Epothilones
Epothilones are 16-membered macrolides , which were first isolated from the myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum in 1987 by Gerhard Höfle and Hans Reichenbach at the former Braunschweig Society for Biotechnological Research (GBF, now the Helmholtz Center for Infection Research ). The natural product attracted attention when it was found to have an effect on tumor cells analogous to paclitaxel and thus aroused interest as a lead structure for cancer research.
Substances
| Epothilones | ||||||||
| Surname | Epothilone A | Epothilone B | Epothilone C | Epothilone D. | Epothilone E. | Epothilone F | ||
| Structural formula |
 Epothilone A (R = H) or B (R = CH 3 ) |
 Epothilone C (R = H) or D (R = CH 3 ) |
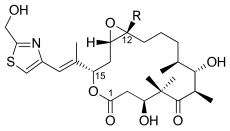 Epothilone E (R = H) or F (R = CH 3 ) |
|||||
| CAS number | 152044-53-6 | 152044-54-7 | 189453-10-9 | |||||
| PubChem | 448799 | 448013 | 9891226 | 447865 | ||||
| Molecular formula | C 26 H 39 NO 6 S | C 27 H 41 NO 6 S | C 26 H 39 NO 5 S | C 27 H 41 NO 5 S | C 26 H 39 NO 7 S | C 27 H 41 NO 7 S | ||
| Molar mass | 493.66 g mol −1 | 507.68 g mol −1 | 477.66 g mol −1 | 491.68 g mol −1 | 509.66 g mol −1 | 523.68 g mol −1 | ||
| Physical state | firmly | |||||||
| Brief description | White dust | |||||||
| Drug class | Cytostatic | |||||||
| Mechanism of action | Stabilization of the microtubules | |||||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|||||||
| H-phrases | see above | |||||||
| P-phrases | see above | |||||||
history
The first epothilone was isolated in 1987 at what was then the Society for Biotechnological Research in Braunschweig and the structure was clarified. It was patented in 1993. The structures only gained attention when an in vitro screening at the American National Cancer Institute (NCI) found the extraordinarily high effect on breast and colon tumor cells. When the paclitaxel-like mechanism of action became known and the fact that epothilone displaces paclitaxel from the target, i.e. has the stronger interactions, epothilone became interesting for pharmaceutical research. The patent was given up before that. On the basis of this lead structure, on the one hand, with the help of combinatorial methods based on the total syntheses and, on the other hand, through chemical derivatization of the microbially formed epothilones, both structure-activity relationships (SAR) and, later, promising drug candidates were developed, which are now in clinical phases or . are about to be launched.
The name epothilone is derived from the structural elements epoxide , thiazole and ketone .
Pharmacological effect
The epothilones have an antifungal effect against Oomycetes . However, this effect is accompanied by a considerable phytotoxic effect, so that the compounds there are no longer of interest today.
The epothilones have a remarkable pharmacological effect as cytostatics . The effect is based on the stabilization of the microtubules , a mechanism of action that so far only paclitaxel has shown. All other previously known microtubule-active substances ( colchicine , podophyllotoxin and vinblastine ) destabilize the microtubules that are involved in cell division and protein secretion. By disrupting the microtubules, mitotic cell division is disrupted and the tumor does not grow any further.
Epothilone is said to be used primarily against paclitaxel-resistant tumors. Compared to paclitaxel, synthetic epothilone derivatives are up to thirty times more effective due to their much higher solubility in water. This also has the advantage that when administered as an active ingredient in aqueous solution without solubilizers, it leads to fewer side effects compared to taxanes. According to a current assessment (March 2009) by the European Medicines Agency, this does not appear to be the case. The high number of neuropathies (nerve damage) in particular led to rejection.
Compared to the active ingredients that are based on paclitaxel as a lead structure, the epothilones have the advantage that they have little tendency to develop resistance.
Current status of the development of the active ingredient
A number of pharmaceutical companies have developed active ingredients based on epothilone. Bristol-Myers Squibb was granted approval of the epothilone derivative Ixabepilon ( trade name : Ixempra ) for the USA in October 2007 . The drug has not been approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in the European Union . The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) considered that patients were at too high a risk compared to the benefits of the drug, particularly because of the possible development of neuropathies when taking Ixempra.
In 2005, what was then Schering AG (now Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals ) reported that they had brought the active ingredient sagopilon (internal name ZK-EPO), which is based on the structure of epothilone, into clinical phase I.
From Novartis AG patupilone (internal name EPO906) developed up to clinical phase III, the substance but in several clinical trials showed no significant survival benefit and an approval was not sought.
Extraction
The extraction of the myxobacterium Sorangium cellulosum from fermenter cultures is, in addition to three total syntheses, of outstanding importance.
Total synthesis
Almost at the same time, Samuel Danishefsky from Colombia University and a short time later Kyriacos Costa Nicolaou from the Californian Scripps Institute and Dieter Schinzer from the Technical University of Braunschweig published total syntheses for epothilones. Due to the topicality of epothilone, further total syntheses were published in later works by Johann Mulzer and Erick M. Carreira . The artificially produced epothilone cannot compete with the natural ones produced in fermenters due to the considerably more expensive total synthesis.
biosynthesis
Epothilone B is a 16-membered polyketide with a methyl thiazole group as a side chain, which is linked to the macrolactone via an olefin . The polycedic macrolactone is produced by a type I polyketide synthase (PKS), and the thiazole ring from a cysteine by a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS). During biosynthesis, both PKS and NRPS use carrier proteins which, after reading out the genetic information from the DNA , i.e. post-translationally, have been modified by phosphopanthetein groups in order to bind to the growing chain. PKS uses the coenzyme A thioester to catalyze the reaction and changes the substrate by selective reduction of the β- carbonyl group to a hydroxyl group (ketoreductase, KR), the alkene (dehydratase, DH) and the alkane (enoyl reductase, ER) . PKS-I is also able to methylate the α-carbon of the substrate . NRPS uses amino acids that have been activated on the enzyme to perform amino-acyladenylation. The synthesis of epothilone B begins with a 2-methyl-4-carboxythiazole building block, which is formed by the translational coupling between PKS, the EPOS A (epoA) building block and NRPS or EPOS p (epoP) building blocks. EPOS A carries a modified β-ketoacyl synthase (malonyl-ACP decarboxylase, KSQ), an acetyltransferase (AT), an enoyl reductase (ER) and an acyl carrier protein domain. The EPOS P contains a domain for the formation of the heterocycle, an oxidase for adenylation and the domain for thiolization. These domains are important because they are involved in the formation of the 5-membered ring of the thiazole heterocycle. The EPOS P activates the cysteine and binds the activated cysteine to the aminoacyl-S-PCP. Once the cysteine is bound, the EPOS A brings an acetate unit into the EPOS P complex. This triggers the formation of the thiazole ring through an intramolecular cyclodehydrogenation. Once the 2-methylthiazole ring has been formed, it is adopted by PKS EPOS B (epoB), EPOS C (epoC), EPOS D (epoD), EPOS E (epoE) and EPOS F (epoF) for a successive extension to to form the double bond or the epoxy. It is noteworthy that the synthesis of the geminal dimethyl group does not result from two successive dimethylations, but rather a derivative of the propionate growth unit, while the second methyl group is introduced by a methyl transferase.
literature
- Review article in: Bernd Buchmann, Ulrich Klar: Ullmann's Encyclopädia of Industrial Chemistry; Epothilones . Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.k09_k01.pub2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ G. Höfle, N. Bedorf, H. Steinmetz, D. Schomburg, K. Gerth, H. Reichenbach: In Angew. Chem .: 108 , 1996 , 1671-1673. Epothilone A and B - novel, 16-membered macrolides with cytotoxic effects: isolation, structure in the crystal and conformation in solution . doi: 10.1002 / anie.19961081342 .
- ↑ Data sheet (-) - Epothilone A, from at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 27, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Data sheet (-) - Epothilone B, from at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 27, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ With regard to its dangerousness, the substance has not yet been classified by the EU, a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ McQueney, J. Zhu, O. Hensens, L. Kopal, J. Liesch, M. Goetz, E. Lazarides, CM Woods: Epothilones, a New Class of Microtubule-stabilizing Agents with Taxol-like Mechanism of Action. In: Cancer Research Volume 55, pp. 2325-2333, PMID 7757983 .
- ↑ Questions and answers on the withdrawal of the marketing authorization for Ixempra. (PDF; 43 kB).
- ↑ Q&A on rejection by the European Medicines Agency (PDF; 52 kB).
- ↑ Novartis press release of May 27, 2010 ( Memento of April 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Novartis press release of May 27, 2010 .
- Bristol-Myers Squibb announces approval for the American market
- Schering AG announces phase I of ZK-EPO
- Mólnar et al .: The biosynthetic gene cluster for the microtubule-stabilizing agents epothilones A and B from Sorangium cellulosum So ce 90
Web links
- Dieter Schinzer, Anja Limberg: Epothilones: New active substances against cancer (PDF; 154 kB) Magdeburg Science Journal, 1/2000
- Bettina Frank, Rolf Müller: How microorganisms help fight cancer . Pharmaceutical newspaper online