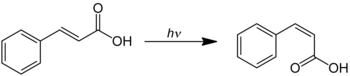Cinnamic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cinnamic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 8 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white crystals with a characteristic odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 148.16 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.25 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
134 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
Decomposition (decarboxylation to styrene) |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
4.44 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Cinnamic acid ( trans -3-phenylacrylic acid , FEMA 2288 ) is a white solid with a characteristic odor. Cinnamic acid occurs naturally in some plants and is non-toxic. In addition to cinnamaldehyde and eugenol , it is an important component of cinnamon . Cinnamic acid is an aromatic compound and is an unsaturated carboxylic acid with a trans -substituted carbon-carbon double bond in the side chain. The isomeric cis -cinnamic acid (allocinnamic acid ) is of little importance. The information in this article relates only to trans -cinnamic acid.
presentation
Cinnamic acid can be produced from benzaldehyde , for example via aldol addition with malonic acid ( Doebner variant ).
A reaction path specially developed for cinnamic acid is the Perkin reaction :
Another synthetic route involves an aldol condensation of benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde .
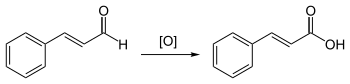
Cinnamic acid is also produced by the oxidation of cinnamaldehyde, which takes place in the air .
properties
Physical Properties
Cinnamic acid crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system in the space group P 2 1 / n (space group no. 14, position 2) and the lattice parameters a = 779 pm , b = 1807 pm, c = 567 pm and β = 97 °. In the unit cell contains four formula units . Two further metastable forms are known with the β and γ modification. The crystal structure of this β modification is isomorphic to 4-chlorocinnamic acid .
Chemical properties
When distilled at 146 ° C and approx. 4 hPa, decomposition by decarboxylation to styrene takes place.
biosynthesis
Cinnamic acid is formed from the amino acid L - phenylalanine in the course of a deamination by the phenylalanine ammonia lyase ( EC 4.3.1.24 ), which also deaminates the amino acid L - tyrosine to para - cumaric acid ( 4-hydroxycinnamic acid ) in an analogous reaction . It is an intermediate product in the biosynthesis of chalcones (and thus a precursor of flavonoid biosynthesis) and stilbenes .
Use and reactivity
Cinnamic acid can be used to prepare phenylacetylene . Some of their esters are used as fragrances . When trans -cinnamic acid is exposed to UV radiation, isomerization occurs with the formation of cis -cinnamic acid (allocinnamic acid ):
Cinnamic acid photochemically dimerizes to form a cyclobutane ring. Depending on the crystal form, two different isomers are created. The α – truxillic acid arises from the α – polymorph. The β – polymorph forms the β – truxic acid. The γ polymorph cannot be photochemically dimerized.
Derivatives
Derivatives substituted on the phenyl ring by a hydroxyl group belong to the group of phenolic acids . The sinapinic acid (3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxy-cinnamic acid) and α-cyano-4-hydroxy-cinnamic acid ( HCCA ), suitable organic matrix in MALDI-MS (Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry) is used. These include, for example, ferulic acid and caffeic acid .
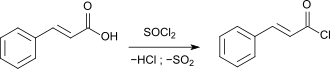
By reacting with thionyl chloride (SOCl 2 ), cinnamic acid is converted into the reactive cinnamic acid chloride.
The aromatic substance ethyl cinnamate can be obtained by esterification with ethanol in the presence of sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid as a catalyst .
toxicology
For rats, the oral LD 50 is 2.5 g / kg and the dermal LD 50 is 5 g / kg. Cinnamic acid causes irritation on rabbit skin. A 4% solution in petroleum jelly does not cause any skin reaction in humans.
Web links
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on FEMA 2288 in the database of the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association of the United States .
- ↑ Entry on CINNAMIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on February 25, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on cinnamic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 6, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ Entry on cinnamic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on 17 July 2014 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for cis-cinnamic acid : CAS number: 102-94-3, EC number: 827-073-9, ECHA InfoCard: 100.262.470 , PubChem : 5372954 , ChemSpider : 10286933 , Wikidata : Q4062664 .
- ↑ R. Brückner: reaction mechanisms: organic reactions, stereochemistry, modern synthesis methods . 3. Edition. Spectrum, 2004, ISBN 3-8274-1579-9 , pp. 569-570 .
- ↑ J. Ladell, TRR McDonald, GMJ Schmidt: The crystal structure of α-trans-cinnamic acid , in: Acta Cryst. , 1956 , 9 , p. 195 ( doi: 10.1107 / S0365110X56000474 ).
- ↑ JH Urbanus, S. Jiang: Polymorphism of trans-cinnamic acid , MSc graduation assignment ( full text (PDF; 153 kB) ).
- ↑ GMJ Schmidt: 385. Topochemistry. Part III. The crystal chemistry of some trans-cinnamic acids , in: J. Chem. Soc. , 1964 , pp. 2014-2021 ( doi: 10.1039 / JR9640002014 ).
- ↑ I. Abdelmoty, V. Buchholz, L. Di, C. Guo, K. Kowitz, V. grandson, G. Wegner, BM Foxman: Polymorphism of Cinnamic and α-Truxillic Acids: New Additions to an Old Story , in: Crystal Growth & Design , 2005 , 5 (6), pp. 2210-2217 ( doi: 10.1021 / cg050160s ).
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organische Chemie , VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindindustrie, Leipzig 1985, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 , p. 407.
- ↑ D. Wöhrle, MW Tausch, W.-D. Stohrer: Photochemistry: Concepts, Methods, Experiments , Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 1998, ISBN 3-527-29545-3 , p. 96.
- ↑ MD Cohen: Photochemistry of organic solids , in: Angew. Chem. , 1975 , 87 , pp. 439-447 ( doi: 10.1002 / anie.19750871204 ).
- ↑ V. Ramamurthy, K. Venkatesan: Photochemical reactions of organic crystals , in: Chem. Rev. , 1987 , 87 , pp. 433-481 ( doi: 10.1021 / cr00078a009 ).
- ↑ CS Marvel, WB King: Ethyl Cinnamate In: Organic Syntheses . 9, 1929, p. 38, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.009.0038 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 252 ( PDF ).
- ↑ E. Fischer , A. Speier: Presentation of the esters , in: Reports of the German Chemical Society , 1895 , 28 , pp. 3252-3258 ( digitized on Gallica ).
- ↑ Wiley-VCH, Wiley-VCH: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry , 2005, Chapter: Cinnamic Acid