, domperidone can hardly cross the blood-brain barrier , it has almost no influence on the central nervous system . As a result, the preparation lacks parkinsonoid side effects such as disorders of the extrapyramidal motor function. It only acts peripherally and on the circumventricular organs (organs of the central nervous system that are not protected by the blood-brain barrier; this means that it can also be used, for example, in restless legs syndrome ), including those for “Central vomiting” is the responsible region Area postrema. The nausea is reduced by blocking the D 2 receptors.
Domperidone peripherally promotes gastric motor skills, which increases the antiemetic (nausea-relieving) effect. The mechanism of action for accelerating gastric emptying is unclear. Initially, it was attributed to an antagonism at dopamine receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. However, their existence has not yet been proven, and other D 2 antagonists such as haloperidol do not accelerate gastric emptying.
Domperidone is also used in combination with central dopamine agonists or L-dopa to minimize the peripheral effects of these drugs and to protect against dopamine-induced vomiting.
Side effects and restrictions on use
A relevant side effect of domperidone is an increase in the prolactin level , which can lead to decreased libido, menstrual disorders and impotence . Another side effect is a prolonged QT time on the heart. There is a risk of ventricular arrhythmia.
The review at European level based on newly reported cases of serious cardiac side effects revealed in 2014 that taking domperidone with a small increased risk of serious ventricular arrhythmias , QTc prolongation , torsades de pointes tachycardias , and sudden cardiac death associated is. A higher risk has been observed in patients older than 60 years, among others. The use of drugs containing domperidone was then further restricted in terms of dosage (not more than 30 mg daily), duration of use (if possible not longer than a week) and indication (contraindicated in patients with moderate to severe liver dysfunction, with existing prolongation of the cardiac conduction interval, with significant disorders in the electrolyte balance, in the presence of heart disease; the joint administration of domperidone with QTc-prolonging drugs and the joint administration with highly effective CYP3A4 inhibitors is also contraindicated).
Use in animals
In dogs, in addition to treating nausea and vomiting, domperidone can also be used to treat leishmaniasis . In one study, a one-month dose resulted in a clinical improvement, an improvement in cellular immunity and, in many animals, a reduction in antibody titers .
Trade names
Domidon (D), Motilium (D, A, CH), Oroperidys (A), various generics (D, A)
Web links
- Entry on domperidone at Vetpharm, accessed November 22, 2011.
- Rote-Hand-Letters on Domperidon since August 2014
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia Commission (ed.): EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOE 5TH EDITION . tape 5.1-5.8 , 2006.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on domperidone in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b data sheet domperidone from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 28, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Referral Procedure on Domperidone-containing medicines , EMA.
- ↑ Klaus Aktories, Ulrich Förstermann, Franz Bernhard Hofmann, Klaus Starke (eds.): General and special pharmacology and toxicology . 2009.
- ↑ ArizonaCERT: Center for Education and Research on Therapeutics .
- ↑ Rote-Hand-Brief on domperidone: Serious cardiac side effects , August 20, 2014.
- ↑ P. Gómez-Ochoa, JA Castillo, M. Gascón, JJ Zarate, F. Alvarez, CG Couto: Use of domperidone in the treatment of canine visceral leishmaniasis: a clinical trial. In: Veterinary journal (London, England: 1997). Volume 179, number 2, February 2009, pp. 259-263, doi : 10.1016 / j.tvjl.2007.09.014 . PMID 18023375 .