Galantamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
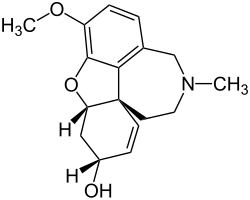
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Galantamine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 287,35 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Galantamine (also galanthamine from galanthus ) is a naturally occurring substance from the group of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids .
Occurrence
Galantamine can be obtained from the little snowdrop ( Galanthus nivalis ), the Caucasian snowdrop ( Galanthus woronowii ) and some types of daffodils such as the yellow daffodil ( daffodil ). It was isolated for the first time in 1953 from the bulbs of the Caucasian snowdrop. Today the active ingredient can also be produced synthetically.
synthesis
biogenesis
The biosynthesis takes place from two amino acids: L- tyrosine changes into tyramine and protocatechualdehyde is formed from L- phenylalanine via cinnamic acid , p-coumaric acid and caffeic acid . The latter reacts with tyramine to form a Schiff base , which is hydrogenated to norbelladine . The formation of the other rings takes place through oxidative coupling and leads to (-) - galantamine.
Technical synthesis
The industrial galantamine synthesis was developed by the Austrian company Sanochemia Pharmazeutika . It is based on a nine-stage procedure published in 1999. Special steps are an oxidative phenol coupling and a crystallization-induced chiral conversion of (±) -Narwedin to (-) - Narwedin. In the last step, the keto group of (-) - narwedine is reduced enantioselectively to the alcohol using L -electride , resulting in (-) - galantamine.
properties
Galantamine has three chiral centers. The naturally occurring variant is (-) - galantamine. The enantiomer (+) - galantamine ( ent- galantamine) can occur as an impurity in the substance derived from chemical synthesis. (4a S , 6 S , 8a S ) -galantamine ( epi- galantamine) is described as the C-6 epimer . Structurally related alkaloids to galantamine are narwedine and lycoramine (1,2-dihydrogalantamine).
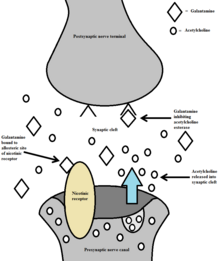
Pharmacologically, galantamine belongs to the group of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors . By inhibiting acetylcholinesterase and modulating nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (dual mechanism of action), the active ingredient leads to an increase in the acetylcholine concentration in the synaptic gap . It is also said to have a strong analgesic effect comparable to that of morphine .
Medical use
application areas
The alkaloid is today mainly as anti-dementia drug for the treatment of dementia , particularly Alzheimer's (this creates a lack of acetylcholine , short ACh, a neurotransmitter ) used. Initially, the active ingredient was used, among other things, to reverse the muscle relaxation triggered by curare compounds during operations. It is still used today because of its competitive antagonism in the case of organophosphate , soman , sarin , VX and tabun poisoning.
Because of its vagotonic ( parasympathomimetic ), cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory (anti-inflammatory) properties, galantamine and a. can also be used for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases ( off-label use ).
Benefit assessment by IQWIG
As early as 2007, the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) submitted a benefit assessment of the active ingredients donepezil , galantamine and rivastigmine, which belong to the group of cholinesterase inhibitors , in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. In the meantime, there are further, partly unpublished, study data on galantamine, which prompted the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) to have the IQWiG re-examine the benefits of galantamine. The committee came to the conclusion that although galantamine can positively influence the ability to think and remember in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease - at least at a higher dose - it has not been proven to be beneficial in healthy patients.
Side effects
Patients taking galantamine were more likely to have nausea or vomiting than those taking placebo . They also stopped the study more often because of undesirable side effects. On September 22nd, 2015 the manufacturer informed Janssen-Cilag about an additional warning for Reminyl . As a result, treatment with galantamine hydrobromide can lead to serious skin reactions ( Stevens-Johnson syndrome , acute generalized exanthemic pustulosis (AGEP)). Patients treated with galantamine hydrobromide should be informed of the symptoms and treatment should be discontinued at the first appearance of a rash.
Trade names
Galantamine was launched in Germany in March 2001 as Reminyl ( Janssen Pharmaceutica ), and as such it is also on the market in Austria and Switzerland. The first generic galantamine with the brand name Galnora (TAD Pharma GmbH) has been on the market since October 2011 . Other preparations include Galafix (A), Galafont (A), Galamil (A), Galatifer (A) and other generics.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c The Merck Index . An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14th edition, 2006, p. 746, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ a b data sheet Galantamine hydrobromide from Lycoris sp. at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 2, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Data sheet Galanthamine, Hydrobromide (PDF) from Calbiochem, accessed on December 8, 2015.
- ↑ E. Teuscher: Biogenic Medicines. 5th edition, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, 1997, p. 331 f. ISBN 3-8047-1482-X .
- ↑ Werner Sommer: Pharmaceutical company and TU chemist synthesized active ingredient for Alzheimer's drug. TU Wien , November 27, 2000, accessed on September 26, 2008 .
- ↑ a b Bernhard Küenburg, Laszlo Czollner, Johannes Fröhlich, Ulrich Jordis: Development of a Pilot Scale Process for the Anti-Alzheimer Drug ( -) - Galantamine Using Large-Scale Phenolic Oxidative Coupling and Crystallization-Induced Chiral Conversion . In: Organic Process Research & Development . tape 3 (6), 1999 , p. 425-431 , doi : 10.1021 / op990019q .
- ^ A. Kleemann, J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances . Galantamine (GP-37267). Ed .: Georg Thieme Verlag. 5th edition, 2009.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to (+) - galantamine : CAS number: 60384-53-4, PubChem : 906210 , ChemSpider : 792444 , Wikidata : Q27270692 .
- ↑ Monograph "Galantamine Hydrobromide" . European Pharmacopoeia. 8th edition, basic work 2014, p. 3442 f .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for epi-galantamine : CAS number: 1668-85-5, EC number: 684-870-2, ECHA InfoCard: 100.210.311 , PubChem : 676392 , ChemSpider : 589108 , Wikidata : Q27286219 .
- ↑ G. Geisslinger et al .: Mutschler drug effects . 11th edition. WVG, Stuttgart 2019, p. 343.
- ↑ RÖMPP Lexikon Chemie . Volume 2: Cm - G. 10th edition, 1996-1999. S. 1449 .
- ^ EX Albuquerque, EFR Pereira, Y. Aracava, WP Fawcett, M. Oliveira, WR Randall, M. Adler: Effective countermeasure against poisoning by organophosphorus insecticides and nerve agents . In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . 103, No. 35, 2006, pp. 13220-13225. doi : 10.1073 / pnas.0605370103 .
- ↑ Peter Nordström, Dorota Religa, Anders Wimo, Bengt Winblad, Maria Eriksdotter: The use of cholinesterase inhibitors and the risk of myocardial infarction and death: a nationwide cohort study in subjects with Alzheimer's disease . In: European Heart Journal . tape 34 , no. 33 , September 1, 2013, p. 2585-2591 , doi : 10.1093 / eurheartj / eht182 ( oup.com ).
- ↑ C.-J. Estler (Ed.): Pharmacology and Toxicology. 4th edition Schattauer, Stuttgart a. New York 1995. ISBN 3-7945-1645-1 . Pp. 41-46.
- ↑ a b Galantamine and rivastigmine patches: positive influence on cognition possible PM of the IQWiG (April 2, 2012).
- ↑ Cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's dementia - supplementary order: Rivastigmine patch and galantamine final report from IQWiG (accessed on April 2, 2012).
- ↑ New on the market - Galantamine (REMINYL) against Alzheimer's , arznei-telegramm, 2001.